* feat: add `apps` & `actions` attributes to Agent (#3504)
* feat: add app attributes to Agent
* feat: add actions attribute to Agent
* chore: resolve linter issues
* refactor: merge the apps and actions parameters into a single one
* fix: remove unnecessary print
* feat: logging error when CrewaiPlatformTools fails
* chore: export CrewaiPlatformTools directly from crewai_tools
* style: resolver linter issues
* test: fix broken tests
* style: solve linter issues
* fix: fix broken test
* feat: monorepo restructure and test/ci updates
- Add crewai workspace member
- Fix vcr cassette paths and restore test dirs
- Resolve ci failures and update linter/pytest rules
* chore: update python version to 3.13 and package metadata
* feat: add crewai-tools workspace and fix tests/dependencies
* feat: add crewai-tools workspace structure
* Squashed 'temp-crewai-tools/' content from commit 9bae5633
git-subtree-dir: temp-crewai-tools
git-subtree-split: 9bae56339096cb70f03873e600192bd2cd207ac9
* feat: configure crewai-tools workspace package with dependencies
* fix: apply ruff auto-formatting to crewai-tools code
* chore: update lockfile
* fix: don't allow tool tests yet
* fix: comment out extra pytest flags for now
* fix: remove conflicting conftest.py from crewai-tools tests
* fix: resolve dependency conflicts and test issues
- Pin vcrpy to 7.0.0 to fix pytest-recording compatibility
- Comment out types-requests to resolve urllib3 conflict
- Update requests requirement in crewai-tools to >=2.32.0
* chore: update CI workflows and docs for monorepo structure
* chore: update CI workflows and docs for monorepo structure
* fix: actions syntax
* chore: ci publish and pin versions
* fix: add permission to action
* chore: bump version to 1.0.0a1 across all packages
- Updated version to 1.0.0a1 in pyproject.toml for crewai and crewai-tools
- Adjusted version in __init__.py files for consistency
* WIP: v1 docs (#3626)
(cherry picked from commit d46e20fa09bcd2f5916282f5553ddeb7183bd92c)
* docs: parity for all translations
* docs: full name of acronym AMP
* docs: fix lingering unused code
* docs: expand contextual options in docs.json
* docs: add contextual action to request feature on GitHub (#3635)
* chore: apply linting fixes to crewai-tools
* feat: add required env var validation for brightdata
Co-authored-by: Greyson Lalonde <greyson.r.lalonde@gmail.com>
* fix: handle properly anyOf oneOf allOf schema's props
Co-authored-by: Greyson Lalonde <greyson.r.lalonde@gmail.com>
* feat: bump version to 1.0.0a2
* Lorenze/native inference sdks (#3619)
* ruff linted
* using native sdks with litellm fallback
* drop exa
* drop print on completion
* Refactor LLM and utility functions for type consistency
- Updated `max_tokens` parameter in `LLM` class to accept `float` in addition to `int`.
- Modified `create_llm` function to ensure consistent type hints and return types, now returning `LLM | BaseLLM | None`.
- Adjusted type hints for various parameters in `create_llm` and `_llm_via_environment_or_fallback` functions for improved clarity and type safety.
- Enhanced test cases to reflect changes in type handling and ensure proper instantiation of LLM instances.
* fix agent_tests
* fix litellm tests and usagemetrics fix
* drop print
* Refactor LLM event handling and improve test coverage
- Removed commented-out event emission for LLM call failures in `llm.py`.
- Added `from_agent` parameter to `CrewAgentExecutor` for better context in LLM responses.
- Enhanced test for LLM call failure to simulate OpenAI API failure and updated assertions for clarity.
- Updated agent and task ID assertions in tests to ensure they are consistently treated as strings.
* fix test_converter
* fixed tests/agents/test_agent.py
* Refactor LLM context length exception handling and improve provider integration
- Renamed `LLMContextLengthExceededException` to `LLMContextLengthExceededExceptionError` for clarity and consistency.
- Updated LLM class to pass the provider parameter correctly during initialization.
- Enhanced error handling in various LLM provider implementations to raise the new exception type.
- Adjusted tests to reflect the updated exception name and ensure proper error handling in context length scenarios.
* Enhance LLM context window handling across providers
- Introduced CONTEXT_WINDOW_USAGE_RATIO to adjust context window sizes dynamically for Anthropic, Azure, Gemini, and OpenAI LLMs.
- Added validation for context window sizes in Azure and Gemini providers to ensure they fall within acceptable limits.
- Updated context window size calculations to use the new ratio, improving consistency and adaptability across different models.
- Removed hardcoded context window sizes in favor of ratio-based calculations for better flexibility.
* fix test agent again
* fix test agent
* feat: add native LLM providers for Anthropic, Azure, and Gemini
- Introduced new completion implementations for Anthropic, Azure, and Gemini, integrating their respective SDKs.
- Added utility functions for tool validation and extraction to support function calling across LLM providers.
- Enhanced context window management and token usage extraction for each provider.
- Created a common utility module for shared functionality among LLM providers.
* chore: update dependencies and improve context management
- Removed direct dependency on `litellm` from the main dependencies and added it under extras for better modularity.
- Updated the `litellm` dependency specification to allow for greater flexibility in versioning.
- Refactored context length exception handling across various LLM providers to use a consistent error class.
- Enhanced platform-specific dependency markers for NVIDIA packages to ensure compatibility across different systems.
* refactor(tests): update LLM instantiation to include is_litellm flag in test cases
- Modified multiple test cases in test_llm.py to set the is_litellm parameter to True when instantiating the LLM class.
- This change ensures that the tests are aligned with the latest LLM configuration requirements and improves consistency across test scenarios.
- Adjusted relevant assertions and comments to reflect the updated LLM behavior.
* linter
* linted
* revert constants
* fix(tests): correct type hint in expected model description
- Updated the expected description in the test_generate_model_description_dict_field function to use 'Dict' instead of 'dict' for consistency with type hinting conventions.
