mirror of
https://github.com/crewAIInc/crewAI.git
synced 2025-12-16 12:28:30 +00:00
Compare commits
53 Commits
lorenze/pa
...
devin/1750
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
56ee5c1e86 | ||
|
|
e9bf07cbdc | ||
|
|
6c8677a2d7 | ||
|
|
c96d4a6823 | ||
|
|
59032817c7 | ||
|
|
e9d8a853ea | ||
|
|
463ea2b97f | ||
|
|
ec2903e5ee | ||
|
|
4364585ebc | ||
|
|
0a6b7c655b | ||
|
|
db1e9e9b9a | ||
|
|
d92382b6cf | ||
|
|
7c8f2a1325 | ||
|
|
a40447df29 | ||
|
|
5d6b467042 | ||
|
|
e0ff30c212 | ||
|
|
a5b5c8ab37 | ||
|
|
7f12e98de5 | ||
|
|
99133104dd | ||
|
|
970a63c13c | ||
|
|
06c991d8c3 | ||
|
|
739eb72fd0 | ||
|
|
b0d2e9fe31 | ||
|
|
5c51349a85 | ||
|
|
5b740467cb | ||
|
|
e9d9dd2a79 | ||
|
|
3e74cb4832 | ||
|
|
db3c8a49bd | ||
|
|
8a37b535ed | ||
|
|
e6ac1311e7 | ||
|
|
b0d89698fd | ||
|
|
21d063a46c | ||
|
|
02912a653e | ||
|
|
f1cfba7527 | ||
|
|
3e075cd48d | ||
|
|
e03ec4d60f | ||
|
|
ba740c6157 | ||
|
|
34c813ed79 | ||
|
|
545cc2ffe4 | ||
|
|
47b97d9b7f | ||
|
|
bf8fbb0a44 | ||
|
|
552921cf83 | ||
|
|
372874fb3a | ||
|
|
2bd6b72aae | ||
|
|
f02e0060fa | ||
|
|
66b7628972 | ||
|
|
c045399d6b | ||
|
|
1da2fd2a5c | ||
|
|
e07e11fbe7 | ||
|
|
55ed91e313 | ||
|
|
e676c83d7f | ||
|
|
844d142f2e | ||
|
|
bcc694348e |
5
.github/workflows/linter.yml
vendored
5
.github/workflows/linter.yml
vendored
@@ -30,4 +30,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Run Ruff on Changed Files
|
||||
if: ${{ steps.changed-files.outputs.files != '' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ steps.changed-files.outputs.files }}" | tr " " "\n" | xargs -I{} ruff check "{}"
|
||||
echo "${{ steps.changed-files.outputs.files }}" \
|
||||
| tr ' ' '\n' \
|
||||
| grep -v 'src/crewai/cli/templates/' \
|
||||
| xargs -I{} ruff check "{}"
|
||||
|
||||
45
.github/workflows/mkdocs.yml
vendored
45
.github/workflows/mkdocs.yml
vendored
@@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Deploy MkDocs
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
release:
|
||||
types: [published]
|
||||
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: write
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: '3.10'
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Calculate requirements hash
|
||||
id: req-hash
|
||||
run: echo "::set-output name=hash::$(sha256sum requirements-doc.txt | awk '{print $1}')"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup cache
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
key: mkdocs-material-${{ steps.req-hash.outputs.hash }}
|
||||
path: .cache
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
mkdocs-material-
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Requirements
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt-get update &&
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pngquant &&
|
||||
pip install mkdocs-material mkdocs-material-extensions pillow cairosvg
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GH_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build and deploy MkDocs
|
||||
run: mkdocs gh-deploy --force
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/tests.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/tests.yml
vendored
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
timeout-minutes: 15
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
python-version: ['3.10', '3.11', '3.12']
|
||||
python-version: ['3.10', '3.11', '3.12', '3.13']
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -161,7 +161,7 @@ To get started with CrewAI, follow these simple steps:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.13 installed on your system. CrewAI uses [UV](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for dependency management and package handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.14 installed on your system. CrewAI uses [UV](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for dependency management and package handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install CrewAI:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -403,7 +403,7 @@ In addition to the sequential process, you can use the hierarchical process, whi
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
CrewAI stands apart as a lean, standalone, high-performance framework delivering simplicity, flexibility, and precise control—free from the complexity and limitations found in other agent frameworks.
|
||||
CrewAI stands apart as a lean, standalone, high-performance multi-AI Agent framework delivering simplicity, flexibility, and precise control—free from the complexity and limitations found in other agent frameworks.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Standalone & Lean**: Completely independent from other frameworks like LangChain, offering faster execution and lighter resource demands.
|
||||
- **Flexible & Precise**: Easily orchestrate autonomous agents through intuitive [Crews](https://docs.crewai.com/concepts/crews) or precise [Flows](https://docs.crewai.com/concepts/flows), achieving perfect balance for your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
18
docs/common-room-tracking.js
Normal file
18
docs/common-room-tracking.js
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
(function() {
|
||||
if (typeof window === 'undefined') return;
|
||||
if (typeof window.signals !== 'undefined') return;
|
||||
var script = document.createElement('script');
|
||||
script.src = 'https://cdn.cr-relay.com/v1/site/883520f4-c431-44be-80e7-e123a1ee7a2b/signals.js';
|
||||
script.async = true;
|
||||
window.signals = Object.assign(
|
||||
[],
|
||||
['page', 'identify', 'form'].reduce(function (acc, method){
|
||||
acc[method] = function () {
|
||||
signals.push([method, arguments]);
|
||||
return signals;
|
||||
};
|
||||
return acc;
|
||||
}, {})
|
||||
);
|
||||
document.head.appendChild(script);
|
||||
})();
|
||||
@@ -43,7 +43,6 @@ The Visual Agent Builder enables:
|
||||
| **Max Iterations** _(optional)_ | `max_iter` | `int` | Maximum iterations before the agent must provide its best answer. Default is 20. |
|
||||
| **Max RPM** _(optional)_ | `max_rpm` | `Optional[int]` | Maximum requests per minute to avoid rate limits. |
|
||||
| **Max Execution Time** _(optional)_ | `max_execution_time` | `Optional[int]` | Maximum time (in seconds) for task execution. |
|
||||
| **Memory** _(optional)_ | `memory` | `bool` | Whether the agent should maintain memory of interactions. Default is True. |
|
||||
| **Verbose** _(optional)_ | `verbose` | `bool` | Enable detailed execution logs for debugging. Default is False. |
|
||||
| **Allow Delegation** _(optional)_ | `allow_delegation` | `bool` | Allow the agent to delegate tasks to other agents. Default is False. |
|
||||
| **Step Callback** _(optional)_ | `step_callback` | `Optional[Any]` | Function called after each agent step, overrides crew callback. |
|
||||
@@ -156,7 +155,6 @@ agent = Agent(
|
||||
"you excel at finding patterns in complex datasets.",
|
||||
llm="gpt-4", # Default: OPENAI_MODEL_NAME or "gpt-4"
|
||||
function_calling_llm=None, # Optional: Separate LLM for tool calling
|
||||
memory=True, # Default: True
|
||||
verbose=False, # Default: False
|
||||
allow_delegation=False, # Default: False
|
||||
max_iter=20, # Default: 20 iterations
|
||||
@@ -297,6 +295,11 @@ multimodal_agent = Agent(
|
||||
- `"safe"`: Uses Docker (recommended for production)
|
||||
- `"unsafe"`: Direct execution (use only in trusted environments)
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
This runs a default Docker image. If you want to configure the docker image, the checkout the Code Interpreter Tool in the tools section.
|
||||
Add the code interpreter tool as a tool in the agent as a tool parameter.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Advanced Features
|
||||
- `multimodal`: Enable multimodal capabilities for processing text and visual content
|
||||
- `reasoning`: Enable agent to reflect and create plans before executing tasks
|
||||
@@ -537,7 +540,6 @@ The context window management feature works automatically in the background. You
|
||||
- Adjust `max_iter` and `max_retry_limit` based on task complexity
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory and Context Management
|
||||
- Use `memory: true` for tasks requiring historical context
|
||||
- Leverage `knowledge_sources` for domain-specific information
|
||||
- Configure `embedder` when using custom embedding models
|
||||
- Use custom templates (`system_template`, `prompt_template`, `response_template`) for fine-grained control over agent behavior
|
||||
@@ -585,7 +587,6 @@ The context window management feature works automatically in the background. You
|
||||
- Review code sandbox settings
|
||||
|
||||
4. **Memory Issues**: If agent responses seem inconsistent:
|
||||
- Verify memory is enabled
|
||||
- Check knowledge source configuration
|
||||
- Review conversation history management
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -200,6 +200,37 @@ Deploy the crew or flow to [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com).
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Reads your local project configuration.
|
||||
- Prompts you to confirm the environment variables (like `OPENAI_API_KEY`, `SERPER_API_KEY`) found locally. These will be securely stored with the deployment on the Enterprise platform. Ensure your sensitive keys are correctly configured locally (e.g., in a `.env` file) before running this.
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. Organization Management
|
||||
|
||||
Manage your CrewAI Enterprise organizations.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell Terminal
|
||||
crewai org [COMMAND] [OPTIONS]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Commands:
|
||||
|
||||
- `list`: List all organizations you belong to
|
||||
```shell Terminal
|
||||
crewai org list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `current`: Display your currently active organization
|
||||
```shell Terminal
|
||||
crewai org current
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `switch`: Switch to a specific organization
|
||||
```shell Terminal
|
||||
crewai org switch <organization_id>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
You must be authenticated to CrewAI Enterprise to use these organization management commands.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
- **Create a deployment** (continued):
|
||||
- Links the deployment to the corresponding remote GitHub repository (it usually detects this automatically).
|
||||
|
||||
- **Deploy the Crew**: Once you are authenticated, you can deploy your crew or flow to CrewAI Enterprise.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -325,12 +325,12 @@ for result in results:
|
||||
|
||||
# Example of using kickoff_async
|
||||
inputs = {'topic': 'AI in healthcare'}
|
||||
async_result = my_crew.kickoff_async(inputs=inputs)
|
||||
async_result = await my_crew.kickoff_async(inputs=inputs)
|
||||
print(async_result)
|
||||
|
||||
# Example of using kickoff_for_each_async
|
||||
inputs_array = [{'topic': 'AI in healthcare'}, {'topic': 'AI in finance'}]
|
||||
async_results = my_crew.kickoff_for_each_async(inputs=inputs_array)
|
||||
async_results = await my_crew.kickoff_for_each_async(inputs=inputs_array)
|
||||
for async_result in async_results:
|
||||
print(async_result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -233,6 +233,11 @@ CrewAI provides a wide range of events that you can listen for:
|
||||
- **KnowledgeQueryFailedEvent**: Emitted when a knowledge query fails
|
||||
- **KnowledgeSearchQueryFailedEvent**: Emitted when a knowledge search query fails
|
||||
|
||||
### LLM Guardrail Events
|
||||
|
||||
- **LLMGuardrailStartedEvent**: Emitted when a guardrail validation starts. Contains details about the guardrail being applied and retry count.
|
||||
- **LLMGuardrailCompletedEvent**: Emitted when a guardrail validation completes. Contains details about validation success/failure, results, and error messages if any.
|
||||
|
||||
### Flow Events
|
||||
|
||||
- **FlowCreatedEvent**: Emitted when a Flow is created
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -602,6 +602,30 @@ agent = Agent(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Configuring Azure OpenAI Embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
When using Azure OpenAI embeddings:
|
||||
1. Make sure you deploy the embedding model in Azure platform first
|
||||
2. Then you need to use the following configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Researcher",
|
||||
goal="Research topics",
|
||||
backstory="Expert researcher",
|
||||
knowledge_sources=[knowledge_source],
|
||||
embedder={
|
||||
"provider": "azure",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"api_key": "your-azure-api-key",
|
||||
"model": "text-embedding-ada-002", # change to the model you are using and is deployed in Azure
|
||||
"api_base": "https://your-azure-endpoint.openai.azure.com/",
|
||||
"api_version": "2024-02-01"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced Features
|
||||
|
||||
### Query Rewriting
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -29,6 +29,10 @@ my_crew = Crew(
|
||||
|
||||
From this point on, your crew will have planning enabled, and the tasks will be planned before each iteration.
|
||||
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
When planning is enabled, crewAI will use `gpt-4o-mini` as the default LLM for planning, which requires a valid OpenAI API key. Since your agents might be using different LLMs, this could cause confusion if you don't have an OpenAI API key configured or if you're experiencing unexpected behavior related to LLM API calls.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Planning LLM
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can define the LLM that will be used to plan the tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,6 +32,7 @@ The Enterprise Tools Repository includes:
|
||||
- **Customizability**: Provides the flexibility to develop custom tools or utilize existing ones, catering to the specific needs of agents.
|
||||
- **Error Handling**: Incorporates robust error handling mechanisms to ensure smooth operation.
|
||||
- **Caching Mechanism**: Features intelligent caching to optimize performance and reduce redundant operations.
|
||||
- **Asynchronous Support**: Handles both synchronous and asynchronous tools, enabling non-blocking operations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using CrewAI Tools
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -177,6 +178,62 @@ class MyCustomTool(BaseTool):
|
||||
return "Tool's result"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Asynchronous Tool Support
|
||||
|
||||
CrewAI supports asynchronous tools, allowing you to implement tools that perform non-blocking operations like network requests, file I/O, or other async operations without blocking the main execution thread.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating Async Tools
|
||||
|
||||
You can create async tools in two ways:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Using the `tool` Decorator with Async Functions
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
from crewai.tools import tool
|
||||
|
||||
@tool("fetch_data_async")
|
||||
async def fetch_data_async(query: str) -> str:
|
||||
"""Asynchronously fetch data based on the query."""
|
||||
# Simulate async operation
|
||||
await asyncio.sleep(1)
|
||||
return f"Data retrieved for {query}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Implementing Async Methods in Custom Tool Classes
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
from crewai.tools import BaseTool
|
||||
|
||||
class AsyncCustomTool(BaseTool):
|
||||
name: str = "async_custom_tool"
|
||||
description: str = "An asynchronous custom tool"
|
||||
|
||||
async def _run(self, query: str = "") -> str:
|
||||
"""Asynchronously run the tool"""
|
||||
# Your async implementation here
|
||||
await asyncio.sleep(1)
|
||||
return f"Processed {query} asynchronously"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Async Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Async tools work seamlessly in both standard Crew workflows and Flow-based workflows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
# In standard Crew
|
||||
agent = Agent(role="researcher", tools=[async_custom_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
# In Flow
|
||||
class MyFlow(Flow):
|
||||
@start()
|
||||
async def begin(self):
|
||||
crew = Crew(agents=[agent])
|
||||
result = await crew.kickoff_async()
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The CrewAI framework automatically handles the execution of both synchronous and asynchronous tools, so you don't need to worry about how to call them differently.
|
||||
|
||||
### Utilizing the `tool` Decorator
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,12 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"favicon": "images/favicon.svg",
|
||||
"contextual": {
|
||||
"options": ["copy", "view", "chatgpt", "claude"]
|
||||
"options": [
|
||||
"copy",
|
||||
"view",
|
||||
"chatgpt",
|
||||
"claude"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"navigation": {
|
||||
"tabs": [
|
||||
@@ -85,7 +90,12 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"group": "MCP Integration",
|
||||
"pages": [
|
||||
"mcp/crewai-mcp-integration"
|
||||
"mcp/overview",
|
||||
"mcp/stdio",
|
||||
"mcp/sse",
|
||||
"mcp/streamable-http",
|
||||
"mcp/multiple-servers",
|
||||
"mcp/security"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -124,7 +134,7 @@
|
||||
"tools/web-scraping/stagehandtool",
|
||||
"tools/web-scraping/firecrawlcrawlwebsitetool",
|
||||
"tools/web-scraping/firecrawlscrapewebsitetool",
|
||||
"tools/web-scraping/firecrawlsearchtool"
|
||||
"tools/web-scraping/oxylabsscraperstool"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -196,6 +206,7 @@
|
||||
"observability/arize-phoenix",
|
||||
"observability/langfuse",
|
||||
"observability/langtrace",
|
||||
"observability/maxim",
|
||||
"observability/mlflow",
|
||||
"observability/openlit",
|
||||
"observability/opik",
|
||||
@@ -208,6 +219,7 @@
|
||||
"group": "Learn",
|
||||
"pages": [
|
||||
"learn/overview",
|
||||
"learn/llm-selection-guide",
|
||||
"learn/conditional-tasks",
|
||||
"learn/coding-agents",
|
||||
"learn/create-custom-tools",
|
||||
@@ -217,7 +229,6 @@
|
||||
"learn/dalle-image-generation",
|
||||
"learn/force-tool-output-as-result",
|
||||
"learn/hierarchical-process",
|
||||
"learn/human-in-the-loop",
|
||||
"learn/human-input-on-execution",
|
||||
"learn/kickoff-async",
|
||||
"learn/kickoff-for-each",
|
||||
@@ -251,7 +262,29 @@
|
||||
"enterprise/features/tool-repository",
|
||||
"enterprise/features/webhook-streaming",
|
||||
"enterprise/features/traces",
|
||||
"enterprise/features/hallucination-guardrail"
|
||||
"enterprise/features/hallucination-guardrail",
|
||||
"enterprise/features/integrations"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"group": "Integration Docs",
|
||||
"pages": [
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/asana",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/box",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/clickup",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/github",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/gmail",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/google_calendar",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/google_sheets",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/hubspot",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/jira",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/linear",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/notion",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/salesforce",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/shopify",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/slack",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/stripe",
|
||||
"enterprise/integrations/zendesk"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -269,6 +302,7 @@
|
||||
"enterprise/guides/slack-trigger",
|
||||
"enterprise/guides/team-management",
|
||||
"enterprise/guides/webhook-automation",
|
||||
"enterprise/guides/human-in-the-loop",
|
||||
"enterprise/guides/zapier-trigger"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,8 +25,13 @@ AI hallucinations occur when language models generate content that appears plaus
|
||||
from crewai.tasks.hallucination_guardrail import HallucinationGuardrail
|
||||
from crewai import LLM
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the guardrail with reference context
|
||||
# Basic usage - will use task's expected_output as context
|
||||
guardrail = HallucinationGuardrail(
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o-mini")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# With explicit reference context
|
||||
context_guardrail = HallucinationGuardrail(
|
||||
context="AI helps with various tasks including analysis and generation.",
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o-mini")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
185
docs/enterprise/features/integrations.mdx
Normal file
185
docs/enterprise/features/integrations.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,185 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Integrations
|
||||
description: "Connected applications for your agents to take actions."
|
||||
icon: "plug"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to authenticate with any OAuth enabled provider and take actions. From Salesforce and HubSpot to Google and GitHub, we've got you covered with 16+ integrated services.
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||

|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Integrations
|
||||
|
||||
### **Communication & Collaboration**
|
||||
- **Gmail** - Manage emails and drafts
|
||||
- **Slack** - Workspace notifications and alerts
|
||||
- **Microsoft** - Office 365 and Teams integration
|
||||
|
||||
### **Project Management**
|
||||
- **Jira** - Issue tracking and project management
|
||||
- **ClickUp** - Task and productivity management
|
||||
- **Asana** - Team task and project coordination
|
||||
- **Notion** - Page and database management
|
||||
- **Linear** - Software project and bug tracking
|
||||
- **GitHub** - Repository and issue management
|
||||
|
||||
### **Customer Relationship Management**
|
||||
- **Salesforce** - CRM account and opportunity management
|
||||
- **HubSpot** - Sales pipeline and contact management
|
||||
- **Zendesk** - Customer support ticket management
|
||||
|
||||
### **Business & Finance**
|
||||
- **Stripe** - Payment processing and customer management
|
||||
- **Shopify** - E-commerce store and product management
|
||||
|
||||
### **Productivity & Storage**
|
||||
- **Google Sheets** - Spreadsheet data synchronization
|
||||
- **Google Calendar** - Event and schedule management
|
||||
- **Box** - File storage and document management
|
||||
|
||||
and more to come!
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using Authentication Integrations, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account. You can get started with a free trial.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Integrations
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com)
|
||||
2. Go to **Integrations** tab - https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** on your desired service from the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
4. Complete the OAuth authentication flow
|
||||
5. Grant necessary permissions for your use case
|
||||
6. Get your Enterprise Token from your [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account page - https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||

|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Integration Tools
|
||||
|
||||
All you need is the latest version of `crewai-tools` package.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Usage
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
All the services you are authenticated into will be available as tools. So all you need to do is add the `CrewaiEnterpriseTools` to your agent and you are good to go.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Gmail tool will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# print the tools
|
||||
print(enterprise_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Gmail capabilities
|
||||
email_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Email Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage and organize email communications",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in email management and communication.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to send an email
|
||||
email_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Draft and send a follow-up email to john@example.com about the project update",
|
||||
agent=email_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Confirmation that email was sent successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[email_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[email_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the crew
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
actions_list=["gmail_find_email"] # only gmail_find_email tool will be available
|
||||
)
|
||||
gmail_tool = enterprise_tools["gmail_find_email"]
|
||||
|
||||
gmail_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Gmail Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage gmail communications and notifications",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that helps coordinate gmail communications.",
|
||||
tools=[gmail_tool]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
notification_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Find the email from john@example.com",
|
||||
agent=gmail_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Email found from john@example.com"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[slack_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[notification_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
### Security
|
||||
- **Principle of Least Privilege**: Only grant the minimum permissions required for your agents' tasks
|
||||
- **Regular Audits**: Periodically review connected integrations and their permissions
|
||||
- **Secure Credentials**: Never hardcode credentials; use CrewAI's secure authentication flow
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Tools
|
||||
On a deployed crew, you can specify which actions are avialbel for each integration from the settings page of the service you connected to.
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||

|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Scoped Deployments for multi user organizations
|
||||
You can deploy your crew and scope each integration to a specific user. For example, a crew that connects to google can use a specific user's gmail account.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
This is useful for multi user organizations where you want to scope the integration to a specific user.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Use the `user_bearer_token` to scope the integration to a specific user so that when the crew is kicked off, it will use the user's bearer token to authenticate with the integration. If user is not logged in, then the crew will not use any connected integrations. Use the default bearer token to authenticate with the integrations thats deployed with the crew.
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||

|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
@@ -21,6 +21,7 @@ Before using the Tool Repository, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account
|
||||
- [CrewAI CLI](https://docs.crewai.com/concepts/cli#cli) installed
|
||||
- uv>=0.5.0 installed. Check out [how to upgrade](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installation/#upgrading-uv)
|
||||
- [Git](https://git-scm.com) installed and configured
|
||||
- Access permissions to publish or install tools in your CrewAI Enterprise organization
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
78
docs/enterprise/guides/human-in-the-loop.mdx
Normal file
78
docs/enterprise/guides/human-in-the-loop.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "HITL Workflows"
|
||||
description: "Learn how to implement Human-In-The-Loop workflows in CrewAI for enhanced decision-making"
|
||||
icon: "user-check"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Human-In-The-Loop (HITL) is a powerful approach that combines artificial intelligence with human expertise to enhance decision-making and improve task outcomes. This guide shows you how to implement HITL within CrewAI.
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up HITL Workflows
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="Configure Your Task">
|
||||
Set up your task with human input enabled:
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="/images/enterprise/crew-human-input.png" alt="Crew Human Input" />
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Provide Webhook URL">
|
||||
When kicking off your crew, include a webhook URL for human input:
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="/images/enterprise/crew-webhook-url.png" alt="Crew Webhook URL" />
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Receive Webhook Notification">
|
||||
Once the crew completes the task requiring human input, you'll receive a webhook notification containing:
|
||||
- **Execution ID**
|
||||
- **Task ID**
|
||||
- **Task output**
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Review Task Output">
|
||||
The system will pause in the `Pending Human Input` state. Review the task output carefully.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Submit Human Feedback">
|
||||
Call the resume endpoint of your crew with the following information:
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="/images/enterprise/crew-resume-endpoint.png" alt="Crew Resume Endpoint" />
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
**Feedback Impact on Task Execution**:
|
||||
It's crucial to exercise care when providing feedback, as the entire feedback content will be incorporated as additional context for further task executions.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
This means:
|
||||
- All information in your feedback becomes part of the task's context.
|
||||
- Irrelevant details may negatively influence it.
|
||||
- Concise, relevant feedback helps maintain task focus and efficiency.
|
||||
- Always review your feedback carefully before submission to ensure it contains only pertinent information that will positively guide the task's execution.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Handle Negative Feedback">
|
||||
If you provide negative feedback:
|
||||
- The crew will retry the task with added context from your feedback.
|
||||
- You'll receive another webhook notification for further review.
|
||||
- Repeat steps 4-6 until satisfied.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Execution Continuation">
|
||||
When you submit positive feedback, the execution will proceed to the next steps.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
## Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
- **Be Specific**: Provide clear, actionable feedback that directly addresses the task at hand
|
||||
- **Stay Relevant**: Only include information that will help improve the task execution
|
||||
- **Be Timely**: Respond to HITL prompts promptly to avoid workflow delays
|
||||
- **Review Carefully**: Double-check your feedback before submitting to ensure accuracy
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||
HITL workflows are particularly valuable for:
|
||||
- Quality assurance and validation
|
||||
- Complex decision-making scenarios
|
||||
- Sensitive or high-stakes operations
|
||||
- Creative tasks requiring human judgment
|
||||
- Compliance and regulatory reviews
|
||||
253
docs/enterprise/integrations/asana.mdx
Normal file
253
docs/enterprise/integrations/asana.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,253 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Asana Integration
|
||||
description: "Team task and project coordination with Asana integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "circle"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage tasks, projects, and team coordination through Asana. Create tasks, update project status, manage assignments, and streamline your team's workflow with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Asana integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- An Asana account with appropriate permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Asana account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Asana Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Asana Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Asana** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for task and project management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_CREATE_COMMENT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a comment in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `task` (string, required): Task ID - The ID of the Task the comment will be added to. The comment will be authored by the currently authenticated user.
|
||||
- `text` (string, required): Text (example: "This is a comment.").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_CREATE_PROJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a project in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `name` (string, required): Name (example: "Stuff to buy").
|
||||
- `workspace` (string, required): Workspace - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which Workspace to create Projects in. Defaults to the user's first Workspace if left blank.
|
||||
- `team` (string, optional): Team - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which Team to share this Project with. Defaults to the user's first Team if left blank.
|
||||
- `notes` (string, optional): Notes (example: "These are things we need to purchase.").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_GET_PROJECTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of projects in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `archived` (string, optional): Archived - Choose "true" to show archived projects, "false" to display only active projects, or "default" to show both archived and active projects.
|
||||
- Options: `default`, `true`, `false`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_GET_PROJECT_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a project by ID in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `projectFilterId` (string, required): Project ID.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_CREATE_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a task in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `name` (string, required): Name (example: "Task Name").
|
||||
- `workspace` (string, optional): Workspace - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which Workspace to create Tasks in. Defaults to the user's first Workspace if left blank..
|
||||
- `project` (string, optional): Project - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which Project to create this Task in.
|
||||
- `notes` (string, optional): Notes.
|
||||
- `dueOnDate` (string, optional): Due On - The date on which this task is due. Cannot be used together with Due At. (example: "YYYY-MM-DD").
|
||||
- `dueAtDate` (string, optional): Due At - The date and time (ISO timestamp) at which this task is due. Cannot be used together with Due On. (example: "2019-09-15T02:06:58.147Z").
|
||||
- `assignee` (string, optional): Assignee - The ID of the Asana user this task will be assigned to. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select an Assignee.
|
||||
- `gid` (string, optional): External ID - An ID from your application to associate this task with. You can use this ID to sync updates to this task later.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_UPDATE_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a task in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `taskId` (string, required): Task ID - The ID of the Task that will be updated.
|
||||
- `completeStatus` (string, optional): Completed Status.
|
||||
- Options: `true`, `false`
|
||||
- `name` (string, optional): Name (example: "Task Name").
|
||||
- `notes` (string, optional): Notes.
|
||||
- `dueOnDate` (string, optional): Due On - The date on which this task is due. Cannot be used together with Due At. (example: "YYYY-MM-DD").
|
||||
- `dueAtDate` (string, optional): Due At - The date and time (ISO timestamp) at which this task is due. Cannot be used together with Due On. (example: "2019-09-15T02:06:58.147Z").
|
||||
- `assignee` (string, optional): Assignee - The ID of the Asana user this task will be assigned to. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select an Assignee.
|
||||
- `gid` (string, optional): External ID - An ID from your application to associate this task with. You can use this ID to sync updates to this task later.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_GET_TASKS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of tasks in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `workspace` (string, optional): Workspace - The ID of the Workspace to filter tasks on. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Workspace.
|
||||
- `project` (string, optional): Project - The ID of the Project to filter tasks on. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Project.
|
||||
- `assignee` (string, optional): Assignee - The ID of the assignee to filter tasks on. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select an Assignee.
|
||||
- `completedSince` (string, optional): Completed since - Only return tasks that are either incomplete or that have been completed since this time (ISO or Unix timestamp). (example: "2014-04-25T16:15:47-04:00").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_GET_TASKS_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of tasks by ID in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `taskId` (string, required): Task ID.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_GET_TASK_BY_EXTERNAL_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a task by external ID in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `gid` (string, required): External ID - The ID that this task is associated or synced with, from your application.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_ADD_TASK_TO_SECTION">
|
||||
**Description:** Add a task to a section in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `sectionId` (string, required): Section ID - The ID of the section to add this task to.
|
||||
- `taskId` (string, required): Task ID - The ID of the task. (example: "1204619611402340").
|
||||
- `beforeTaskId` (string, optional): Before Task ID - The ID of a task in this section that this task will be inserted before. Cannot be used with After Task ID. (example: "1204619611402340").
|
||||
- `afterTaskId` (string, optional): After Task ID - The ID of a task in this section that this task will be inserted after. Cannot be used with Before Task ID. (example: "1204619611402340").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_GET_TEAMS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of teams in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `workspace` (string, required): Workspace - Returns the teams in this workspace visible to the authorized user.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ASANA_GET_WORKSPACES">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of workspaces in Asana.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:** None required.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Asana Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Asana tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Asana capabilities
|
||||
asana_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Project Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage tasks and projects in Asana efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in project management and task coordination.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new project
|
||||
create_project_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new project called 'Q1 Marketing Campaign' in the Marketing workspace",
|
||||
agent=asana_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Confirmation that the project was created successfully with project ID"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[asana_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_project_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Asana Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Asana tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["asana_create_task", "asana_update_task", "asana_get_tasks"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
task_manager_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Task Manager",
|
||||
goal="Create and manage tasks efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on task creation and management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create and assign a task
|
||||
task_management = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a task called 'Review quarterly reports' and assign it to the appropriate team member",
|
||||
agent=task_manager_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Task created and assigned successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[task_manager_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[task_management]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Project Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
project_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Project Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Coordinate project activities and track progress",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced project coordinator who ensures projects run smoothly.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving multiple Asana operations
|
||||
coordination_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Get all active projects in the workspace
|
||||
2. For each project, get the list of incomplete tasks
|
||||
3. Create a summary report task in the 'Management Reports' project
|
||||
4. Add comments to overdue tasks to request status updates
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=project_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Summary report created and status update requests sent for overdue tasks"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[project_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[coordination_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
268
docs/enterprise/integrations/box.mdx
Normal file
268
docs/enterprise/integrations/box.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,268 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Box Integration
|
||||
description: "File storage and document management with Box integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "box"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage files, folders, and documents through Box. Upload files, organize folder structures, search content, and streamline your team's document management with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Box integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Box account with appropriate permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Box account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Box Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Box Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Box** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for file and folder management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_SAVE_FILE">
|
||||
**Description:** Save a file from URL in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `fileAttributes` (object, required): Attributes - File metadata including name, parent folder, and timestamps.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"content_created_at": "2012-12-12T10:53:43-08:00",
|
||||
"content_modified_at": "2012-12-12T10:53:43-08:00",
|
||||
"name": "qwerty.png",
|
||||
"parent": { "id": "1234567" }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `file` (string, required): File URL - Files must be smaller than 50MB in size. (example: "https://picsum.photos/200/300").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_SAVE_FILE_FROM_OBJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Save a file in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `file` (string, required): File - Accepts a File Object containing file data. Files must be smaller than 50MB in size.
|
||||
- `fileName` (string, required): File Name (example: "qwerty.png").
|
||||
- `folder` (string, optional): Folder - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select the File's Folder destination. Defaults to the user's root folder if left blank.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_GET_FILE_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a file by ID in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `fileId` (string, required): File ID - The unique identifier that represents a file. (example: "12345").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_LIST_FILES">
|
||||
**Description:** List files in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `folderId` (string, required): Folder ID - The unique identifier that represents a folder. (example: "0").