- This change ensures that the test accurately reflects the expected output format for model descriptions.
* refactor(llm): enhance LLM instantiation and error handling
- Updated the LLM class to include validation for the model parameter, ensuring it is a non-empty string.
- Improved error handling by logging warnings when the native SDK fails, allowing for a fallback to LiteLLM.
- Adjusted the instantiation of LLM in test cases to consistently include the is_litellm flag, aligning with recent changes in LLM configuration.
- Modified relevant tests to reflect these updates, ensuring better coverage and accuracy in testing scenarios.
* fixed test
* refactor(llm): enhance token usage tracking and add copy methods
- Updated the LLM class to track token usage and log callbacks in streaming mode, improving monitoring capabilities.
- Introduced shallow and deep copy methods for the LLM instance, allowing for better management of LLM configurations and parameters.
- Adjusted test cases to instantiate LLM with the is_litellm flag, ensuring alignment with recent changes in LLM configuration.
* refactor(tests): reorganize imports and enhance error messages in test cases
- Cleaned up import statements in test_crew.py for better organization and readability.
- Enhanced error messages in test cases to use `re.escape` for improved regex matching, ensuring more robust error handling.
- Adjusted comments for clarity and consistency across test scenarios.
- Ensured that all necessary modules are imported correctly to avoid potential runtime issues.
* feat: add base devtooling
* fix: ensure dep refs are updated for devtools
* fix: allow pre-release
* feat: allow release after tag
* feat: bump versions to 1.0.0a3
Co-authored-by: Greyson LaLonde <greyson.r.lalonde@gmail.com>
* fix: match tag and release title, ignore devtools build for pypi
* fix: allow failed pypi publish
* feat: introduce trigger listing and execution commands for local development (#3643)
* chore: exclude tests from ruff linting
* chore: exclude tests from GitHub Actions linter
* fix: replace print statements with logger in agent and memory handling
* chore: add noqa for intentional print in printer utility
* fix: resolve linting errors across codebase
* feat: update docs with new approach to consume Platform Actions (#3675)
* fix: remove duplicate line and add explicit env var
* feat: bump versions to 1.0.0a4 (#3686)
* Update triggers docs (#3678)
* docs: introduce triggers list & triggers run command
* docs: add KO triggers docs
* docs: ensure CREWAI_PLATFORM_INTEGRATION_TOKEN is mentioned on docs (#3687)
* Lorenze/bedrock llm (#3693)
* feat: add AWS Bedrock support and update dependencies
- Introduced BedrockCompletion class for AWS Bedrock integration in LLM.
- Added boto3 as a new dependency in both pyproject.toml and uv.lock.
- Updated LLM class to support Bedrock provider.
- Created new files for Bedrock provider implementation.
* using converse api
* converse
* linted
* refactor: update BedrockCompletion class to improve parameter handling
- Changed max_tokens from a fixed integer to an optional integer.
- Simplified model ID assignment by removing the inference profile mapping method.
- Cleaned up comments and unnecessary code related to tool specifications and model-specific parameters.
* feat: improve event bus thread safety and async support
Add thread-safe, async-compatible event bus with read–write locking and
handler dependency ordering. Remove blinker dependency and implement
direct dispatch. Improve type safety, error handling, and deterministic
event synchronization.
Refactor tests to auto-wait for async handlers, ensure clean teardown,
and add comprehensive concurrency coverage. Replace thread-local state
in AgentEvaluator with instance-based locking for correct cross-thread
access. Enhance tracing reliability and event finalization.
* feat: enhance OpenAICompletion class with additional client parameters (#3701)
* feat: enhance OpenAICompletion class with additional client parameters
- Added support for default_headers, default_query, and client_params in the OpenAICompletion class.
- Refactored client initialization to use a dedicated method for client parameter retrieval.
- Introduced new test cases to validate the correct usage of OpenAICompletion with various parameters.
* fix: correct test case for unsupported OpenAI model
- Updated the test_openai.py to ensure that the LLM instance is created before calling the method, maintaining proper error handling for unsupported models.
- This change ensures that the test accurately checks for the NotFoundError when an invalid model is specified.
* fix: enhance error handling in OpenAICompletion class
- Added specific exception handling for NotFoundError and APIConnectionError in the OpenAICompletion class to provide clearer error messages and improve logging.
- Updated the test case for unsupported models to ensure it raises a ValueError with the appropriate message when a non-existent model is specified.
- This change improves the robustness of the OpenAI API integration and enhances the clarity of error reporting.
* fix: improve test for unsupported OpenAI model handling
- Refactored the test case in test_openai.py to create the LLM instance after mocking the OpenAI client, ensuring proper error handling for unsupported models.
- This change enhances the clarity of the test by accurately checking for ValueError when a non-existent model is specified, aligning with recent improvements in error handling for the OpenAICompletion class.
* feat: bump versions to 1.0.0b1 (#3706)
* Lorenze/tools drop litellm (#3710)
* completely drop litellm and correctly pass config for qdrant
* feat: add support for additional embedding models in EmbeddingService
- Expanded the list of supported embedding models to include Google Vertex, Hugging Face, Jina, Ollama, OpenAI, Roboflow, Watson X, custom embeddings, Sentence Transformers, Text2Vec, OpenClip, and Instructor.
- This enhancement improves the versatility of the EmbeddingService by allowing integration with a wider range of embedding providers.
* fix: update collection parameter handling in CrewAIRagAdapter
- Changed the condition for setting vectors_config in the CrewAIRagAdapter to check for QdrantConfig instance instead of using hasattr. This improves type safety and ensures proper configuration handling for Qdrant integration.
* moved stagehand as optional dep (#3712)
* feat: bump versions to 1.0.0b2 (#3713)
* feat: enhance AnthropicCompletion class with additional client parame… (#3707)
* feat: enhance AnthropicCompletion class with additional client parameters and tool handling
- Added support for client_params in the AnthropicCompletion class to allow for additional client configuration.