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "direction",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringExactlyMatches",
|
||||
"value": "ASC"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_CREATE_FOLDER">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a folder in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `folderName` (string, required): Name - The name for the new folder. (example: "New Folder").
|
||||
- `folderParent` (object, required): Parent Folder - The parent folder where the new folder will be created.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "123456"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_MOVE_FOLDER">
|
||||
**Description:** Move a folder in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `folderId` (string, required): Folder ID - The unique identifier that represents a folder. (example: "0").
|
||||
- `folderName` (string, required): Name - The name for the folder. (example: "New Folder").
|
||||
- `folderParent` (object, required): Parent Folder - The new parent folder destination.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "123456"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_GET_FOLDER_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a folder by ID in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `folderId` (string, required): Folder ID - The unique identifier that represents a folder. (example: "0").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_SEARCH_FOLDERS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search folders in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `folderId` (string, required): Folder ID - The folder to search within.
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "sort",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringExactlyMatches",
|
||||
"value": "name"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="BOX_DELETE_FOLDER">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a folder in Box.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `folderId` (string, required): Folder ID - The unique identifier that represents a folder. (example: "0").
|
||||
- `recursive` (boolean, optional): Recursive - Delete a folder that is not empty by recursively deleting the folder and all of its content.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Box Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Box tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Box capabilities
|
||||
box_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Document Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage files and folders in Box efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in document management and file organization.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a folder structure
|
||||
create_structure_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a folder called 'Project Files' in the root directory and upload a document from URL",
|
||||
agent=box_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Folder created and file uploaded successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[box_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_structure_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Box Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Box tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["box_create_folder", "box_save_file", "box_list_files"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
file_organizer_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="File Organizer",
|
||||
goal="Organize and manage file storage efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on file organization and storage management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to organize files
|
||||
organization_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a folder structure for the marketing team and organize existing files",
|
||||
agent=file_organizer_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Folder structure created and files organized"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[file_organizer_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[organization_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced File Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
file_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="File Manager",
|
||||
goal="Maintain organized file structure and manage document lifecycle",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced file manager who ensures documents are properly organized and accessible.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving multiple Box operations
|
||||
management_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. List all files in the root folder
|
||||
2. Create monthly archive folders for the current year
|
||||
3. Move old files to appropriate archive folders
|
||||
4. Generate a summary report of the file organization
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=file_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Files organized into archive structure with summary report"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[file_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[management_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
293
docs/enterprise/integrations/clickup.mdx
Normal file
293
docs/enterprise/integrations/clickup.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,293 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ClickUp Integration
|
||||
description: "Task and productivity management with ClickUp integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "list-check"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage tasks, projects, and productivity workflows through ClickUp. Create and update tasks, organize projects, manage team assignments, and streamline your productivity management with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the ClickUp integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A ClickUp account with appropriate permissions
|
||||
- Connected your ClickUp account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up ClickUp Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your ClickUp Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **ClickUp** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for task and project management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_SEARCH_TASKS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for tasks in ClickUp using advanced filters.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `taskFilterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "statuses%5B%5D",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringExactlyMatches",
|
||||
"value": "open"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available fields: `space_ids%5B%5D`, `project_ids%5B%5D`, `list_ids%5B%5D`, `statuses%5B%5D`, `include_closed`, `assignees%5B%5D`, `tags%5B%5D`, `due_date_gt`, `due_date_lt`, `date_created_gt`, `date_created_lt`, `date_updated_gt`, `date_updated_lt`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_GET_TASK_IN_LIST">
|
||||
**Description:** Get tasks in a specific list in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listId` (string, required): List - Select a List to get tasks from. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow users to select a ClickUp List.
|
||||
- `taskFilterFormula` (string, optional): Search for tasks that match specified filters. For example: name=task1.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_CREATE_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a task in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listId` (string, required): List - Select a List to create this task in. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow users to select a ClickUp List.
|
||||
- `name` (string, required): Name - The task name.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description - Task description.
|
||||
- `status` (string, optional): Status - Select a Status for this task. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow users to select a ClickUp Status.
|
||||
- `assignees` (string, optional): Assignees - Select a Member (or an array of member IDs) to be assigned to this task. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow users to select a ClickUp Member.
|
||||
- `dueDate` (string, optional): Due Date - Specify a date for this task to be due on.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (string, optional): Additional Fields - Specify additional fields to include on this task as JSON.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_UPDATE_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a task in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `taskId` (string, required): Task ID - The ID of the task to update.
|
||||
- `listId` (string, required): List - Select a List to create this task in. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow users to select a ClickUp List.
|
||||
- `name` (string, optional): Name - The task name.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description - Task description.
|
||||
- `status` (string, optional): Status - Select a Status for this task. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow users to select a ClickUp Status.
|
||||
- `assignees` (string, optional): Assignees - Select a Member (or an array of member IDs) to be assigned to this task. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow users to select a ClickUp Member.
|
||||
- `dueDate` (string, optional): Due Date - Specify a date for this task to be due on.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (string, optional): Additional Fields - Specify additional fields to include on this task as JSON.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_DELETE_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a task in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `taskId` (string, required): Task ID - The ID of the task to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_GET_LIST">
|
||||
**Description:** Get List information in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `spaceId` (string, required): Space ID - The ID of the space containing the lists.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_GET_CUSTOM_FIELDS_IN_LIST">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Custom Fields in a List in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listId` (string, required): List ID - The ID of the list to get custom fields from.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_GET_ALL_FIELDS_IN_LIST">
|
||||
**Description:** Get All Fields in a List in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listId` (string, required): List ID - The ID of the list to get all fields from.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_GET_SPACE">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Space information in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `spaceId` (string, optional): Space ID - The ID of the space to retrieve.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_GET_FOLDERS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Folders in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `spaceId` (string, required): Space ID - The ID of the space containing the folders.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="CLICKUP_GET_MEMBER">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Member information in ClickUp.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:** None required.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic ClickUp Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (ClickUp tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with ClickUp capabilities
|
||||
clickup_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Task Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage tasks and projects in ClickUp efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in task management and productivity coordination.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new task
|
||||
create_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a task called 'Review Q1 Reports' in the Marketing list with high priority",
|
||||
agent=clickup_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Task created successfully with task ID"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[clickup_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific ClickUp Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific ClickUp tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["clickup_create_task", "clickup_update_task", "clickup_search_tasks"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
task_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Task Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Create and manage tasks efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on task creation and status management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage task workflow
|
||||
task_workflow = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a task for project planning and assign it to the development team",
|
||||
agent=task_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Task created and assigned successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[task_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[task_workflow]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Project Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
project_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Project Manager",
|
||||
goal="Coordinate project activities and track team productivity",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced project manager who ensures projects are delivered on time.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving multiple ClickUp operations
|
||||
project_coordination = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Get all open tasks in the current space
|
||||
2. Identify overdue tasks and update their status
|
||||
3. Create a weekly report task summarizing project progress
|
||||
4. Assign the report task to the team lead
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=project_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Project status updated and weekly report task created and assigned"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[project_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[project_coordination]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Task Search and Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
task_analyst = Agent(
|
||||
role="Task Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze task patterns and optimize team productivity",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that analyzes task data to improve team efficiency.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to analyze and optimize task distribution
|
||||
task_analysis = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
Search for all tasks assigned to team members in the last 30 days,
|
||||
analyze completion patterns, and create optimization recommendations
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=task_analyst,
|
||||
expected_output="Task analysis report with optimization recommendations"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[task_analyst],
|
||||
tasks=[task_analysis]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with ClickUp integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
323
docs/enterprise/integrations/github.mdx
Normal file
323
docs/enterprise/integrations/github.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,323 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: GitHub Integration
|
||||
description: "Repository and issue management with GitHub integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "github"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage repositories, issues, and releases through GitHub. Create and update issues, manage releases, track project development, and streamline your software development workflow with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the GitHub integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A GitHub account with appropriate repository permissions
|
||||
- Connected your GitHub account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up GitHub Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your GitHub Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **GitHub** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for repository and issue management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_CREATE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Create an issue in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Issue. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Issue.
|
||||
- `title` (string, required): Issue Title - Specify the title of the issue to create.
|
||||
- `body` (string, optional): Issue Body - Specify the body contents of the issue to create.
|
||||
- `assignees` (string, optional): Assignees - Specify the assignee(s)' GitHub login as an array of strings for this issue. (example: `["octocat"]`).
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_UPDATE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an issue in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Issue. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Issue.
|
||||
- `issue_number` (string, required): Issue Number - Specify the number of the issue to update.
|
||||
- `title` (string, required): Issue Title - Specify the title of the issue to update.
|
||||
- `body` (string, optional): Issue Body - Specify the body contents of the issue to update.
|
||||
- `assignees` (string, optional): Assignees - Specify the assignee(s)' GitHub login as an array of strings for this issue. (example: `["octocat"]`).
|
||||
- `state` (string, optional): State - Specify the updated state of the issue.
|
||||
- Options: `open`, `closed`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_GET_ISSUE_BY_NUMBER">
|
||||
**Description:** Get an issue by number in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Issue. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Issue.
|
||||
- `issue_number` (string, required): Issue Number - Specify the number of the issue to fetch.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_LOCK_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Lock an issue in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Issue. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Issue.
|
||||
- `issue_number` (string, required): Issue Number - Specify the number of the issue to lock.
|
||||
- `lock_reason` (string, required): Lock Reason - Specify a reason for locking the issue or pull request conversation.
|
||||
- Options: `off-topic`, `too heated`, `resolved`, `spam`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_SEARCH_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for issues in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Issue. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Issue.
|
||||
- `filter` (object, required): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "assignee",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringExactlyMatches",
|
||||
"value": "octocat"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available fields: `assignee`, `creator`, `mentioned`, `labels`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_CREATE_RELEASE">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a release in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Release. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Release.
|
||||
- `tag_name` (string, required): Name - Specify the name of the release tag to be created. (example: "v1.0.0").
|
||||
- `target_commitish` (string, optional): Target - Specify the target of the release. This can either be a branch name or a commit SHA. Defaults to the main branch. (example: "master").
|
||||
- `body` (string, optional): Body - Specify a description for this release.
|
||||
- `draft` (string, optional): Draft - Specify whether the created release should be a draft (unpublished) release.
|
||||
- Options: `true`, `false`
|
||||
- `prerelease` (string, optional): Prerelease - Specify whether the created release should be a prerelease.
|
||||
- Options: `true`, `false`
|
||||
- `discussion_category_name` (string, optional): Discussion Category Name - If specified, a discussion of the specified category is created and linked to the release. The value must be a category that already exists in the repository.
|
||||
- `generate_release_notes` (string, optional): Release Notes - Specify whether the created release should automatically create release notes using the provided name and body specified.
|
||||
- Options: `true`, `false`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_UPDATE_RELEASE">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a release in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Release. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Release.
|
||||
- `id` (string, required): Release ID - Specify the ID of the release to update.
|
||||
- `tag_name` (string, optional): Name - Specify the name of the release tag to be updated. (example: "v1.0.0").
|
||||
- `target_commitish` (string, optional): Target - Specify the target of the release. This can either be a branch name or a commit SHA. Defaults to the main branch. (example: "master").
|
||||
- `body` (string, optional): Body - Specify a description for this release.
|
||||
- `draft` (string, optional): Draft - Specify whether the created release should be a draft (unpublished) release.
|
||||
- Options: `true`, `false`
|
||||
- `prerelease` (string, optional): Prerelease - Specify whether the created release should be a prerelease.
|
||||
- Options: `true`, `false`
|
||||
- `discussion_category_name` (string, optional): Discussion Category Name - If specified, a discussion of the specified category is created and linked to the release. The value must be a category that already exists in the repository.
|
||||
- `generate_release_notes` (string, optional): Release Notes - Specify whether the created release should automatically create release notes using the provided name and body specified.
|
||||
- Options: `true`, `false`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_GET_RELEASE_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a release by ID in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Release. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Release.
|
||||
- `id` (string, required): Release ID - Specify the release ID of the release to fetch.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_GET_RELEASE_BY_TAG_NAME">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a release by tag name in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Release. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Release.
|
||||
- `tag_name` (string, required): Name - Specify the tag of the release to fetch. (example: "v1.0.0").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GITHUB_DELETE_RELEASE">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a release in GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `owner` (string, required): Owner - Specify the name of the account owner of the associated repository for this Release. (example: "abc").
|
||||
- `repo` (string, required): Repository - Specify the name of the associated repository for this Release.
|
||||
- `id` (string, required): Release ID - Specify the ID of the release to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic GitHub Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (GitHub tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with GitHub capabilities
|
||||
github_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Repository Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage GitHub repositories, issues, and releases efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in repository management and issue tracking.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new issue
|
||||
create_issue_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a bug report issue for the login functionality in the main repository",
|
||||
agent=github_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Issue created successfully with issue number"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[github_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_issue_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific GitHub Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific GitHub tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["github_create_issue", "github_update_issue", "github_search_issue"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
issue_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Issue Manager",
|
||||
goal="Create and manage GitHub issues efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on issue tracking and management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage issue workflow
|
||||
issue_workflow = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a feature request issue and assign it to the development team",
|
||||
agent=issue_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Feature request issue created and assigned successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[issue_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[issue_workflow]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Release Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
release_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Release Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage software releases and versioning",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced release manager who handles version control and release processes.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new release
|
||||
release_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
Create a new release v2.1.0 for the project with:
|
||||
- Auto-generated release notes
|
||||
- Target the main branch
|
||||
- Include a description of new features and bug fixes
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=release_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Release v2.1.0 created successfully with release notes"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[release_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[release_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Issue Tracking and Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
project_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Project Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Track and coordinate project issues and development progress",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that helps coordinate development work and track project progress.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving multiple GitHub operations
|
||||
coordination_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for all open issues assigned to the current milestone
|
||||
2. Identify overdue issues and update their priority labels
|
||||
3. Create a weekly progress report issue
|
||||
4. Lock resolved issues that have been inactive for 30 days
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=project_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Project coordination completed with progress report and issue management"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[project_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[coordination_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with GitHub integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
356
docs/enterprise/integrations/gmail.mdx
Normal file
356
docs/enterprise/integrations/gmail.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,356 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Gmail Integration
|
||||
description: "Email and contact management with Gmail integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "envelope"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage emails, contacts, and drafts through Gmail. Send emails, search messages, manage contacts, create drafts, and streamline your email communications with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Gmail integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Gmail account with appropriate permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Gmail account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Gmail Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Gmail Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Gmail** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for email and contact management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_SEND_EMAIL">
|
||||
**Description:** Send an email in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `toRecipients` (array, required): To - Specify the recipients as either a single string or a JSON array.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
"recipient1@domain.com",
|
||||
"recipient2@domain.com"
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `from` (string, required): From - Specify the email of the sender.
|
||||
- `subject` (string, required): Subject - Specify the subject of the message.
|
||||
- `messageContent` (string, required): Message Content - Specify the content of the email message as plain text or HTML.
|
||||
- `attachments` (string, optional): Attachments - Accepts either a single file object or a JSON array of file objects.
|
||||
- `additionalHeaders` (object, optional): Additional Headers - Specify any additional header fields here.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"reply-to": "Sender Name <sender@domain.com>"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_GET_EMAIL_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get an email by ID in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `userId` (string, required): User ID - Specify the user's email address. (example: "user@domain.com").
|
||||
- `messageId` (string, required): Message ID - Specify the ID of the message to retrieve.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_SEARCH_FOR_EMAIL">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for emails in Gmail using advanced filters.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `emailFilterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "from",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringContains",
|
||||
"value": "example@domain.com"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available fields: `from`, `to`, `date`, `label`, `subject`, `cc`, `bcc`, `category`, `deliveredto:`, `size`, `filename`, `older_than`, `newer_than`, `list`, `is:important`, `is:unread`, `is:snoozed`, `is:starred`, `is:read`, `has:drive`, `has:document`, `has:spreadsheet`, `has:presentation`, `has:attachment`, `has:youtube`, `has:userlabels`
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination Parameters.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pageCursor": "page_cursor_string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_DELETE_EMAIL">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete an email in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `userId` (string, required): User ID - Specify the user's email address. (example: "user@domain.com").
|
||||
- `messageId` (string, required): Message ID - Specify the ID of the message to trash.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_CREATE_A_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a contact in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `givenName` (string, required): Given Name - Specify the Given Name of the Contact to create. (example: "John").
|
||||
- `familyName` (string, required): Family Name - Specify the Family Name of the Contact to create. (example: "Doe").
|
||||
- `email` (string, required): Email - Specify the Email Address of the Contact to create.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional Fields - Additional contact information.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"addresses": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"streetAddress": "1000 North St.",
|
||||
"city": "Los Angeles"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_GET_CONTACT_BY_RESOURCE_NAME">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a contact by resource name in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `resourceName` (string, required): Resource Name - Specify the resource name of the contact to fetch.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_SEARCH_FOR_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for a contact in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `searchTerm` (string, required): Term - Specify a search term to search for near or exact matches on the names, nickNames, emailAddresses, phoneNumbers, or organizations Contact properties.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_DELETE_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a contact in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `resourceName` (string, required): Resource Name - Specify the resource name of the contact to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GMAIL_CREATE_DRAFT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a draft in Gmail.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `toRecipients` (array, optional): To - Specify the recipients as either a single string or a JSON array.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
"recipient1@domain.com",
|
||||
"recipient2@domain.com"
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `from` (string, optional): From - Specify the email of the sender.
|
||||
- `subject` (string, optional): Subject - Specify the subject of the message.
|
||||
- `messageContent` (string, optional): Message Content - Specify the content of the email message as plain text or HTML.
|
||||
- `attachments` (string, optional): Attachments - Accepts either a single file object or a JSON array of file objects.
|
||||
- `additionalHeaders` (object, optional): Additional Headers - Specify any additional header fields here.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"reply-to": "Sender Name <sender@domain.com>"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Gmail Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Gmail tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Gmail capabilities
|
||||
gmail_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Email Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage email communications and contacts efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in email management and communication.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to send a follow-up email
|
||||
send_email_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Send a follow-up email to john@example.com about the project update meeting",
|
||||
agent=gmail_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Email sent successfully with confirmation"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[gmail_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[send_email_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Gmail Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Gmail tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["gmail_send_email", "gmail_search_for_email", "gmail_create_draft"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
email_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Email Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Coordinate email communications and manage drafts",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on email coordination and draft management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to prepare and send emails
|
||||
email_coordination = Task(
|
||||
description="Search for emails from the marketing team, create a summary draft, and send it to stakeholders",
|
||||
agent=email_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Summary email sent to stakeholders"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[email_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[email_coordination]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Contact Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
contact_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Contact Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage and organize email contacts efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced contact manager who maintains organized contact databases.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage contacts
|
||||
contact_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for contacts from the 'example.com' domain
|
||||
2. Create new contacts for recent email senders not in the contact list
|
||||
3. Update contact information with recent interaction data
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=contact_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Contact database updated with new contacts and recent interactions"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[contact_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[contact_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Email Search and Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
email_analyst = Agent(
|
||||
role="Email Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze email patterns and provide insights",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that analyzes email data to provide actionable insights.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to analyze email patterns
|
||||
analysis_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
Search for all unread emails from the last 7 days,
|
||||
categorize them by sender domain,
|
||||
and create a summary report of communication patterns
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=email_analyst,
|
||||
expected_output="Email analysis report with communication patterns and recommendations"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[email_analyst],
|
||||
tasks=[analysis_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automated Email Workflows
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
workflow_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Email Workflow Manager",
|
||||
goal="Automate email workflows and responses",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that manages automated email workflows and responses.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving multiple Gmail operations
|
||||
workflow_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for emails with 'urgent' in the subject from the last 24 hours
|
||||
2. Create draft responses for each urgent email
|
||||
3. Send automated acknowledgment emails to senders
|
||||
4. Create a summary report of urgent items requiring attention
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=workflow_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Urgent emails processed with automated responses and summary report"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[workflow_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[workflow_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Gmail integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
391
docs/enterprise/integrations/google_calendar.mdx
Normal file
391
docs/enterprise/integrations/google_calendar.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,391 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Google Calendar Integration
|
||||
description: "Event and schedule management with Google Calendar integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "calendar"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage calendar events, schedules, and availability through Google Calendar. Create and update events, manage attendees, check availability, and streamline your scheduling workflows with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Google Calendar integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Google account with Google Calendar access
|
||||
- Connected your Google account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Google Calendar Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Google Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Google Calendar** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for calendar and contact access
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_CREATE_EVENT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create an event in Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `eventName` (string, required): Event name.
|
||||
- `startTime` (string, required): Start time - Accepts Unix timestamp or ISO8601 date formats.
|
||||
- `endTime` (string, optional): End time - Defaults to one hour after the start time if left blank.
|
||||
- `calendar` (string, optional): Calendar - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which calendar the event will be added to. Defaults to the user's primary calendar if left blank.
|
||||
- `attendees` (string, optional): Attendees - Accepts an array of email addresses or email addresses separated by commas.
|
||||
- `eventLocation` (string, optional): Event location.
|
||||
- `eventDescription` (string, optional): Event description.
|
||||
- `eventId` (string, optional): Event ID - An ID from your application to associate this event with. You can use this ID to sync updates to this event later.
|
||||
- `includeMeetLink` (boolean, optional): Include Google Meet link? - Automatically creates Google Meet conference link for this event.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_UPDATE_EVENT">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing event in Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `eventId` (string, required): Event ID - The ID of the event to update.
|
||||
- `eventName` (string, optional): Event name.
|
||||
- `startTime` (string, optional): Start time - Accepts Unix timestamp or ISO8601 date formats.
|
||||
- `endTime` (string, optional): End time - Defaults to one hour after the start time if left blank.
|
||||
- `calendar` (string, optional): Calendar - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which calendar the event will be added to. Defaults to the user's primary calendar if left blank.
|
||||
- `attendees` (string, optional): Attendees - Accepts an array of email addresses or email addresses separated by commas.
|
||||
- `eventLocation` (string, optional): Event location.
|
||||
- `eventDescription` (string, optional): Event description.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_LIST_EVENTS">
|
||||
**Description:** List events from Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `calendar` (string, optional): Calendar - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which calendar the event will be added to. Defaults to the user's primary calendar if left blank.
|
||||
- `after` (string, optional): After - Filters events that start after the provided date (Unix in milliseconds or ISO timestamp). (example: "2025-04-12T10:00:00Z or 1712908800000").
|
||||
- `before` (string, optional): Before - Filters events that end before the provided date (Unix in milliseconds or ISO timestamp). (example: "2025-04-12T10:00:00Z or 1712908800000").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_GET_EVENT_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a specific event by ID from Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `eventId` (string, required): Event ID.
|
||||
- `calendar` (string, optional): Calendar - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which calendar the event will be added to. Defaults to the user's primary calendar if left blank.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_DELETE_EVENT">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete an event from Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `eventId` (string, required): Event ID - The ID of the calendar event to be deleted.
|
||||
- `calendar` (string, optional): Calendar - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which calendar the event will be added to. Defaults to the user's primary calendar if left blank.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_GET_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get contacts from Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination Parameters.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pageCursor": "page_cursor_string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_SEARCH_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for contacts in Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `query` (string, optional): Search query to search contacts.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_LIST_DIRECTORY_PEOPLE">
|
||||
**Description:** List directory people.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination Parameters.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pageCursor": "page_cursor_string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_SEARCH_DIRECTORY_PEOPLE">
|
||||
**Description:** Search directory people.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `query` (string, required): Search query to search contacts.
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination Parameters.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pageCursor": "page_cursor_string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_LIST_OTHER_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** List other contacts.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination Parameters.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pageCursor": "page_cursor_string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_SEARCH_OTHER_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search other contacts.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `query` (string, optional): Search query to search contacts.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_CALENDAR_GET_AVAILABILITY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get availability information for calendars.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `timeMin` (string, required): The start of the interval. In ISO format.
|
||||
- `timeMax` (string, required): The end of the interval. In ISO format.
|
||||
- `timeZone` (string, optional): Time zone used in the response. Optional. The default is UTC.
|
||||
- `items` (array, optional): List of calendars and/or groups to query. Defaults to the user default calendar.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "calendar_id_1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "calendar_id_2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Calendar Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Google Calendar tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Google Calendar capabilities
|
||||
calendar_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Schedule Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage calendar events and scheduling efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in calendar management and scheduling coordination.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a meeting
|
||||
create_meeting_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a team standup meeting for tomorrow at 9 AM with the development team",
|
||||
agent=calendar_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Meeting created successfully with Google Meet link"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[calendar_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_meeting_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Calendar Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Google Calendar tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["google_calendar_create_event", "google_calendar_list_events", "google_calendar_get_availability"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
meeting_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Meeting Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Coordinate meetings and check availability",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on meeting scheduling and availability management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to schedule a meeting with availability check
|
||||
schedule_meeting = Task(
|
||||
description="Check availability for next week and schedule a project review meeting with stakeholders",
|
||||
agent=meeting_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Meeting scheduled after checking availability of all participants"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[meeting_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[schedule_meeting]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Event Management and Updates
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
event_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Event Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage and update calendar events efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced event manager who handles event logistics and updates.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage event updates
|
||||
event_management = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. List all events for this week
|
||||
2. Update any events that need location changes to include video conference links
|
||||
3. Send calendar invitations to new team members for recurring meetings
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=event_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Weekly events updated with proper locations and new attendees added"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[event_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[event_management]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Contact and Availability Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
availability_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Availability Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Coordinate availability and manage contacts for scheduling",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that specializes in availability management and contact coordination.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to coordinate availability
|
||||
availability_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for contacts in the engineering department
|
||||
2. Check availability for all engineers next Friday afternoon
|
||||
3. Create a team meeting for the first available 2-hour slot
|
||||
4. Include Google Meet link and send invitations
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=availability_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Team meeting scheduled based on availability with all engineers invited"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[availability_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[availability_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automated Scheduling Workflows
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
scheduling_automator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Scheduling Automator",
|
||||
goal="Automate scheduling workflows and calendar management",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that automates complex scheduling scenarios and calendar workflows.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex scheduling automation task
|
||||
automation_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. List all upcoming events for the next two weeks
|
||||
2. Identify any scheduling conflicts or back-to-back meetings
|
||||
3. Suggest optimal meeting times by checking availability
|
||||
4. Create buffer time between meetings where needed
|
||||
5. Update event descriptions with agenda items and meeting links
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=scheduling_automator,
|
||||
expected_output="Calendar optimized with resolved conflicts, buffer times, and updated meeting details"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[scheduling_automator],
|
||||
tasks=[automation_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues
|
||||
|
||||
**Authentication Errors**
|
||||
- Ensure your Google account has the necessary permissions for calendar access
|
||||
- Verify that the OAuth connection includes all required scopes for Google Calendar API
|
||||
- Check if calendar sharing settings allow the required access level
|
||||
|
||||
**Event Creation Issues**
|
||||
- Verify that time formats are correct (ISO8601 or Unix timestamps)
|
||||
- Ensure attendee email addresses are properly formatted
|
||||
- Check that the target calendar exists and is accessible
|
||||
- Verify time zones are correctly specified
|
||||
|
||||
**Availability and Time Conflicts**
|
||||
- Use proper ISO format for time ranges when checking availability
|
||||
- Ensure time zones are consistent across all operations
|
||||
- Verify that calendar IDs are correct when checking multiple calendars
|
||||
|
||||
**Contact and People Search**
|
||||
- Ensure search queries are properly formatted
|
||||
- Check that directory access permissions are granted
|
||||
- Verify that contact information is up to date and accessible
|
||||
|
||||
**Event Updates and Deletions**
|
||||
- Verify that event IDs are correct and events exist
|
||||
- Ensure you have edit permissions for the events
|
||||
- Check that calendar ownership allows modifications
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Google Calendar integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
321
docs/enterprise/integrations/google_sheets.mdx
Normal file
321
docs/enterprise/integrations/google_sheets.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,321 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Google Sheets Integration
|
||||
description: "Spreadsheet data synchronization with Google Sheets integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "google"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage spreadsheet data through Google Sheets. Read rows, create new entries, update existing data, and streamline your data management workflows with AI-powered automation. Perfect for data tracking, reporting, and collaborative data management.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Google Sheets integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Google account with Google Sheets access
|
||||
- Connected your Google account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
- Spreadsheets with proper column headers for data operations
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Google Sheets Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Google Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Google Sheets** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for spreadsheet access
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_SHEETS_GET_ROW">
|
||||
**Description:** Get rows from a Google Sheets spreadsheet.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `spreadsheetId` (string, required): Spreadsheet - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a spreadsheet. Defaults to using the first worksheet in the selected spreadsheet.
|
||||
- `limit` (string, optional): Limit rows - Limit the maximum number of rows to return.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_SHEETS_CREATE_ROW">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new row in a Google Sheets spreadsheet.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `spreadsheetId` (string, required): Spreadsheet - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a spreadsheet. Defaults to using the first worksheet in the selected spreadsheet..
|
||||
- `worksheet` (string, required): Worksheet - Your worksheet must have column headers.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, required): Fields - Include fields to create this row with, as an object with keys of Column Names. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Column Mapping.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"columnName1": "columnValue1",
|
||||
"columnName2": "columnValue2",
|
||||
"columnName3": "columnValue3",
|
||||
"columnName4": "columnValue4"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="GOOGLE_SHEETS_UPDATE_ROW">
|
||||
**Description:** Update existing rows in a Google Sheets spreadsheet.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `spreadsheetId` (string, required): Spreadsheet - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a spreadsheet. Defaults to using the first worksheet in the selected spreadsheet.
|
||||
- `worksheet` (string, required): Worksheet - Your worksheet must have column headers.