- Refactored client initialization to use a dedicated method for retrieving client parameters.
- Implemented a new method to handle tool use conversation flow, ensuring proper execution and response handling.
- Introduced comprehensive test cases to validate the functionality of the AnthropicCompletion class, including tool use scenarios and parameter handling.
* drop print statements
* test: add fixture to mock ANTHROPIC_API_KEY for tests
- Introduced a pytest fixture to automatically mock the ANTHROPIC_API_KEY environment variable for all tests in the test_anthropic.py module.
- This change ensures that tests can run without requiring a real API key, improving test isolation and reliability.
* refactor: streamline streaming message handling in AnthropicCompletion class
- Removed the 'stream' parameter from the API call as it is set internally by the SDK.
- Simplified the handling of tool use events and response construction by extracting token usage from the final message.
- Enhanced the flow for managing tool use conversation, ensuring proper integration with the streaming API response.
* fix streaming here too
* fix: improve error handling in tool conversion for AnthropicCompletion class
- Enhanced exception handling during tool conversion by catching KeyError and ValueError.
- Added logging for conversion errors to aid in debugging and maintain robustness in tool integration.
* feat: enhance GeminiCompletion class with client parameter support (#3717)
* feat: enhance GeminiCompletion class with client parameter support
- Added support for client_params in the GeminiCompletion class to allow for additional client configuration.
- Refactored client initialization into a dedicated method for improved parameter handling.
- Introduced a new method to retrieve client parameters, ensuring compatibility with the base class.
- Enhanced error handling during client initialization to provide clearer messages for missing configuration.
- Updated documentation to reflect the changes in client parameter usage.
* add optional dependancies
* refactor: update test fixture to mock GOOGLE_API_KEY
- Renamed the fixture from `mock_anthropic_api_key` to `mock_google_api_key` to reflect the change in the environment variable being mocked.
- This update ensures that all tests in the module can run with a mocked GOOGLE_API_KEY, improving test isolation and reliability.
* fix tests
* feat: enhance BedrockCompletion class with advanced features
* feat: enhance BedrockCompletion class with advanced features and error handling
- Added support for guardrail configuration, additional model request fields, and custom response field paths in the BedrockCompletion class.
- Improved error handling for AWS exceptions and added token usage tracking with stop reason logging.
- Enhanced streaming response handling with comprehensive event management, including tool use and content block processing.
- Updated documentation to reflect new features and initialization parameters.
- Introduced a new test suite for BedrockCompletion to validate functionality and ensure robust integration with AWS Bedrock APIs.
* chore: add boto typing
* fix: use typing_extensions.Required for Python 3.10 compatibility
---------
Co-authored-by: Greyson Lalonde <greyson.r.lalonde@gmail.com>
* feat: azure native tests
* feat: add Azure AI Inference support and related tests
- Introduced the `azure-ai-inference` package with version `1.0.0b9` and its dependencies in `uv.lock` and `pyproject.toml`.
- Added new test files for Azure LLM functionality, including tests for Azure completion and tool handling.
- Implemented comprehensive test cases to validate Azure-specific behavior and integration with the CrewAI framework.
- Enhanced the testing framework to mock Azure credentials and ensure proper isolation during tests.
* feat: enhance AzureCompletion class with Azure OpenAI support
- Added support for the Azure OpenAI endpoint in the AzureCompletion class, allowing for flexible endpoint configurations.
- Implemented endpoint validation and correction to ensure proper URL formats for Azure OpenAI deployments.
- Enhanced error handling to provide clearer messages for common HTTP errors, including authentication and rate limit issues.
- Updated tests to validate the new endpoint handling and error messaging, ensuring robust integration with Azure AI Inference.
- Refactored parameter preparation to conditionally include the model parameter based on the endpoint type.
* refactor: convert project module to metaclass with full typing
* Lorenze/OpenAI base url backwards support (#3723)
* fix: enhance OpenAICompletion class base URL handling
- Updated the base URL assignment in the OpenAICompletion class to prioritize the new `api_base` attribute and fallback to the environment variable `OPENAI_BASE_URL` if both are not set.
- Added `api_base` to the list of parameters in the OpenAICompletion class to ensure proper configuration and flexibility in API endpoint management.
* feat: enhance OpenAICompletion class with api_base support
- Added the `api_base` parameter to the OpenAICompletion class to allow for flexible API endpoint configuration.
- Updated the `_get_client_params` method to prioritize `base_url` over `api_base`, ensuring correct URL handling.
- Introduced comprehensive tests to validate the behavior of `api_base` and `base_url` in various scenarios, including environment variable fallback.
- Enhanced test coverage for client parameter retrieval, ensuring robust integration with the OpenAI API.
* fix: improve OpenAICompletion class configuration handling
- Added a debug print statement to log the client configuration parameters during initialization for better traceability.
- Updated the base URL assignment logic to ensure it defaults to None if no valid base URL is provided, enhancing robustness in API endpoint configuration.
- Refined the retrieval of the `api_base` environment variable to streamline the configuration process.
* drop print
* feat: improvements on import native sdk support (#3725)
* feat: add support for Anthropic provider and enhance logging
- Introduced the `anthropic` package with version `0.69.0` in `pyproject.toml` and `uv.lock`, allowing for integration with the Anthropic API.
- Updated logging in the LLM class to provide clearer error messages when importing native providers, enhancing debugging capabilities.
- Improved error handling in the AnthropicCompletion class to guide users on installation via the updated error message format.
- Refactored import error handling in other provider classes to maintain consistency in error messaging and installation instructions.
* feat: enhance LLM support with Bedrock provider and update dependencies
- Added support for the `bedrock` provider in the LLM class, allowing integration with AWS Bedrock APIs.
- Updated `uv.lock` to replace `boto3` with `bedrock` in the dependencies, reflecting the new provider structure.
- Introduced `SUPPORTED_NATIVE_PROVIDERS` to include `bedrock` and ensure proper error handling when instantiating native providers.