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions to identify which rows to update.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "status",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringExactlyMatches",
|
||||
"value": "pending"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available operators: `$stringContains`, `$stringDoesNotContain`, `$stringExactlyMatches`, `$stringDoesNotExactlyMatch`, `$stringStartsWith`, `$stringDoesNotStartWith`, `$stringEndsWith`, `$stringDoesNotEndWith`, `$numberGreaterThan`, `$numberLessThan`, `$numberEquals`, `$numberDoesNotEqual`, `$dateTimeAfter`, `$dateTimeBefore`, `$dateTimeEquals`, `$booleanTrue`, `$booleanFalse`, `$exists`, `$doesNotExist`
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, required): Fields - Include fields to update, as an object with keys of Column Names. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Column Mapping.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"columnName1": "newValue1",
|
||||
"columnName2": "newValue2",
|
||||
"columnName3": "newValue3",
|
||||
"columnName4": "newValue4"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Google Sheets Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Google Sheets tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Google Sheets capabilities
|
||||
sheets_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Data Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage spreadsheet data and track information efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in data management and spreadsheet operations.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to add new data to a spreadsheet
|
||||
data_entry_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Add a new customer record to the customer database spreadsheet with name, email, and signup date",
|
||||
agent=sheets_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="New customer record added successfully to the spreadsheet"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[sheets_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[data_entry_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Google Sheets Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Google Sheets tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["google_sheets_get_row", "google_sheets_create_row"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_collector = Agent(
|
||||
role="Data Collector",
|
||||
goal="Collect and organize data in spreadsheets",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on data collection and organization.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to collect and organize data
|
||||
data_collection = Task(
|
||||
description="Retrieve current inventory data and add new product entries to the inventory spreadsheet",
|
||||
agent=data_collector,
|
||||
expected_output="Inventory data retrieved and new products added successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[data_collector],
|
||||
tasks=[data_collection]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Data Analysis and Reporting
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_analyst = Agent(
|
||||
role="Data Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze spreadsheet data and generate insights",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced data analyst who extracts insights from spreadsheet data.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to analyze data and create reports
|
||||
analysis_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Retrieve all sales data from the current month's spreadsheet
|
||||
2. Analyze the data for trends and patterns
|
||||
3. Create a summary report in a new row with key metrics
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=data_analyst,
|
||||
expected_output="Sales data analyzed and summary report created with key insights"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[data_analyst],
|
||||
tasks=[analysis_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automated Data Updates
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_updater = Agent(
|
||||
role="Data Updater",
|
||||
goal="Automatically update and maintain spreadsheet data",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that maintains data accuracy and updates records automatically.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to update data based on conditions
|
||||
update_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Find all pending orders in the orders spreadsheet
|
||||
2. Update their status to 'processing'
|
||||
3. Add a timestamp for when the status was updated
|
||||
4. Log the changes in a separate tracking sheet
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=data_updater,
|
||||
expected_output="All pending orders updated to processing status with timestamps logged"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[data_updater],
|
||||
tasks=[update_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Complex Data Management Workflow
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
workflow_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Data Workflow Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage complex data workflows across multiple spreadsheets",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that orchestrates complex data operations across multiple spreadsheets.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex workflow task
|
||||
workflow_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Get all customer data from the main customer spreadsheet
|
||||
2. Create monthly summary entries for active customers
|
||||
3. Update customer status based on activity in the last 30 days
|
||||
4. Generate a monthly report with customer metrics
|
||||
5. Archive inactive customer records to a separate sheet
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=workflow_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Monthly customer workflow completed with updated statuses and generated reports"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[workflow_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[workflow_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues
|
||||
|
||||
**Permission Errors**
|
||||
- Ensure your Google account has edit access to the target spreadsheets
|
||||
- Verify that the OAuth connection includes required scopes for Google Sheets API
|
||||
- Check that spreadsheets are shared with the authenticated account
|
||||
|
||||
**Spreadsheet Structure Issues**
|
||||
- Ensure worksheets have proper column headers before creating or updating rows
|
||||
- Verify that column names in `additionalFields` match the actual column headers
|
||||
- Check that the specified worksheet exists in the spreadsheet
|
||||
|
||||
**Data Type and Format Issues**
|
||||
- Ensure data values match the expected format for each column
|
||||
- Use proper date formats for date columns (ISO format recommended)
|
||||
- Verify that numeric values are properly formatted for number columns
|
||||
|
||||
**Filter Formula Issues**
|
||||
- Ensure filter formulas follow the correct JSON structure for disjunctive normal form
|
||||
- Use valid field names that match actual column headers
|
||||
- Test simple filters before building complex multi-condition queries
|
||||
- Verify that operator types match the data types in the columns
|
||||
|
||||
**Row Limits and Performance**
|
||||
- Be mindful of row limits when using `GOOGLE_SHEETS_GET_ROW`
|
||||
- Consider pagination for large datasets
|
||||
- Use specific filters to reduce the amount of data processed
|
||||
|
||||
**Update Operations**
|
||||
- Ensure filter conditions properly identify the intended rows for updates
|
||||
- Test filter conditions with small datasets before large updates
|
||||
- Verify that all required fields are included in update operations
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Google Sheets integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
579
docs/enterprise/integrations/hubspot.mdx
Normal file
579
docs/enterprise/integrations/hubspot.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,579 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "HubSpot Integration"
|
||||
description: "Manage companies and contacts in HubSpot with CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "briefcase"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage companies and contacts within HubSpot. Create new records and streamline your CRM processes with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the HubSpot integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription.
|
||||
- A HubSpot account with appropriate permissions.
|
||||
- Connected your HubSpot account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors).
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up HubSpot Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your HubSpot Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors).
|
||||
2. Find **HubSpot** in the Authentication Integrations section.
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow.
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for company and contact management.
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account).
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_CREATE_RECORD_COMPANIES">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new company record in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `name` (string, required): Name of the company.
|
||||
- `domain` (string, optional): Company Domain Name.
|
||||
- `industry` (string, optional): Industry. Must be one of the predefined values from HubSpot.
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): Phone Number.
|
||||
- `hubspot_owner_id` (string, optional): Company owner ID.
|
||||
- `type` (string, optional): Type of the company. Available values: `PROSPECT`, `PARTNER`, `RESELLER`, `VENDOR`, `OTHER`.
|
||||
- `city` (string, optional): City.
|
||||
- `state` (string, optional): State/Region.
|
||||
- `zip` (string, optional): Postal Code.
|
||||
- `numberofemployees` (number, optional): Number of Employees.
|
||||
- `annualrevenue` (number, optional): Annual Revenue.
|
||||
- `timezone` (string, optional): Time Zone.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description.
|
||||
- `linkedin_company_page` (string, optional): LinkedIn Company Page URL.
|
||||
- `company_email` (string, optional): Company Email.
|
||||
- `first_name` (string, optional): First Name of a contact at the company.
|
||||
- `last_name` (string, optional): Last Name of a contact at the company.
|
||||
- `about_us` (string, optional): About Us.
|
||||
- `hs_csm_sentiment` (string, optional): CSM Sentiment. Available values: `at_risk`, `neutral`, `healthy`.
|
||||
- `closedate` (string, optional): Close Date.
|
||||
- `hs_keywords` (string, optional): Company Keywords. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `country` (string, optional): Country/Region.
|
||||
- `hs_country_code` (string, optional): Country/Region Code.
|
||||
- `hs_employee_range` (string, optional): Employee range.
|
||||
- `facebook_company_page` (string, optional): Facebook Company Page URL.
|
||||
- `facebookfans` (number, optional): Number of Facebook Fans.
|
||||
- `hs_gps_coordinates` (string, optional): GPS Coordinates.
|
||||
- `hs_gps_error` (string, optional): GPS Error.
|
||||
- `googleplus_page` (string, optional): Google Plus Page URL.
|
||||
- `owneremail` (string, optional): HubSpot Owner Email.
|
||||
- `ownername` (string, optional): HubSpot Owner Name.
|
||||
- `hs_ideal_customer_profile` (string, optional): Ideal Customer Profile Tier. Available values: `tier_1`, `tier_2`, `tier_3`.
|
||||
- `hs_industry_group` (string, optional): Industry group.
|
||||
- `is_public` (boolean, optional): Is Public.
|
||||
- `hs_last_metered_enrichment_timestamp` (string, optional): Last Metered Enrichment Timestamp.
|
||||
- `hs_lead_status` (string, optional): Lead Status. Available values: `NEW`, `OPEN`, `IN_PROGRESS`, `OPEN_DEAL`, `UNQUALIFIED`, `ATTEMPTED_TO_CONTACT`, `CONNECTED`, `BAD_TIMING`.
|
||||
- `lifecyclestage` (string, optional): Lifecycle Stage. Available values: `subscriber`, `lead`, `marketingqualifiedlead`, `salesqualifiedlead`, `opportunity`, `customer`, `evangelist`, `other`.
|
||||
- `linkedinbio` (string, optional): LinkedIn Bio.
|
||||
- `hs_linkedin_handle` (string, optional): LinkedIn handle.
|
||||
- `hs_live_enrichment_deadline` (string, optional): Live enrichment deadline.
|
||||
- `hs_logo_url` (string, optional): Logo URL.
|
||||
- `hs_analytics_source` (string, optional): Original Traffic Source.
|
||||
- `hs_pinned_engagement_id` (number, optional): Pinned Engagement ID.
|
||||
- `hs_quick_context` (string, optional): Quick context.
|
||||
- `hs_revenue_range` (string, optional): Revenue range.
|
||||
- `hs_state_code` (string, optional): State/Region Code.
|
||||
- `address` (string, optional): Street Address.
|
||||
- `address2` (string, optional): Street Address 2.
|
||||
- `hs_is_target_account` (boolean, optional): Target Account.
|
||||
- `hs_target_account` (string, optional): Target Account Tier. Available values: `tier_1`, `tier_2`, `tier_3`.
|
||||
- `hs_target_account_recommendation_snooze_time` (string, optional): Target Account Recommendation Snooze Time.
|
||||
- `hs_target_account_recommendation_state` (string, optional): Target Account Recommendation State. Available values: `DISMISSED`, `NONE`, `SNOOZED`.
|
||||
- `total_money_raised` (string, optional): Total Money Raised.
|
||||
- `twitterbio` (string, optional): Twitter Bio.
|
||||
- `twitterfollowers` (number, optional): Twitter Followers.
|
||||
- `twitterhandle` (string, optional): Twitter Handle.
|
||||
- `web_technologies` (string, optional): Web Technologies used. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `website` (string, optional): Website URL.
|
||||
- `founded_year` (string, optional): Year Founded.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_CREATE_RECORD_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new contact record in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `email` (string, required): Email address of the contact.
|
||||
- `firstname` (string, optional): First Name.
|
||||
- `lastname` (string, optional): Last Name.
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): Phone Number.
|
||||
- `hubspot_owner_id` (string, optional): Contact owner.
|
||||
- `lifecyclestage` (string, optional): Lifecycle Stage. Available values: `subscriber`, `lead`, `marketingqualifiedlead`, `salesqualifiedlead`, `opportunity`, `customer`, `evangelist`, `other`.
|
||||
- `hs_lead_status` (string, optional): Lead Status. Available values: `NEW`, `OPEN`, `IN_PROGRESS`, `OPEN_DEAL`, `UNQUALIFIED`, `ATTEMPTED_TO_CONTACT`, `CONNECTED`, `BAD_TIMING`.
|
||||
- `annualrevenue` (string, optional): Annual Revenue.
|
||||
- `hs_buying_role` (string, optional): Buying Role.
|
||||
- `cc_emails` (string, optional): CC Emails.
|
||||
- `ch_customer_id` (string, optional): Chargify Customer ID.
|
||||
- `ch_customer_reference` (string, optional): Chargify Customer Reference.
|
||||
- `chargify_sites` (string, optional): Chargify Site(s).
|
||||
- `city` (string, optional): City.
|
||||
- `hs_facebook_ad_clicked` (boolean, optional): Clicked Facebook ad.
|
||||
- `hs_linkedin_ad_clicked` (string, optional): Clicked LinkedIn Ad.
|
||||
- `hs_clicked_linkedin_ad` (string, optional): Clicked on a LinkedIn Ad.
|
||||
- `closedate` (string, optional): Close Date.
|
||||
- `company` (string, optional): Company Name.
|
||||
- `company_size` (string, optional): Company size.
|
||||
- `country` (string, optional): Country/Region.
|
||||
- `hs_country_region_code` (string, optional): Country/Region Code.
|
||||
- `date_of_birth` (string, optional): Date of birth.
|
||||
- `degree` (string, optional): Degree.
|
||||
- `hs_email_customer_quarantined_reason` (string, optional): Email address quarantine reason.
|
||||
- `hs_role` (string, optional): Employment Role. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `hs_seniority` (string, optional): Employment Seniority. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `hs_sub_role` (string, optional): Employment Sub Role. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `hs_employment_change_detected_date` (string, optional): Employment change detected date.
|
||||
- `hs_enriched_email_bounce_detected` (boolean, optional): Enriched Email Bounce Detected.
|
||||
- `hs_facebookid` (string, optional): Facebook ID.
|
||||
- `hs_facebook_click_id` (string, optional): Facebook click id.
|
||||
- `fax` (string, optional): Fax Number.
|
||||
- `field_of_study` (string, optional): Field of study.
|
||||
- `followercount` (number, optional): Follower Count.
|
||||
- `gender` (string, optional): Gender.
|
||||
- `hs_google_click_id` (string, optional): Google ad click id.
|
||||
- `graduation_date` (string, optional): Graduation date.
|
||||
- `owneremail` (string, optional): HubSpot Owner Email (legacy).
|
||||
- `ownername` (string, optional): HubSpot Owner Name (legacy).
|
||||
- `industry` (string, optional): Industry.
|
||||
- `hs_inferred_language_codes` (string, optional): Inferred Language Codes. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `jobtitle` (string, optional): Job Title.
|
||||
- `hs_job_change_detected_date` (string, optional): Job change detected date.
|
||||
- `job_function` (string, optional): Job function.
|
||||
- `hs_journey_stage` (string, optional): Journey Stage. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `kloutscoregeneral` (number, optional): Klout Score.
|
||||
- `hs_last_metered_enrichment_timestamp` (string, optional): Last Metered Enrichment Timestamp.
|
||||
- `hs_latest_source` (string, optional): Latest Traffic Source.
|
||||
- `hs_latest_source_timestamp` (string, optional): Latest Traffic Source Date.
|
||||
- `hs_legal_basis` (string, optional): Legal basis for processing contact's data.
|
||||
- `linkedinbio` (string, optional): LinkedIn Bio.
|
||||
- `linkedinconnections` (number, optional): LinkedIn Connections.
|
||||
- `hs_linkedin_url` (string, optional): LinkedIn URL.
|
||||
- `hs_linkedinid` (string, optional): Linkedin ID.
|
||||
- `hs_live_enrichment_deadline` (string, optional): Live enrichment deadline.
|
||||
- `marital_status` (string, optional): Marital Status.
|
||||
- `hs_content_membership_email` (string, optional): Member email.
|
||||
- `hs_content_membership_notes` (string, optional): Membership Notes.
|
||||
- `message` (string, optional): Message.
|
||||
- `military_status` (string, optional): Military status.
|
||||
- `mobilephone` (string, optional): Mobile Phone Number.
|
||||
- `numemployees` (string, optional): Number of Employees.
|
||||
- `hs_analytics_source` (string, optional): Original Traffic Source.
|
||||
- `photo` (string, optional): Photo.
|
||||
- `hs_pinned_engagement_id` (number, optional): Pinned engagement ID.
|
||||
- `zip` (string, optional): Postal Code.
|
||||
- `hs_language` (string, optional): Preferred language. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `associatedcompanyid` (number, optional): Primary Associated Company ID.
|
||||
- `hs_email_optout_survey_reason` (string, optional): Reason for opting out of email.
|
||||
- `relationship_status` (string, optional): Relationship Status.
|
||||
- `hs_returning_to_office_detected_date` (string, optional): Returning to office detected date.
|
||||
- `salutation` (string, optional): Salutation.
|
||||
- `school` (string, optional): School.
|
||||
- `seniority` (string, optional): Seniority.
|
||||
- `hs_feedback_show_nps_web_survey` (boolean, optional): Should be shown an NPS web survey.
|
||||
- `start_date` (string, optional): Start date.
|
||||
- `state` (string, optional): State/Region.
|
||||
- `hs_state_code` (string, optional): State/Region Code.
|
||||
- `hs_content_membership_status` (string, optional): Status.
|
||||
- `address` (string, optional): Street Address.
|
||||
- `tax_exempt` (string, optional): Tax Exempt.
|
||||
- `hs_timezone` (string, optional): Time Zone. Must be one of the predefined values.
|
||||
- `twitterbio` (string, optional): Twitter Bio.
|
||||
- `hs_twitterid` (string, optional): Twitter ID.
|
||||
- `twitterprofilephoto` (string, optional): Twitter Profile Photo.
|
||||
- `twitterhandle` (string, optional): Twitter Username.
|
||||
- `vat_number` (string, optional): VAT Number.
|
||||
- `ch_verified` (string, optional): Verified for ACH/eCheck Payments.
|
||||
- `website` (string, optional): Website URL.
|
||||
- `hs_whatsapp_phone_number` (string, optional): WhatsApp Phone Number.
|
||||
- `work_email` (string, optional): Work email.
|
||||
- `hs_googleplusid` (string, optional): googleplus ID.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_CREATE_RECORD_DEALS">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new deal record in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `dealname` (string, required): Name of the deal.
|
||||
- `amount` (number, optional): The value of the deal.
|
||||
- `dealstage` (string, optional): The pipeline stage of the deal.
|
||||
- `pipeline` (string, optional): The pipeline the deal belongs to.
|
||||
- `closedate` (string, optional): The date the deal is expected to close.
|
||||
- `hubspot_owner_id` (string, optional): The owner of the deal.
|
||||
- `dealtype` (string, optional): The type of deal. Available values: `newbusiness`, `existingbusiness`.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): A description of the deal.
|
||||
- `hs_priority` (string, optional): The priority of the deal. Available values: `low`, `medium`, `high`.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_CREATE_RECORD_ENGAGEMENTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new engagement (e.g., note, email, call, meeting, task) in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `engagementType` (string, required): The type of engagement. Available values: `NOTE`, `EMAIL`, `CALL`, `MEETING`, `TASK`.
|
||||
- `hubspot_owner_id` (string, optional): The user the activity is assigned to.
|
||||
- `hs_timestamp` (string, optional): The date and time of the activity.
|
||||
- `hs_note_body` (string, optional): The body of the note. (Used for `NOTE`)
|
||||
- `hs_task_subject` (string, optional): The title of the task. (Used for `TASK`)
|
||||
- `hs_task_body` (string, optional): The notes for the task. (Used for `TASK`)
|
||||
- `hs_task_status` (string, optional): The status of the task. (Used for `TASK`)
|
||||
- `hs_meeting_title` (string, optional): The title of the meeting. (Used for `MEETING`)
|
||||
- `hs_meeting_body` (string, optional): The description for the meeting. (Used for `MEETING`)
|
||||
- `hs_meeting_start_time` (string, optional): The start time of the meeting. (Used for `MEETING`)
|
||||
- `hs_meeting_end_time` (string, optional): The end time of the meeting. (Used for `MEETING`)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_UPDATE_RECORD_COMPANIES">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing company record in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the company to update.
|
||||
- `name` (string, optional): Name of the company.
|
||||
- `domain` (string, optional): Company Domain Name.
|
||||
- `industry` (string, optional): Industry.
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): Phone Number.
|
||||
- `city` (string, optional): City.
|
||||
- `state` (string, optional): State/Region.
|
||||
- `zip` (string, optional): Postal Code.
|
||||
- `numberofemployees` (number, optional): Number of Employees.
|
||||
- `annualrevenue` (number, optional): Annual Revenue.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_CREATE_RECORD_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a record for a specified object type in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): The object type ID of the custom object.
|
||||
- Additional parameters depend on the custom object's schema.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_UPDATE_RECORD_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing contact record in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the contact to update.
|
||||
- `firstname` (string, optional): First Name.
|
||||
- `lastname` (string, optional): Last Name.
|
||||
- `email` (string, optional): Email address.
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): Phone Number.
|
||||
- `company` (string, optional): Company Name.
|
||||
- `jobtitle` (string, optional): Job Title.
|
||||
- `lifecyclestage` (string, optional): Lifecycle Stage.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_UPDATE_RECORD_DEALS">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing deal record in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the deal to update.
|
||||
- `dealname` (string, optional): Name of the deal.
|
||||
- `amount` (number, optional): The value of the deal.
|
||||
- `dealstage` (string, optional): The pipeline stage of the deal.
|
||||
- `pipeline` (string, optional): The pipeline the deal belongs to.
|
||||
- `closedate` (string, optional): The date the deal is expected to close.
|
||||
- `dealtype` (string, optional): The type of deal.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_UPDATE_RECORD_ENGAGEMENTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing engagement in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the engagement to update.
|
||||
- `hs_note_body` (string, optional): The body of the note.
|
||||
- `hs_task_subject` (string, optional): The title of the task.
|
||||
- `hs_task_body` (string, optional): The notes for the task.
|
||||
- `hs_task_status` (string, optional): The status of the task.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_UPDATE_RECORD_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a record for a specified object type in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to update.
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): The object type ID of the custom object.
|
||||
- Additional parameters depend on the custom object's schema.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORDS_COMPANIES">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of company records from HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORDS_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of contact records from HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORDS_DEALS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of deal records from HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORDS_ENGAGEMENTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of engagement records from HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `objectName` (string, required): The type of engagement to fetch (e.g., "notes").
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORDS_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a list of records for any specified object type in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): The object type ID of the custom object.
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_COMPANIES">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a single company record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the company to retrieve.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a single contact record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the contact to retrieve.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_DEALS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a single deal record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the deal to retrieve.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_ENGAGEMENTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a single engagement record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the engagement to retrieve.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a single record of any specified object type by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): The object type ID of the custom object.
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to retrieve.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_SEARCH_RECORDS_COMPANIES">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for company records in HubSpot using a filter formula.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form (OR of ANDs).
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_SEARCH_RECORDS_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for contact records in HubSpot using a filter formula.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form (OR of ANDs).
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_SEARCH_RECORDS_DEALS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for deal records in HubSpot using a filter formula.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form (OR of ANDs).
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_SEARCH_RECORDS_ENGAGEMENTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for engagement records in HubSpot using a filter formula.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `engagementFilterFormula` (object, optional): A filter for engagements.
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_SEARCH_RECORDS_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for records of any specified object type in HubSpot.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): The object type ID to search.
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (string, optional): The filter formula to apply.
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` to fetch subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_DELETE_RECORD_COMPANIES">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a company record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the company to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_DELETE_RECORD_CONTACTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a contact record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the contact to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_DELETE_RECORD_DEALS">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a deal record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the deal to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_DELETE_RECORD_ENGAGEMENTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete an engagement record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the engagement to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_DELETE_RECORD_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a record of any specified object type by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): The object type ID of the custom object.
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to delete.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_GET_CONTACTS_BY_LIST_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get contacts from a specific list by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listId` (string, required): The ID of the list to get contacts from.
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Use `pageCursor` for subsequent pages.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="HUBSPOT_DESCRIBE_ACTION_SCHEMA">
|
||||
**Description:** Get the expected schema for a given object type and operation.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): The object type ID (e.g., 'companies').
|
||||
- `operation` (string, required): The operation type (e.g., 'CREATE_RECORD').
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic HubSpot Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (HubSpot tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with HubSpot capabilities
|
||||
hubspot_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="CRM Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage company and contact records in HubSpot",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in CRM management.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new company
|
||||
create_company_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new company in HubSpot with name 'Innovate Corp' and domain 'innovatecorp.com'.",
|
||||
agent=hubspot_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Company created successfully with confirmation"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[hubspot_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_company_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific HubSpot Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only the tool to create contacts
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["hubspot_create_record_contacts"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
contact_creator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Contact Creator",
|
||||
goal="Create new contacts in HubSpot",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on creating new contact entries in the CRM.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a contact
|
||||
create_contact = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new contact for 'John Doe' with email 'john.doe@example.com'.",
|
||||
agent=contact_creator,
|
||||
expected_output="Contact created successfully in HubSpot."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[contact_creator],
|
||||
tasks=[create_contact]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Contact Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crm_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="CRM Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage and organize HubSpot contacts efficiently.",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced CRM manager who maintains an organized contact database.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage contacts
|
||||
contact_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new contact for 'Jane Smith' at 'Global Tech Inc.' with email 'jane.smith@globaltech.com'.",
|
||||
agent=crm_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Contact database updated with the new contact."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[crm_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[contact_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with HubSpot integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
394
docs/enterprise/integrations/jira.mdx
Normal file
394
docs/enterprise/integrations/jira.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,394 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Jira Integration
|
||||
description: "Issue tracking and project management with Jira integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "bug"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage issues, projects, and workflows through Jira. Create and update issues, track project progress, manage assignments, and streamline your project management with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Jira integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Jira account with appropriate project permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Jira account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Jira Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Jira Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Jira** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for issue and project management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_CREATE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Create an issue in Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `summary` (string, required): Summary - A brief one-line summary of the issue. (example: "The printer stopped working").
|
||||
- `project` (string, optional): Project - The project which the issue belongs to. Defaults to the user's first project if not provided. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Project.
|
||||
- `issueType` (string, optional): Issue type - Defaults to Task if not provided.
|
||||
- `jiraIssueStatus` (string, optional): Status - Defaults to the project's first status if not provided.
|
||||
- `assignee` (string, optional): Assignee - Defaults to the authenticated user if not provided.
|
||||
- `descriptionType` (string, optional): Description Type - Select the Description Type.
|
||||
- Options: `description`, `descriptionJSON`
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description - A detailed description of the issue. This field appears only when 'descriptionType' = 'description'.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (string, optional): Additional Fields - Specify any other fields that should be included in JSON format. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select which Issue Fields to update.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"customfield_10001": "value"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_UPDATE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an issue in Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `issueKey` (string, required): Issue Key (example: "TEST-1234").
|
||||
- `summary` (string, optional): Summary - A brief one-line summary of the issue. (example: "The printer stopped working").
|
||||
- `issueType` (string, optional): Issue type - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select an Issue Type.
|
||||
- `jiraIssueStatus` (string, optional): Status - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Status.
|
||||
- `assignee` (string, optional): Assignee - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select an Assignee.
|
||||
- `descriptionType` (string, optional): Description Type - Select the Description Type.
|
||||
- Options: `description`, `descriptionJSON`
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description - A detailed description of the issue. This field appears only when 'descriptionType' = 'description'.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (string, optional): Additional Fields - Specify any other fields that should be included in JSON format.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_GET_ISSUE_BY_KEY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get an issue by key in Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `issueKey` (string, required): Issue Key (example: "TEST-1234").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_FILTER_ISSUES">
|
||||
**Description:** Search issues in Jira using filters.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `jqlQuery` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "status",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringExactlyMatches",
|
||||
"value": "Open"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available operators: `$stringExactlyMatches`, `$stringDoesNotExactlyMatch`, `$stringIsIn`, `$stringIsNotIn`, `$stringContains`, `$stringDoesNotContain`, `$stringGreaterThan`, `$stringLessThan`
|
||||
- `limit` (string, optional): Limit results - Limit the maximum number of issues to return. Defaults to 10 if left blank.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_SEARCH_BY_JQL">
|
||||
**Description:** Search issues by JQL in Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `jqlQuery` (string, required): JQL Query (example: "project = PROJECT").
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination parameters for paginated results.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pageCursor": "cursor_string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_UPDATE_ISSUE_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Update any issue in Jira. Use DESCRIBE_ACTION_SCHEMA to get properties schema for this function.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:** No specific parameters - use JIRA_DESCRIBE_ACTION_SCHEMA first to get the expected schema.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_DESCRIBE_ACTION_SCHEMA">
|
||||
**Description:** Get the expected schema for an issue type. Use this function first if no other function matches the issue type you want to operate on.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `issueTypeId` (string, required): Issue Type ID.
|
||||
- `projectKey` (string, required): Project key.
|
||||
- `operation` (string, required): Operation Type value, for example CREATE_ISSUE or UPDATE_ISSUE.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_GET_PROJECTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Projects in Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination Parameters.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"pageCursor": "cursor_string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_GET_ISSUE_TYPES_BY_PROJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Issue Types by project in Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `project` (string, required): Project key.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_GET_ISSUE_TYPES">
|
||||
**Description:** Get all Issue Types in Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:** None required.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_GET_ISSUE_STATUS_BY_PROJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get issue statuses for a given project.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `project` (string, required): Project key.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="JIRA_GET_ALL_ASSIGNEES_BY_PROJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get assignees for a given project.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `project` (string, required): Project key.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Jira Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Jira tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Jira capabilities
|
||||
jira_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Issue Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage Jira issues and track project progress efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in issue tracking and project management.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a bug report
|
||||
create_bug_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a bug report for the login functionality with high priority and assign it to the development team",
|
||||
agent=jira_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Bug report created successfully with issue key"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[jira_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_bug_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Jira Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Jira tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["jira_create_issue", "jira_update_issue", "jira_search_by_jql"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
issue_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Issue Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Create and manage Jira issues efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on issue creation and management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage issue workflow
|
||||
issue_workflow = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a feature request issue and update the status of related issues",
|
||||
agent=issue_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Feature request created and related issues updated"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[issue_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[issue_workflow]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Project Analysis and Reporting
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
project_analyst = Agent(
|
||||
role="Project Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze project data and generate insights from Jira",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced project analyst who extracts insights from project management data.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to analyze project status
|
||||
analysis_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Get all projects and their issue types
|
||||
2. Search for all open issues across projects
|
||||
3. Analyze issue distribution by status and assignee
|
||||
4. Create a summary report issue with findings
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=project_analyst,
|
||||
expected_output="Project analysis completed with summary report created"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[project_analyst],
|
||||
tasks=[analysis_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automated Issue Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
automation_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Automation Manager",
|
||||
goal="Automate issue management and workflow processes",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that automates repetitive issue management tasks.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to automate issue management
|
||||
automation_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for all unassigned issues using JQL
|
||||
2. Get available assignees for each project
|
||||
3. Automatically assign issues based on workload and expertise
|
||||
4. Update issue priorities based on age and type
|
||||
5. Create weekly sprint planning issues
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=automation_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Issues automatically assigned and sprint planning issues created"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[automation_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[automation_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Schema-Based Operations
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
schema_specialist = Agent(
|
||||
role="Schema Specialist",
|
||||
goal="Handle complex Jira operations using dynamic schemas",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that can work with dynamic Jira schemas and custom issue types.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task using schema-based operations
|
||||
schema_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Get all projects and their custom issue types
|
||||
2. For each custom issue type, describe the action schema
|
||||
3. Create issues using the dynamic schema for complex custom fields
|
||||
4. Update issues with custom field values based on business rules
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=schema_specialist,
|
||||
expected_output="Custom issues created and updated using dynamic schemas"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[schema_specialist],
|
||||
tasks=[schema_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues
|
||||
|
||||
**Permission Errors**
|
||||
- Ensure your Jira account has necessary permissions for the target projects
|
||||
- Verify that the OAuth connection includes required scopes for Jira API
|
||||
- Check if you have create/edit permissions for issues in the specified projects
|
||||
|
||||
**Invalid Project or Issue Keys**
|
||||
- Double-check project keys and issue keys for correct format (e.g., "PROJ-123")
|
||||
- Ensure projects exist and are accessible to your account
|
||||
- Verify that issue keys reference existing issues
|
||||
|
||||
**Issue Type and Status Issues**
|
||||
- Use JIRA_GET_ISSUE_TYPES_BY_PROJECT to get valid issue types for a project
|
||||
- Use JIRA_GET_ISSUE_STATUS_BY_PROJECT to get valid statuses
|
||||
- Ensure issue types and statuses are available in the target project
|
||||
|
||||
**JQL Query Problems**
|
||||
- Test JQL queries in Jira's issue search before using in API calls
|
||||
- Ensure field names in JQL are spelled correctly and exist in your Jira instance
|
||||
- Use proper JQL syntax for complex queries
|
||||
|
||||
**Custom Fields and Schema Issues**
|
||||
- Use JIRA_DESCRIBE_ACTION_SCHEMA to get the correct schema for complex issue types
|
||||
- Ensure custom field IDs are correct (e.g., "customfield_10001")
|
||||
- Verify that custom fields are available in the target project and issue type
|
||||
|
||||
**Filter Formula Issues**
|
||||
- Ensure filter formulas follow the correct JSON structure for disjunctive normal form
|
||||
- Use valid field names that exist in your Jira configuration
|
||||
- Test simple filters before building complex multi-condition queries
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Jira integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
453
docs/enterprise/integrations/linear.mdx
Normal file
453
docs/enterprise/integrations/linear.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,453 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Linear Integration
|
||||
description: "Software project and bug tracking with Linear integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "list-check"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage issues, projects, and development workflows through Linear. Create and update issues, manage project timelines, organize teams, and streamline your software development process with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Linear integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Linear account with appropriate workspace permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Linear account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Linear Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Linear Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Linear** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for issue and project management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_CREATE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new issue in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `teamId` (string, required): Team ID - Specify the Team ID of the parent for this new issue. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Team ID. (example: "a70bdf0f-530a-4887-857d-46151b52b47c").
|
||||
- `title` (string, required): Title - Specify a title for this issue.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description - Specify a description for this issue.
|
||||
- `statusId` (string, optional): Status - Specify the state or status of this issue.
|
||||
- `priority` (string, optional): Priority - Specify the priority of this issue as an integer.
|
||||
- `dueDate` (string, optional): Due Date - Specify the due date of this issue in ISO 8601 format.
|
||||
- `cycleId` (string, optional): Cycle ID - Specify the cycle associated with this issue.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional Fields.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"assigneeId": "a70bdf0f-530a-4887-857d-46151b52b47c",
|
||||
"labelIds": ["a70bdf0f-530a-4887-857d-46151b52b47c"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_UPDATE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an issue in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `issueId` (string, required): Issue ID - Specify the Issue ID of the issue to update. (example: "90fbc706-18cd-42c9-ae66-6bd344cc8977").
|
||||
- `title` (string, optional): Title - Specify a title for this issue.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description - Specify a description for this issue.
|
||||
- `statusId` (string, optional): Status - Specify the state or status of this issue.
|
||||
- `priority` (string, optional): Priority - Specify the priority of this issue as an integer.
|
||||
- `dueDate` (string, optional): Due Date - Specify the due date of this issue in ISO 8601 format.
|
||||
- `cycleId` (string, optional): Cycle ID - Specify the cycle associated with this issue.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional Fields.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"assigneeId": "a70bdf0f-530a-4887-857d-46151b52b47c",
|
||||
"labelIds": ["a70bdf0f-530a-4887-857d-46151b52b47c"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_GET_ISSUE_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get an issue by ID in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `issueId` (string, required): Issue ID - Specify the record ID of the issue to fetch. (example: "90fbc706-18cd-42c9-ae66-6bd344cc8977").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_GET_ISSUE_BY_ISSUE_IDENTIFIER">
|
||||
**Description:** Get an issue by issue identifier in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `externalId` (string, required): External ID - Specify the human-readable Issue identifier of the issue to fetch. (example: "ABC-1").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_SEARCH_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Search issues in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `queryTerm` (string, required): Query Term - The search term to look for.
|
||||
- `issueFilterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "title",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringContains",
|
||||
"value": "bug"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available fields: `title`, `number`, `project`, `createdAt`
|
||||
Available operators: `$stringExactlyMatches`, `$stringDoesNotExactlyMatch`, `$stringIsIn`, `$stringIsNotIn`, `$stringStartsWith`, `$stringDoesNotStartWith`, `$stringEndsWith`, `$stringDoesNotEndWith`, `$stringContains`, `$stringDoesNotContain`, `$stringGreaterThan`, `$stringLessThan`, `$numberGreaterThanOrEqualTo`, `$numberLessThanOrEqualTo`, `$numberGreaterThan`, `$numberLessThan`, `$dateTimeAfter`, `$dateTimeBefore`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_DELETE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete an issue in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `issueId` (string, required): Issue ID - Specify the record ID of the issue to delete. (example: "90fbc706-18cd-42c9-ae66-6bd344cc8977").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_ARCHIVE_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Archive an issue in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `issueId` (string, required): Issue ID - Specify the record ID of the issue to archive. (example: "90fbc706-18cd-42c9-ae66-6bd344cc8977").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_CREATE_SUB_ISSUE">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a sub-issue in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `parentId` (string, required): Parent ID - Specify the Issue ID for the parent of this new issue.
|
||||
- `teamId` (string, required): Team ID - Specify the Team ID of the parent for this new sub-issue. Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a Team ID. (example: "a70bdf0f-530a-4887-857d-46151b52b47c").
|
||||
- `title` (string, required): Title - Specify a title for this issue.