- Enhanced error handling in the LLM class to raise informative errors when native provider instantiation fails.
- Added tests to validate the behavior of the new Bedrock provider and ensure fallback mechanisms work correctly for unsupported providers.
* test: update native provider fallback tests to expect ImportError
* adjust the test with the expected bevaior - raising ImportError
* this is exoecting the litellm format, all gemini native tests are in test_google.py
---------
Co-authored-by: Greyson LaLonde <greyson.r.lalonde@gmail.com>
* fix: remove stdout prints, improve test determinism, and update trace handling
Removed `print` statements from the `LLMStreamChunkEvent` handler to prevent
LLM response chunks from being written directly to stdout. The listener now
only tracks chunks internally.
Fixes #3715
Added explicit return statements for trace-related tests.
Updated cassette for `test_failed_evaluation` to reflect new behavior where
an empty trace dict is used instead of returning early.
Ensured deterministic cleanup order in test fixtures by making
`clear_event_bus_handlers` depend on `setup_test_environment`. This guarantees
event bus shutdown and file handle cleanup occur before temporary directory
deletion, resolving intermittent “Directory not empty” errors in CI.
* chore: remove lib/crewai exclusion from pre-commit hooks
* feat: enhance task guardrail functionality and validation
* feat: enhance task guardrail functionality and validation
- Introduced support for multiple guardrails in the Task class, allowing for sequential processing of guardrails.
- Added a new `guardrails` field to the Task model to accept a list of callable guardrails or string descriptions.
- Implemented validation to ensure guardrails are processed correctly, including handling of retries and error messages.
- Enhanced the `_invoke_guardrail_function` method to manage guardrail execution and integrate with existing task output processing.
- Updated tests to cover various scenarios involving multiple guardrails, including success, failure, and retry mechanisms.
This update improves the flexibility and robustness of task execution by allowing for more complex validation scenarios.
* refactor: enhance guardrail type handling in Task model
- Updated the Task class to improve guardrail type definitions, introducing GuardrailType and GuardrailsType for better clarity and type safety.
- Simplified the validation logic for guardrails, ensuring that both single and multiple guardrails are processed correctly.
- Enhanced error messages for guardrail validation to provide clearer feedback when incorrect types are provided.
- This refactor improves the maintainability and robustness of task execution by standardizing guardrail handling.
* feat: implement per-guardrail retry tracking in Task model
- Introduced a new private attribute `_guardrail_retry_counts` to the Task class for tracking retry attempts on a per-guardrail basis.
- Updated the guardrail processing logic to utilize the new retry tracking, allowing for independent retry counts for each guardrail.
- Enhanced error handling to provide clearer feedback when guardrails fail validation after exceeding retry limits.
- Modified existing tests to validate the new retry tracking behavior, ensuring accurate assertions on guardrail retries.
This update improves the robustness and flexibility of task execution by allowing for more granular control over guardrail validation and retry mechanisms.
* chore: 1.0.0b3 bump (#3734)
* chore: full ruff and mypy
improved linting, pre-commit setup, and internal architecture. Configured Ruff to respect .gitignore, added stricter rules, and introduced a lock pre-commit hook with virtualenv activation. Fixed type shadowing in EXASearchTool using a type_ alias to avoid PEP 563 conflicts and resolved circular imports in agent executor and guardrail modules. Removed agent-ops attributes, deprecated watson alias, and dropped crewai-enterprise tools with corresponding test updates. Refactored cache and memoization for thread safety and cleaned up structured output adapters and related logic.
* New MCL DSL (#3738)
* Adding MCP implementation
* New tests for MCP implementation
* fix tests
* update docs
* Revert "New tests for MCP implementation"
This reverts commit 0bbe6dee90.
* linter
* linter
* fix
* verify mcp pacakge exists
* adjust docs to be clear only remote servers are supported
* reverted
* ensure args schema generated properly
* properly close out
---------
Co-authored-by: lorenzejay <lorenzejaytech@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Greyson Lalonde <greyson.r.lalonde@gmail.com>
* feat: a2a experimental
experimental a2a support
---------
Co-authored-by: Lucas Gomide <lucaslg200@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Greyson LaLonde <greyson.r.lalonde@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Tony Kipkemboi <iamtonykipkemboi@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Mike Plachta <mplachta@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: João Moura <joaomdmoura@gmail.com>
Homepage · Docs · Start Cloud Trial · Blog · Forum
Fast and Flexible Multi-Agent Automation Framework
CrewAI is a lean, lightning-fast Python framework built entirely from scratch—completely independent of LangChain or other agent frameworks. It empowers developers with both high-level simplicity and precise low-level control, ideal for creating autonomous AI agents tailored to any scenario.
- CrewAI Crews: Optimize for autonomy and collaborative intelligence.
- CrewAI Flows: Enable granular, event-driven control, single LLM calls for precise task orchestration and supports Crews natively
With over 100,000 developers certified through our community courses at learn.crewai.com, CrewAI is rapidly becoming the standard for enterprise-ready AI automation.
CrewAI AMP Suite
CrewAI AMP Suite is a comprehensive bundle tailored for organizations that require secure, scalable, and easy-to-manage agent-driven automation.
You can try one part of the suite the Crew Control Plane for free
Crew Control Plane Key Features:
- Tracing & Observability: Monitor and track your AI agents and workflows in real-time, including metrics, logs, and traces.
- Unified Control Plane: A centralized platform for managing, monitoring, and scaling your AI agents and workflows.
- Seamless Integrations: Easily connect with existing enterprise systems, data sources, and cloud infrastructure.
- Advanced Security: Built-in robust security and compliance measures ensuring safe deployment and management.
- Actionable Insights: Real-time analytics and reporting to optimize performance and decision-making.
- 24/7 Support: Dedicated enterprise support to ensure uninterrupted operation and quick resolution of issues.
- On-premise and Cloud Deployment Options: Deploy CrewAI AMP on-premise or in the cloud, depending on your security and compliance requirements.