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Description - Specify a description for this issue.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional Fields.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"lead": "linear_user_id"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_CREATE_PROJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new project in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `teamIds` (object, required): Team ID - Specify the team ID(s) this project is associated with as a string or a JSON array. Use Connect Portal User Settings to allow your user to select a Team ID.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
"a70bdf0f-530a-4887-857d-46151b52b47c",
|
||||
"4ac7..."
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `projectName` (string, required): Project Name - Specify the name of the project. (example: "My Linear Project").
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Project Description - Specify a description for this project.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional Fields.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"state": "planned",
|
||||
"description": ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_UPDATE_PROJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a project in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `projectId` (string, required): Project ID - Specify the ID of the project to update. (example: "a6634484-6061-4ac7-9739-7dc5e52c796b").
|
||||
- `projectName` (string, optional): Project Name - Specify the name of the project to update. (example: "My Linear Project").
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Project Description - Specify a description for this project.
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional Fields.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"state": "planned",
|
||||
"description": ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_GET_PROJECT_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a project by ID in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `projectId` (string, required): Project ID - Specify the Project ID of the project to fetch. (example: "a6634484-6061-4ac7-9739-7dc5e52c796b").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_DELETE_PROJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a project in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `projectId` (string, required): Project ID - Specify the Project ID of the project to delete. (example: "a6634484-6061-4ac7-9739-7dc5e52c796b").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="LINEAR_SEARCH_TEAMS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search teams in Linear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `teamFilterFormula` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "name",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringContains",
|
||||
"value": "Engineering"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available fields: `id`, `name`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Linear Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Linear tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Linear capabilities
|
||||
linear_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Development Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage Linear issues and track development progress efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in software development project management.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a bug report
|
||||
create_bug_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a high-priority bug report for the authentication system and assign it to the backend team",
|
||||
agent=linear_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Bug report created successfully with issue ID"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[linear_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_bug_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Linear Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Linear tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["linear_create_issue", "linear_update_issue", "linear_search_issue"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
issue_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Issue Manager",
|
||||
goal="Create and manage Linear issues efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on issue creation and lifecycle management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage issue workflow
|
||||
issue_workflow = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a feature request issue and update the status of related issues to reflect current progress",
|
||||
agent=issue_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Feature request created and related issues updated"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[issue_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[issue_workflow]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Project and Team Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
project_coordinator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Project Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Coordinate projects and teams in Linear efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced project coordinator who manages development cycles and team workflows.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to coordinate project setup
|
||||
project_coordination = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for engineering teams in Linear
|
||||
2. Create a new project for Q2 feature development
|
||||
3. Associate the project with relevant teams
|
||||
4. Create initial project milestones as issues
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=project_coordinator,
|
||||
expected_output="Q2 project created with teams assigned and initial milestones established"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[project_coordinator],
|
||||
tasks=[project_coordination]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Issue Hierarchy and Sub-task Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
task_organizer = Agent(
|
||||
role="Task Organizer",
|
||||
goal="Organize complex issues into manageable sub-tasks",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that breaks down complex development work into organized sub-tasks.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create issue hierarchy
|
||||
hierarchy_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for large feature issues that need to be broken down
|
||||
2. For each complex issue, create sub-issues for different components
|
||||
3. Update the parent issues with proper descriptions and links to sub-issues
|
||||
4. Assign sub-issues to appropriate team members based on expertise
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=task_organizer,
|
||||
expected_output="Complex issues broken down into manageable sub-tasks with proper assignments"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[task_organizer],
|
||||
tasks=[hierarchy_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automated Development Workflow
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
workflow_automator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Workflow Automator",
|
||||
goal="Automate development workflow processes in Linear",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that automates repetitive development workflow tasks.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex workflow automation task
|
||||
automation_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for issues that have been in progress for more than 7 days
|
||||
2. Update their priorities based on due dates and project importance
|
||||
3. Create weekly sprint planning issues for each team
|
||||
4. Archive completed issues from the previous cycle
|
||||
5. Generate project status reports as new issues
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=workflow_automator,
|
||||
expected_output="Development workflow automated with updated priorities, sprint planning, and status reports"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[workflow_automator],
|
||||
tasks=[automation_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues
|
||||
|
||||
**Permission Errors**
|
||||
- Ensure your Linear account has necessary permissions for the target workspace
|
||||
- Verify that the OAuth connection includes required scopes for Linear API
|
||||
- Check if you have create/edit permissions for issues and projects in the workspace
|
||||
|
||||
**Invalid IDs and References**
|
||||
- Double-check team IDs, issue IDs, and project IDs for correct UUID format
|
||||
- Ensure referenced entities (teams, projects, cycles) exist and are accessible
|
||||
- Verify that issue identifiers follow the correct format (e.g., "ABC-1")
|
||||
|
||||
**Team and Project Association Issues**
|
||||
- Use LINEAR_SEARCH_TEAMS to get valid team IDs before creating issues or projects
|
||||
- Ensure teams exist and are active in your workspace
|
||||
- Verify that team IDs are properly formatted as UUIDs
|
||||
|
||||
**Issue Status and Priority Problems**
|
||||
- Check that status IDs reference valid workflow states for the team
|
||||
- Ensure priority values are within the valid range for your Linear configuration
|
||||
- Verify that custom fields and labels exist before referencing them
|
||||
|
||||
**Date and Time Format Issues**
|
||||
- Use ISO 8601 format for due dates and timestamps
|
||||
- Ensure time zones are handled correctly for due date calculations
|
||||
- Verify that date values are valid and in the future for due dates
|
||||
|
||||
**Search and Filter Issues**
|
||||
- Ensure search queries are properly formatted and not empty
|
||||
- Use valid field names in filter formulas: `title`, `number`, `project`, `createdAt`
|
||||
- Test simple filters before building complex multi-condition queries
|
||||
- Verify that operator types match the data types of the fields being filtered
|
||||
|
||||
**Sub-issue Creation Problems**
|
||||
- Ensure parent issue IDs are valid and accessible
|
||||
- Verify that the team ID for sub-issues matches or is compatible with the parent issue's team
|
||||
- Check that parent issues are not already archived or deleted
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Linear integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
509
docs/enterprise/integrations/notion.mdx
Normal file
509
docs/enterprise/integrations/notion.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,509 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Notion Integration
|
||||
description: "Page and database management with Notion integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "book"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage pages, databases, and content through Notion. Create and update pages, manage content blocks, organize knowledge bases, and streamline your documentation workflows with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Notion integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Notion account with appropriate workspace permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Notion account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting Up Notion Integration
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Connect Your Notion Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to [CrewAI Enterprise Integrations](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/connectors)
|
||||
2. Find **Notion** in the Authentication Integrations section
|
||||
3. Click **Connect** and complete the OAuth flow
|
||||
4. Grant the necessary permissions for page and database management
|
||||
5. Copy your Enterprise Token from [Account Settings](https://app.crewai.com/crewai_plus/settings/account)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Required Package
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uv add crewai-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Actions
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_CREATE_PAGE">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a page in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `parent` (object, required): Parent - The parent page or database where the new page is inserted, represented as a JSON object with a page_id or database_id key.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"database_id": "DATABASE_ID"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `properties` (object, required): Properties - The values of the page's properties. If the parent is a database, then the schema must match the parent database's properties.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"title": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"content": "My Page"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `icon` (object, required): Icon - The page icon.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"emoji": "🥬"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `children` (object, optional): Children - Content blocks to add to the page.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"object": "block",
|
||||
"type": "heading_2",
|
||||
"heading_2": {
|
||||
"rich_text": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "text",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"content": "Lacinato kale"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `cover` (object, optional): Cover - The page cover image.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"external": {
|
||||
"url": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/62/Tuscankale.jpg"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_UPDATE_PAGE">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a page in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `pageId` (string, required): Page ID - Specify the ID of the Page to Update. (example: "59833787-2cf9-4fdf-8782-e53db20768a5").
|
||||
- `icon` (object, required): Icon - The page icon.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"emoji": "🥬"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `archived` (boolean, optional): Archived - Whether the page is archived (deleted). Set to true to archive a page. Set to false to un-archive (restore) a page.
|
||||
- `properties` (object, optional): Properties - The property values to update for the page.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"title": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"content": "My Updated Page"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `cover` (object, optional): Cover - The page cover image.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"external": {
|
||||
"url": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/62/Tuscankale.jpg"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_GET_PAGE_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a page by ID in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `pageId` (string, required): Page ID - Specify the ID of the Page to Get. (example: "59833787-2cf9-4fdf-8782-e53db20768a5").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_ARCHIVE_PAGE">
|
||||
**Description:** Archive a page in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `pageId` (string, required): Page ID - Specify the ID of the Page to Archive. (example: "59833787-2cf9-4fdf-8782-e53db20768a5").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_SEARCH_PAGES">
|
||||
**Description:** Search pages in Notion using filters.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `searchByTitleFilterSearch` (object, optional): A filter in disjunctive normal form - OR of AND groups of single conditions.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "OR",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"operator": "AND",
|
||||
"conditions": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"field": "query",
|
||||
"operator": "$stringExactlyMatches",
|
||||
"value": "meeting notes"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available fields: `query`, `filter.value`, `direction`, `page_size`
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_GET_PAGE_CONTENT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get page content (blocks) in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `blockId` (string, required): Page ID - Specify a Block or Page ID to receive all of its block's children in order. (example: "59833787-2cf9-4fdf-8782-e53db20768a5").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_UPDATE_BLOCK">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a block in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `blockId` (string, required): Block ID - Specify the ID of the Block to Update. (example: "9bc30ad4-9373-46a5-84ab-0a7845ee52e6").
|
||||
- `archived` (boolean, optional): Archived - Set to true to archive (delete) a block. Set to false to un-archive (restore) a block.
|
||||
- `paragraph` (object, optional): Paragraph content.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"rich_text": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "text",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"content": "Lacinato kale",
|
||||
"link": null
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"color": "default"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `image` (object, optional): Image block.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "external",
|
||||
"external": {
|
||||
"url": "https://website.domain/images/image.png"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `bookmark` (object, optional): Bookmark block.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"caption": [],
|
||||
"url": "https://companywebsite.com"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `code` (object, optional): Code block.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"rich_text": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "text",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"content": "const a = 3"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"language": "javascript"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `pdf` (object, optional): PDF block.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "external",
|
||||
"external": {
|
||||
"url": "https://website.domain/files/doc.pdf"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `table` (object, optional): Table block.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"table_width": 2,
|
||||
"has_column_header": false,
|
||||
"has_row_header": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `tableOfContent` (object, optional): Table of Contents block.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"color": "default"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional block types.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"child_page": {
|
||||
"title": "Lacinato kale"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"child_database": {
|
||||
"title": "My database"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_GET_BLOCK_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a block by ID in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `blockId` (string, required): Block ID - Specify the ID of the Block to Get. (example: "9bc30ad4-9373-46a5-84ab-0a7845ee52e6").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="NOTION_DELETE_BLOCK">
|
||||
**Description:** Delete a block in Notion.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `blockId` (string, required): Block ID - Specify the ID of the Block to Delete. (example: "9bc30ad4-9373-46a5-84ab-0a7845ee52e6").