CrewAI AMP is designed for enterprises seeking a powerful, reliable solution to transform complex business processes into efficient, intelligent automations.
Table of contents
- Why CrewAI?
- Getting Started
- Key Features
- Understanding Flows and Crews
- CrewAI vs LangGraph
- Examples
- Connecting Your Crew to a Model
- How CrewAI Compares
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Contribution
- Telemetry
- License
Why CrewAI?
CrewAI unlocks the true potential of multi-agent automation, delivering the best-in-class combination of speed, flexibility, and control with either Crews of AI Agents or Flows of Events:
- Standalone Framework: Built from scratch, independent of LangChain or any other agent framework.
- High Performance: Optimized for speed and minimal resource usage, enabling faster execution.
- Flexible Low Level Customization: Complete freedom to customize at both high and low levels - from overall workflows and system architecture to granular agent behaviors, internal prompts, and execution logic.
- Ideal for Every Use Case: Proven effective for both simple tasks and highly complex, real-world, enterprise-grade scenarios.
- Robust Community: Backed by a rapidly growing community of over 100,000 certified developers offering comprehensive support and resources.
CrewAI empowers developers and enterprises to confidently build intelligent automations, bridging the gap between simplicity, flexibility, and performance.
Getting Started
Setup and run your first CrewAI agents by following this tutorial.
Learning Resources
Learn CrewAI through our comprehensive courses:
- Multi AI Agent Systems with CrewAI - Master the fundamentals of multi-agent systems
- Practical Multi AI Agents and Advanced Use Cases - Deep dive into advanced implementations
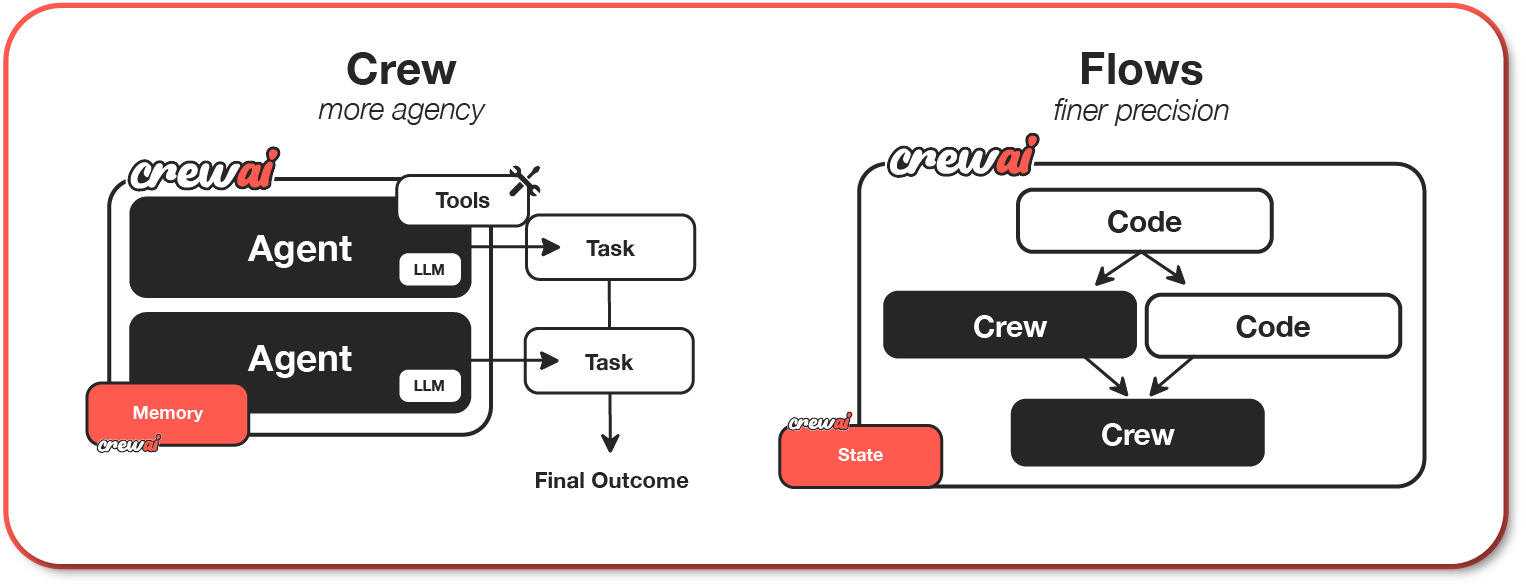
Understanding Flows and Crews
CrewAI offers two powerful, complementary approaches that work seamlessly together to build sophisticated AI applications:
-
Crews: Teams of AI agents with true autonomy and agency, working together to accomplish complex tasks through role-based collaboration. Crews enable:
- Natural, autonomous decision-making between agents
- Dynamic task delegation and collaboration
- Specialized roles with defined goals and expertise
- Flexible problem-solving approaches
-
Flows: Production-ready, event-driven workflows that deliver precise control over complex automations. Flows provide:
- Fine-grained control over execution paths for real-world scenarios
- Secure, consistent state management between tasks
- Clean integration of AI agents with production Python code
- Conditional branching for complex business logic
The true power of CrewAI emerges when combining Crews and Flows. This synergy allows you to:
- Build complex, production-grade applications
- Balance autonomy with precise control
- Handle sophisticated real-world scenarios
- Maintain clean, maintainable code structure
Getting Started with Installation
To get started with CrewAI, follow these simple steps:
1. Installation
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.14 installed on your system. CrewAI uses UV for dependency management and package handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
First, install CrewAI:
pip install crewai
If you want to install the 'crewai' package along with its optional features that include additional tools for agents, you can do so by using the following command:
pip install 'crewai[tools]'
The command above installs the basic package and also adds extra components which require more dependencies to function.
Troubleshooting Dependencies
If you encounter issues during installation or usage, here are some common solutions:
Common Issues
-
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tiktoken'
- Install tiktoken explicitly:
pip install 'crewai[embeddings]' - If using embedchain or other tools:
pip install 'crewai[tools]'
- Install tiktoken explicitly:
-
Failed building wheel for tiktoken
- Ensure Rust compiler is installed (see installation steps above)
- For Windows: Verify Visual C++ Build Tools are installed
- Try upgrading pip:
pip install --upgrade pip - If issues persist, use a pre-built wheel:
pip install tiktoken --prefer-binary
2. Setting Up Your Crew with the YAML Configuration
To create a new CrewAI project, run the following CLI (Command Line Interface) command:
crewai create crew <project_name>
This command creates a new project folder with the following structure:
my_project/
├── .gitignore
├── pyproject.toml
├── README.md
├── .env
└── src/
└── my_project/
├── __init__.py
├── main.py
├── crew.py
├── tools/
│ ├── custom_tool.py
│ └── __init__.py
└── config/
├── agents.yaml
└── tasks.yaml
You can now start developing your crew by editing the files in the src/my_project folder. The main.py file is the entry point of the project, the crew.py file is where you define your crew, the agents.yaml file is where you define your agents, and the tasks.yaml file is where you define your tasks.
To customize your project, you can:
- Modify
src/my_project/config/agents.yamlto define your agents. - Modify
src/my_project/config/tasks.yamlto define your tasks. - Modify
src/my_project/crew.pyto add your own logic, tools, and specific arguments. - Modify
src/my_project/main.pyto add custom inputs for your agents and tasks. - Add your environment variables into the
.envfile.
Example of a simple crew with a sequential process:
Instantiate your crew:
crewai create crew latest-ai-development
Modify the files as needed to fit your use case:
agents.yaml
# src/my_project/config/agents.yaml
researcher:
role: >
{topic} Senior Data Researcher
goal: >
Uncover cutting-edge developments in {topic}
backstory: >
You're a seasoned researcher with a knack for uncovering the latest
developments in {topic}. Known for your ability to find the most relevant
information and present it in a clear and concise manner.
reporting_analyst:
role: >
{topic} Reporting Analyst
goal: >
Create detailed reports based on {topic} data analysis and research findings
backstory: >
You're a meticulous analyst with a keen eye for detail. You're known for
your ability to turn complex data into clear and concise reports, making
it easy for others to understand and act on the information you provide.
tasks.yaml
# src/my_project/config/tasks.yaml
research_task:
description: >
Conduct a thorough research about {topic}
Make sure you find any interesting and relevant information given
the current year is 2025.
expected_output: >
A list with 10 bullet points of the most relevant information about {topic}
agent: researcher
reporting_task:
description: >
Review the context you got and expand each topic into a full section for a report.
Make sure the report is detailed and contains any and all relevant information.
expected_output: >
A fully fledge reports with the mains topics, each with a full section of information.
Formatted as markdown without '```'
agent: reporting_analyst
output_file: report.md
crew.py
# src/my_project/crew.py
from crewai import Agent, Crew, Process, Task
from crewai.project import CrewBase, agent, crew, task
from crewai_tools import SerperDevTool
from crewai.agents.agent_builder.base_agent import BaseAgent
from typing import List
@CrewBase
class LatestAiDevelopmentCrew():
"""LatestAiDevelopment crew"""
agents: List[BaseAgent]
tasks: List[Task]
@agent
def researcher(self) -> Agent:
return Agent(
config=self.agents_config['researcher'],
verbose=True,
tools=[SerperDevTool()]
)
@agent
def reporting_analyst(self) -> Agent:
return Agent(
config=self.agents_config['reporting_analyst'],
verbose=True
)
@task
def research_task(self) -> Task:
return Task(
config=self.tasks_config['research_task'],
)
@task
def reporting_task(self) -> Task:
return Task(
config=self.tasks_config['reporting_task'],
output_file='report.md'
)
@crew
def crew(self) -> Crew:
"""Creates the LatestAiDevelopment crew"""
return Crew(
agents=self.agents, # Automatically created by the @agent decorator
tasks=self.tasks, # Automatically created by the @task decorator
process=Process.sequential,
verbose=True,
)
main.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# src/my_project/main.py
import sys
from latest_ai_development.crew import LatestAiDevelopmentCrew
def run():
"""
Run the crew.
"""
inputs = {
'topic': 'AI Agents'
}
LatestAiDevelopmentCrew().crew().kickoff(inputs=inputs)
3. Running Your Crew
Before running your crew, make sure you have the following keys set as environment variables in your .env file:
- An OpenAI API key (or other LLM API key):
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-... - A Serper.dev API key:
SERPER_API_KEY=YOUR_KEY_HERE
Lock the dependencies and install them by using the CLI command but first, navigate to your project directory:
cd my_project
crewai install (Optional)
To run your crew, execute the following command in the root of your project:
crewai run
or
python src/my_project/main.py
If an error happens due to the usage of poetry, please run the following command to update your crewai package:
crewai update
You should see the output in the console and the report.md file should be created in the root of your project with the full final report.
In addition to the sequential process, you can use the hierarchical process, which automatically assigns a manager to the defined crew to properly coordinate the planning and execution of tasks through delegation and validation of results. See more about the processes here.
Key Features
CrewAI stands apart as a lean, standalone, high-performance multi-AI Agent framework delivering simplicity, flexibility, and precise control—free from the complexity and limitations found in other agent frameworks.
- Standalone & Lean: Completely independent from other frameworks like LangChain, offering faster execution and lighter resource demands.
- Flexible & Precise: Easily orchestrate autonomous agents through intuitive Crews or precise Flows, achieving perfect balance for your needs.
- Seamless Integration: Effortlessly combine Crews (autonomy) and Flows (precision) to create complex, real-world automations.
- Deep Customization: Tailor every aspect—from high-level workflows down to low-level internal prompts and agent behaviors.
- Reliable Performance: Consistent results across simple tasks and complex, enterprise-level automations.
- Thriving Community: Backed by robust documentation and over 100,000 certified developers, providing exceptional support and guidance.
Choose CrewAI to easily build powerful, adaptable, and production-ready AI automations.
Examples
You can test different real life examples of AI crews in the CrewAI-examples repo:
Quick Tutorial
Write Job Descriptions
Check out code for this example or watch a video below:
Trip Planner
Check out code for this example or watch a video below:
Stock Analysis
Check out code for this example or watch a video below:
Using Crews and Flows Together
CrewAI's power truly shines when combining Crews with Flows to create sophisticated automation pipelines.
CrewAI flows support logical operators like or_ and and_ to combine multiple conditions. This can be used with @start, @listen, or @router decorators to create complex triggering conditions.
or_: Triggers when any of the specified conditions are met.and_Triggers when all of the specified conditions are met.
Here's how you can orchestrate multiple Crews within a Flow:
from crewai.flow.flow import Flow, listen, start, router, or_
from crewai import Crew, Agent, Task, Process
from pydantic import BaseModel
# Define structured state for precise control
class MarketState(BaseModel):
sentiment: str = "neutral"
confidence: float = 0.0
recommendations: list = []
class AdvancedAnalysisFlow(Flow[MarketState]):
@start()
def fetch_market_data(self):
# Demonstrate low-level control with structured state
self.state.sentiment = "analyzing"
return {"sector": "tech", "timeframe": "1W"} # These parameters match the task description template
@listen(fetch_market_data)
def analyze_with_crew(self, market_data):
# Show crew agency through specialized roles
analyst = Agent(
role="Senior Market Analyst",
goal="Conduct deep market analysis with expert insight",
backstory="You're a veteran analyst known for identifying subtle market patterns"
)
researcher = Agent(
role="Data Researcher",
goal="Gather and validate supporting market data",
backstory="You excel at finding and correlating multiple data sources"
)
analysis_task = Task(
description="Analyze {sector} sector data for the past {timeframe}",
expected_output="Detailed market analysis with confidence score",
agent=analyst
)
research_task = Task(
description="Find supporting data to validate the analysis",
expected_output="Corroborating evidence and potential contradictions",
agent=researcher
)
# Demonstrate crew autonomy
analysis_crew = Crew(
agents=[analyst, researcher],
tasks=[analysis_task, research_task],
process=Process.sequential,
verbose=True
)
return analysis_crew.kickoff(inputs=market_data) # Pass market_data as named inputs
@router(analyze_with_crew)
def determine_next_steps(self):
# Show flow control with conditional routing
if self.state.confidence > 0.8:
return "high_confidence"
elif self.state.confidence > 0.5:
return "medium_confidence"
return "low_confidence"
@listen("high_confidence")
def execute_strategy(self):
# Demonstrate complex decision making
strategy_crew = Crew(
agents=[
Agent(role="Strategy Expert",
goal="Develop optimal market strategy")
],
tasks=[
Task(description="Create detailed strategy based on analysis",
expected_output="Step-by-step action plan")
]
)
return strategy_crew.kickoff()
@listen(or_("medium_confidence", "low_confidence"))
def request_additional_analysis(self):
self.state.recommendations.append("Gather more data")
return "Additional analysis required"
This example demonstrates how to:
- Use Python code for basic data operations
- Create and execute Crews as steps in your workflow
- Use Flow decorators to manage the sequence of operations
- Implement conditional branching based on Crew results
Connecting Your Crew to a Model
CrewAI supports using various LLMs through a variety of connection options. By default your agents will use the OpenAI API when querying the model. However, there are several other ways to allow your agents to connect to models. For example, you can configure your agents to use a local model via the Ollama tool.
Please refer to the Connect CrewAI to LLMs page for details on configuring your agents' connections to models.
How CrewAI Compares
CrewAI's Advantage: CrewAI combines autonomous agent intelligence with precise workflow control through its unique Crews and Flows architecture. The framework excels at both high-level orchestration and low-level customization, enabling complex, production-grade systems with granular control.
- LangGraph: While LangGraph provides a foundation for building agent workflows, its approach requires significant boilerplate code and complex state management patterns. The framework's tight coupling with LangChain can limit flexibility when implementing custom agent behaviors or integrating with external systems.
P.S. CrewAI demonstrates significant performance advantages over LangGraph, executing 5.76x faster in certain cases like this QA task example (see comparison) while achieving higher evaluation scores with faster completion times in certain coding tasks, like in this example (detailed analysis).
- Autogen: While Autogen excels at creating conversational agents capable of working together, it lacks an inherent concept of process. In Autogen, orchestrating agents' interactions requires additional programming, which can become complex and cumbersome as the scale of tasks grows.
- ChatDev: ChatDev introduced the idea of processes into the realm of AI agents, but its implementation is quite rigid. Customizations in ChatDev are limited and not geared towards production environments, which can hinder scalability and flexibility in real-world applications.
Contribution
CrewAI is open-source and we welcome contributions. If you're looking to contribute, please:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch for your feature.
- Add your feature or improvement.
- Send a pull request.
- We appreciate your input!
Installing Dependencies
uv lock
uv sync
Virtual Env
uv venv
Pre-commit hooks
pre-commit install
Running Tests
uv run pytest .
Running static type checks
uvx mypy src
Packaging
uv build
Installing Locally
pip install dist/*.tar.gz
Telemetry
CrewAI uses anonymous telemetry to collect usage data with the main purpose of helping us improve the library by focusing our efforts on the most used features, integrations and tools.
It's pivotal to understand that NO data is collected concerning prompts, task descriptions, agents' backstories or goals, usage of tools, API calls, responses, any data processed by the agents, or secrets and environment variables, with the exception of the conditions mentioned. When the share_crew feature is enabled, detailed data including task descriptions, agents' backstories or goals, and other specific attributes are collected to provide deeper insights while respecting user privacy. Users can disable telemetry by setting the environment variable OTEL_SDK_DISABLED to true.
Data collected includes:
- Version of CrewAI
- So we can understand how many users are using the latest version
- Version of Python
- So we can decide on what versions to better support
- General OS (e.g. number of CPUs, macOS/Windows/Linux)
- So we know what OS we should focus on and if we could build specific OS related features
- Number of agents and tasks in a crew
- So we make sure we are testing internally with similar use cases and educate people on the best practices
- Crew Process being used
- Understand where we should focus our efforts
- If Agents are using memory or allowing delegation
- Understand if we improved the features or maybe even drop them
- If Tasks are being executed in parallel or sequentially
- Understand if we should focus more on parallel execution
- Language model being used
- Improved support on most used languages
- Roles of agents in a crew
- Understand high level use cases so we can build better tools, integrations and examples about it
- Tools names available
- Understand out of the publicly available tools, which ones are being used the most so we can improve them
Users can opt-in to Further Telemetry, sharing the complete telemetry data by setting the share_crew attribute to True on their Crews. Enabling share_crew results in the collection of detailed crew and task execution data, including goal, backstory, context, and output of tasks. This enables a deeper insight into usage patterns while respecting the user's choice to share.
License
CrewAI is released under the MIT License.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
General
- What exactly is CrewAI?
- How do I install CrewAI?
- Does CrewAI depend on LangChain?
- Is CrewAI open-source?
- Does CrewAI collect data from users?
Features and Capabilities
- Can CrewAI handle complex use cases?
- Can I use CrewAI with local AI models?
- What makes Crews different from Flows?
- How is CrewAI better than LangChain?
- Does CrewAI support fine-tuning or training custom models?
Resources and Community
Enterprise Features
- What additional features does CrewAI AMP offer?
- Is CrewAI AMP available for cloud and on-premise deployments?
- Can I try CrewAI AMP for free?
Q: What exactly is CrewAI?
A: CrewAI is a standalone, lean, and fast Python framework built specifically for orchestrating autonomous AI agents. Unlike frameworks like LangChain, CrewAI does not rely on external dependencies, making it leaner, faster, and simpler.
Q: How do I install CrewAI?
A: Install CrewAI using pip:
pip install crewai
For additional tools, use:
pip install 'crewai[tools]'
Q: Does CrewAI depend on LangChain?
A: No. CrewAI is built entirely from the ground up, with no dependencies on LangChain or other agent frameworks. This ensures a lean, fast, and flexible experience.
Q: Can CrewAI handle complex use cases?
A: Yes. CrewAI excels at both simple and highly complex real-world scenarios, offering deep customization options at both high and low levels, from internal prompts to sophisticated workflow orchestration.
Q: Can I use CrewAI with local AI models?
A: Absolutely! CrewAI supports various language models, including local ones. Tools like Ollama and LM Studio allow seamless integration. Check the LLM Connections documentation for more details.
Q: What makes Crews different from Flows?
A: Crews provide autonomous agent collaboration, ideal for tasks requiring flexible decision-making and dynamic interaction. Flows offer precise, event-driven control, ideal for managing detailed execution paths and secure state management. You can seamlessly combine both for maximum effectiveness.
Q: How is CrewAI better than LangChain?
A: CrewAI provides simpler, more intuitive APIs, faster execution speeds, more reliable and consistent results, robust documentation, and an active community—addressing common criticisms and limitations associated with LangChain.
Q: Is CrewAI open-source?
A: Yes, CrewAI is open-source and actively encourages community contributions and collaboration.
Q: Does CrewAI collect data from users?
A: CrewAI collects anonymous telemetry data strictly for improvement purposes. Sensitive data such as prompts, tasks, or API responses are never collected unless explicitly enabled by the user.
Q: Where can I find real-world CrewAI examples?
A: Check out practical examples in the CrewAI-examples repository, covering use cases like trip planners, stock analysis, and job postings.
Q: How can I contribute to CrewAI?
A: Contributions are warmly welcomed! Fork the repository, create your branch, implement your changes, and submit a pull request. See the Contribution section of the README for detailed guidelines.
Q: What additional features does CrewAI AMP offer?
A: CrewAI AMP provides advanced features such as a unified control plane, real-time observability, secure integrations, advanced security, actionable insights, and dedicated 24/7 enterprise support.
Q: Is CrewAI AMP available for cloud and on-premise deployments?
A: Yes, CrewAI AMP supports both cloud-based and on-premise deployment options, allowing enterprises to meet their specific security and compliance requirements.
Q: Can I try CrewAI AMP for free?
A: Yes, you can explore part of the CrewAI AMP Suite by accessing the Crew Control Plane for free.
Q: Does CrewAI support fine-tuning or training custom models?
A: Yes, CrewAI can integrate with custom-trained or fine-tuned models, allowing you to enhance your agents with domain-specific knowledge and accuracy.
Q: Can CrewAI agents interact with external tools and APIs?
A: Absolutely! CrewAI agents can easily integrate with external tools, APIs, and databases, empowering them to leverage real-world data and resources.
Q: Is CrewAI suitable for production environments?
A: Yes, CrewAI is explicitly designed with production-grade standards, ensuring reliability, stability, and scalability for enterprise deployments.
Q: How scalable is CrewAI?
A: CrewAI is highly scalable, supporting simple automations and large-scale enterprise workflows involving numerous agents and complex tasks simultaneously.
Q: Does CrewAI offer debugging and monitoring tools?
A: Yes, CrewAI AMP includes advanced debugging, tracing, and real-time observability features, simplifying the management and troubleshooting of your automations.
Q: What programming languages does CrewAI support?
A: CrewAI is primarily Python-based but easily integrates with services and APIs written in any programming language through its flexible API integration capabilities.
Q: Does CrewAI offer educational resources for beginners?
A: Yes, CrewAI provides extensive beginner-friendly tutorials, courses, and documentation through learn.crewai.com, supporting developers at all skill levels.
Q: Can CrewAI automate human-in-the-loop workflows?
A: Yes, CrewAI fully supports human-in-the-loop workflows, allowing seamless collaboration between human experts and AI agents for enhanced decision-making.