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Notion Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Notion tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Notion capabilities
|
||||
notion_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Documentation Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage documentation and knowledge base in Notion efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in content management and documentation.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a meeting notes page
|
||||
create_notes_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new meeting notes page in the team database with today's date and agenda items",
|
||||
agent=notion_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Meeting notes page created successfully with structured content"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[notion_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_notes_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Notion Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Notion tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["notion_create_page", "notion_update_block", "notion_search_pages"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
content_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Content Manager",
|
||||
goal="Create and manage content pages efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that focuses on content creation and management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage content workflow
|
||||
content_workflow = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new project documentation page and add structured content blocks for requirements and specifications",
|
||||
agent=content_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Project documentation created with organized content sections"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[content_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[content_workflow]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Knowledge Base Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
knowledge_curator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Knowledge Curator",
|
||||
goal="Curate and organize knowledge base content in Notion",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced knowledge manager who organizes and maintains comprehensive documentation.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to curate knowledge base
|
||||
curation_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for existing documentation pages related to our new product feature
|
||||
2. Create a comprehensive feature documentation page with proper structure
|
||||
3. Add code examples, images, and links to related resources
|
||||
4. Update existing pages with cross-references to the new documentation
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=knowledge_curator,
|
||||
expected_output="Feature documentation created and integrated with existing knowledge base"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[knowledge_curator],
|
||||
tasks=[curation_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Content Structure and Organization
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
content_organizer = Agent(
|
||||
role="Content Organizer",
|
||||
goal="Organize and structure content blocks for optimal readability",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that specializes in content structure and user experience.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to organize content structure
|
||||
organization_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Get content from existing project pages
|
||||
2. Analyze the structure and identify improvement opportunities
|
||||
3. Update content blocks to use proper headings, tables, and formatting
|
||||
4. Add table of contents and improve navigation between related pages
|
||||
5. Create templates for future documentation consistency
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=content_organizer,
|
||||
expected_output="Content reorganized with improved structure and navigation"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[content_organizer],
|
||||
tasks=[organization_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automated Documentation Workflows
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
doc_automator = Agent(
|
||||
role="Documentation Automator",
|
||||
goal="Automate documentation workflows and maintenance",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that automates repetitive documentation tasks.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex documentation automation task
|
||||
automation_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for pages that haven't been updated in the last 30 days
|
||||
2. Review and update outdated content blocks
|
||||
3. Create weekly team update pages with consistent formatting
|
||||
4. Add status indicators and progress tracking to project pages
|
||||
5. Generate monthly documentation health reports
|
||||
6. Archive completed project pages and organize them in archive sections
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=doc_automator,
|
||||
expected_output="Documentation automated with updated content, weekly reports, and organized archives"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[doc_automator],
|
||||
tasks=[automation_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues
|
||||
|
||||
**Permission Errors**
|
||||
- Ensure your Notion account has edit access to the target workspace
|
||||
- Verify that the OAuth connection includes required scopes for Notion API
|
||||
- Check that pages and databases are shared with the authenticated integration
|
||||
|
||||
**Invalid Page and Block IDs**
|
||||
- Double-check page IDs and block IDs for correct UUID format
|
||||
- Ensure referenced pages and blocks exist and are accessible
|
||||
- Verify that parent page or database IDs are valid when creating new pages
|
||||
|
||||
**Property Schema Issues**
|
||||
- Ensure page properties match the database schema when creating pages in databases
|
||||
- Verify that property names and types are correct for the target database
|
||||
- Check that required properties are included when creating or updating pages
|
||||
|
||||
**Content Block Structure**
|
||||
- Ensure block content follows Notion's rich text format specifications
|
||||
- Verify that nested block structures are properly formatted
|
||||
- Check that media URLs are accessible and properly formatted
|
||||
|
||||
**Search and Filter Issues**
|
||||
- Ensure search queries are properly formatted and not empty
|
||||
- Use valid field names in filter formulas: `query`, `filter.value`, `direction`, `page_size`
|
||||
- Test simple searches before building complex filter conditions
|
||||
|
||||
**Parent-Child Relationships**
|
||||
- Verify that parent page or database exists before creating child pages
|
||||
- Ensure proper permissions exist for the parent container
|
||||
- Check that database schemas allow the properties you're trying to set
|
||||
|
||||
**Rich Text and Media Content**
|
||||
- Ensure URLs for external images, PDFs, and bookmarks are accessible
|
||||
- Verify that rich text formatting follows Notion's API specifications
|
||||
- Check that code block language types are supported by Notion
|
||||
|
||||
**Archive and Deletion Operations**
|
||||
- Understand the difference between archiving (reversible) and deleting (permanent)
|
||||
- Verify that you have permissions to archive or delete the target content
|
||||
- Be cautious with bulk operations that might affect multiple pages or blocks
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Notion integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
632
docs/enterprise/integrations/salesforce.mdx
Normal file
632
docs/enterprise/integrations/salesforce.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,632 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Salesforce Integration
|
||||
description: "CRM and sales automation with Salesforce integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "salesforce"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage customer relationships, sales processes, and data through Salesforce. Create and update records, manage leads and opportunities, execute SOQL queries, and streamline your CRM workflows with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Salesforce integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Salesforce account with appropriate permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Salesforce account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/integrations)
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### **Record Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_RECORD_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new Contact record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `FirstName` (string, optional): First Name
|
||||
- `LastName` (string, required): Last Name - This field is required
|
||||
- `accountId` (string, optional): Account ID - The Account that the Contact belongs to
|
||||
- `Email` (string, optional): Email address
|
||||
- `Title` (string, optional): Title of the contact, such as CEO or Vice President
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): A description of the Contact
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Contact fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_RECORD_LEAD">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new Lead record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `FirstName` (string, optional): First Name
|
||||
- `LastName` (string, required): Last Name - This field is required
|
||||
- `Company` (string, required): Company - This field is required
|
||||
- `Email` (string, optional): Email address
|
||||
- `Phone` (string, optional): Phone number
|
||||
- `Website` (string, optional): Website URL
|
||||
- `Title` (string, optional): Title of the contact, such as CEO or Vice President
|
||||
- `Status` (string, optional): Lead Status - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to select Lead Status
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): A description of the Lead
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Lead fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_RECORD_OPPORTUNITY">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new Opportunity record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `Name` (string, required): The Opportunity name - This field is required
|
||||
- `StageName` (string, optional): Opportunity Stage - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to select stage
|
||||
- `CloseDate` (string, optional): Close Date in YYYY-MM-DD format - Defaults to 30 days from current date
|
||||
- `AccountId` (string, optional): The Account that the Opportunity belongs to
|
||||
- `Amount` (string, optional): Estimated total sale amount
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): A description of the Opportunity
|
||||
- `OwnerId` (string, optional): The Salesforce user assigned to work on this Opportunity
|
||||
- `NextStep` (string, optional): Description of next task in closing Opportunity
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Opportunity fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_RECORD_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new Task record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `whatId` (string, optional): Related to ID - The ID of the Account or Opportunity this Task is related to
|
||||
- `whoId` (string, optional): Name ID - The ID of the Contact or Lead this Task is related to
|
||||
- `subject` (string, required): Subject of the task
|
||||
- `activityDate` (string, optional): Activity Date in YYYY-MM-DD format
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): A description of the Task
|
||||
- `taskSubtype` (string, required): Task Subtype - Options: task, email, listEmail, call
|
||||
- `Status` (string, optional): Status - Options: Not Started, In Progress, Completed
|
||||
- `ownerId` (string, optional): Assigned To ID - The Salesforce user assigned to this Task
|
||||
- `callDurationInSeconds` (string, optional): Call Duration in seconds
|
||||
- `isReminderSet` (boolean, optional): Whether reminder is set
|
||||
- `reminderDateTime` (string, optional): Reminder Date/Time in ISO format
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Task fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_RECORD_ACCOUNT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new Account record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `Name` (string, required): The Account name - This field is required
|
||||
- `OwnerId` (string, optional): The Salesforce user assigned to this Account
|
||||
- `Website` (string, optional): Website URL
|
||||
- `Phone` (string, optional): Phone number
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): Account description
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Account fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_RECORD_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a record of any object type in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** This is a flexible tool for creating records of custom or unknown object types.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Record Updates**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_UPDATE_RECORD_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing Contact record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to update
|
||||
- `FirstName` (string, optional): First Name
|
||||
- `LastName` (string, optional): Last Name
|
||||
- `accountId` (string, optional): Account ID - The Account that the Contact belongs to
|
||||
- `Email` (string, optional): Email address
|
||||
- `Title` (string, optional): Title of the contact
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): A description of the Contact
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Contact fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_UPDATE_RECORD_LEAD">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing Lead record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to update
|
||||
- `FirstName` (string, optional): First Name
|
||||
- `LastName` (string, optional): Last Name
|
||||
- `Company` (string, optional): Company name
|
||||
- `Email` (string, optional): Email address
|
||||
- `Phone` (string, optional): Phone number
|
||||
- `Website` (string, optional): Website URL
|
||||
- `Title` (string, optional): Title of the contact
|
||||
- `Status` (string, optional): Lead Status
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): A description of the Lead
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Lead fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_UPDATE_RECORD_OPPORTUNITY">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing Opportunity record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to update
|
||||
- `Name` (string, optional): The Opportunity name
|
||||
- `StageName` (string, optional): Opportunity Stage
|
||||
- `CloseDate` (string, optional): Close Date in YYYY-MM-DD format
|
||||
- `AccountId` (string, optional): The Account that the Opportunity belongs to
|
||||
- `Amount` (string, optional): Estimated total sale amount
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): A description of the Opportunity
|
||||
- `OwnerId` (string, optional): The Salesforce user assigned to work on this Opportunity
|
||||
- `NextStep` (string, optional): Description of next task in closing Opportunity
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Opportunity fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_UPDATE_RECORD_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing Task record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to update
|
||||
- `whatId` (string, optional): Related to ID - The ID of the Account or Opportunity this Task is related to
|
||||
- `whoId` (string, optional): Name ID - The ID of the Contact or Lead this Task is related to
|
||||
- `subject` (string, optional): Subject of the task
|
||||
- `activityDate` (string, optional): Activity Date in YYYY-MM-DD format
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): A description of the Task
|
||||
- `Status` (string, optional): Status - Options: Not Started, In Progress, Completed
|
||||
- `ownerId` (string, optional): Assigned To ID - The Salesforce user assigned to this Task
|
||||
- `callDurationInSeconds` (string, optional): Call Duration in seconds
|
||||
- `isReminderSet` (boolean, optional): Whether reminder is set
|
||||
- `reminderDateTime` (string, optional): Reminder Date/Time in ISO format
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Task fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_UPDATE_RECORD_ACCOUNT">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing Account record in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): The ID of the record to update
|
||||
- `Name` (string, optional): The Account name
|
||||
- `OwnerId` (string, optional): The Salesforce user assigned to this Account
|
||||
- `Website` (string, optional): Website URL
|
||||
- `Phone` (string, optional): Phone number
|
||||
- `Description` (string, optional): Account description
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional fields in JSON format for custom Account fields
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_UPDATE_RECORD_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Update a record of any object type in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** This is a flexible tool for updating records of custom or unknown object types.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Record Retrieval**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a Contact record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): Record ID of the Contact
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_LEAD">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a Lead record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): Record ID of the Lead
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_OPPORTUNITY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get an Opportunity record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): Record ID of the Opportunity
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a Task record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): Record ID of the Task
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_ACCOUNT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get an Account record by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): Record ID of the Account
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_ID_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get a record of any object type by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): Record Type (e.g., "CustomObject__c")
|
||||
- `recordId` (string, required): Record ID
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Record Search**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_SEARCH_RECORDS_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for Contact records with advanced filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): Advanced filter in disjunctive normal form with field-specific operators
|
||||
- `sortBy` (string, optional): Sort field (e.g., "CreatedDate")
|
||||
- `sortDirection` (string, optional): Sort direction - Options: ASC, DESC
|
||||
- `includeAllFields` (boolean, optional): Include all fields in results
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_SEARCH_RECORDS_LEAD">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for Lead records with advanced filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): Advanced filter in disjunctive normal form with field-specific operators
|
||||
- `sortBy` (string, optional): Sort field (e.g., "CreatedDate")
|
||||
- `sortDirection` (string, optional): Sort direction - Options: ASC, DESC
|
||||
- `includeAllFields` (boolean, optional): Include all fields in results
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_SEARCH_RECORDS_OPPORTUNITY">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for Opportunity records with advanced filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): Advanced filter in disjunctive normal form with field-specific operators
|
||||
- `sortBy` (string, optional): Sort field (e.g., "CreatedDate")
|
||||
- `sortDirection` (string, optional): Sort direction - Options: ASC, DESC
|
||||
- `includeAllFields` (boolean, optional): Include all fields in results
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_SEARCH_RECORDS_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for Task records with advanced filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): Advanced filter in disjunctive normal form with field-specific operators
|
||||
- `sortBy` (string, optional): Sort field (e.g., "CreatedDate")
|
||||
- `sortDirection` (string, optional): Sort direction - Options: ASC, DESC
|
||||
- `includeAllFields` (boolean, optional): Include all fields in results
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_SEARCH_RECORDS_ACCOUNT">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for Account records with advanced filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): Advanced filter in disjunctive normal form with field-specific operators
|
||||
- `sortBy` (string, optional): Sort field (e.g., "CreatedDate")
|
||||
- `sortDirection` (string, optional): Sort direction - Options: ASC, DESC
|
||||
- `includeAllFields` (boolean, optional): Include all fields in results
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_SEARCH_RECORDS_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for records of any object type.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): Record Type to search
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (string, optional): Filter search criteria
|
||||
- `includeAllFields` (boolean, optional): Include all fields in results
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **List View Retrieval**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_VIEW_ID_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Contact records from a specific List View.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listViewId` (string, required): List View ID
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_VIEW_ID_LEAD">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Lead records from a specific List View.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listViewId` (string, required): List View ID
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_VIEW_ID_OPPORTUNITY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Opportunity records from a specific List View.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listViewId` (string, required): List View ID
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_VIEW_ID_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Task records from a specific List View.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listViewId` (string, required): List View ID
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_VIEW_ID_ACCOUNT">
|
||||
**Description:** Get Account records from a specific List View.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `listViewId` (string, required): List View ID
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_GET_RECORD_BY_VIEW_ID_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Get records of any object type from a specific List View.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): Record Type
|
||||
- `listViewId` (string, required): List View ID
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings with pageCursor
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Custom Fields**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_CUSTOM_FIELD_CONTACT">
|
||||
**Description:** Deploy custom fields for Contact objects.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `label` (string, required): Field Label for displays and internal reference
|
||||
- `type` (string, required): Field Type - Options: Checkbox, Currency, Date, Email, Number, Percent, Phone, Picklist, MultiselectPicklist, Text, TextArea, LongTextArea, Html, Time, Url
|
||||
- `defaultCheckboxValue` (boolean, optional): Default value for checkbox fields
|
||||
- `length` (string, required): Length for numeric/text fields
|
||||
- `decimalPlace` (string, required): Decimal places for numeric fields
|
||||
- `pickListValues` (string, required): Values for picklist fields (separated by new lines)
|
||||
- `visibleLines` (string, required): Visible lines for multiselect/text area fields
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Field description
|
||||
- `helperText` (string, optional): Helper text shown on hover
|
||||
- `defaultFieldValue` (string, optional): Default field value
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_CUSTOM_FIELD_LEAD">
|
||||
**Description:** Deploy custom fields for Lead objects.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `label` (string, required): Field Label for displays and internal reference
|
||||
- `type` (string, required): Field Type - Options: Checkbox, Currency, Date, Email, Number, Percent, Phone, Picklist, MultiselectPicklist, Text, TextArea, LongTextArea, Html, Time, Url
|
||||
- `defaultCheckboxValue` (boolean, optional): Default value for checkbox fields
|
||||
- `length` (string, required): Length for numeric/text fields
|
||||
- `decimalPlace` (string, required): Decimal places for numeric fields
|
||||
- `pickListValues` (string, required): Values for picklist fields (separated by new lines)
|
||||
- `visibleLines` (string, required): Visible lines for multiselect/text area fields
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Field description
|
||||
- `helperText` (string, optional): Helper text shown on hover
|
||||
- `defaultFieldValue` (string, optional): Default field value
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_CUSTOM_FIELD_OPPORTUNITY">
|
||||
**Description:** Deploy custom fields for Opportunity objects.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `label` (string, required): Field Label for displays and internal reference
|
||||
- `type` (string, required): Field Type - Options: Checkbox, Currency, Date, Email, Number, Percent, Phone, Picklist, MultiselectPicklist, Text, TextArea, LongTextArea, Html, Time, Url
|
||||
- `defaultCheckboxValue` (boolean, optional): Default value for checkbox fields
|
||||
- `length` (string, required): Length for numeric/text fields
|
||||
- `decimalPlace` (string, required): Decimal places for numeric fields
|
||||
- `pickListValues` (string, required): Values for picklist fields (separated by new lines)
|
||||
- `visibleLines` (string, required): Visible lines for multiselect/text area fields
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Field description
|
||||
- `helperText` (string, optional): Helper text shown on hover
|
||||
- `defaultFieldValue` (string, optional): Default field value
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_CUSTOM_FIELD_TASK">
|
||||
**Description:** Deploy custom fields for Task objects.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `label` (string, required): Field Label for displays and internal reference
|
||||
- `type` (string, required): Field Type - Options: Checkbox, Currency, Date, Email, Number, Percent, Phone, Picklist, MultiselectPicklist, Text, TextArea, Time, Url
|
||||
- `defaultCheckboxValue` (boolean, optional): Default value for checkbox fields
|
||||
- `length` (string, required): Length for numeric/text fields
|
||||
- `decimalPlace` (string, required): Decimal places for numeric fields
|
||||
- `pickListValues` (string, required): Values for picklist fields (separated by new lines)
|
||||
- `visibleLines` (string, required): Visible lines for multiselect fields
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Field description
|
||||
- `helperText` (string, optional): Helper text shown on hover
|
||||
- `defaultFieldValue` (string, optional): Default field value
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_CUSTOM_FIELD_ACCOUNT">
|
||||
**Description:** Deploy custom fields for Account objects.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `label` (string, required): Field Label for displays and internal reference
|
||||
- `type` (string, required): Field Type - Options: Checkbox, Currency, Date, Email, Number, Percent, Phone, Picklist, MultiselectPicklist, Text, TextArea, LongTextArea, Html, Time, Url
|
||||
- `defaultCheckboxValue` (boolean, optional): Default value for checkbox fields
|
||||
- `length` (string, required): Length for numeric/text fields
|
||||
- `decimalPlace` (string, required): Decimal places for numeric fields
|
||||
- `pickListValues` (string, required): Values for picklist fields (separated by new lines)
|
||||
- `visibleLines` (string, required): Visible lines for multiselect/text area fields
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Field description
|
||||
- `helperText` (string, optional): Helper text shown on hover
|
||||
- `defaultFieldValue` (string, optional): Default field value
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_CUSTOM_FIELD_ANY">
|
||||
**Description:** Deploy custom fields for any object type.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** This is a flexible tool for creating custom fields on custom or unknown object types.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Advanced Operations**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_WRITE_SOQL_QUERY">
|
||||
**Description:** Execute custom SOQL queries against your Salesforce data.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `query` (string, required): SOQL Query (e.g., "SELECT Id, Name FROM Account WHERE Name = 'Example'")
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_CREATE_CUSTOM_OBJECT">
|
||||
**Description:** Deploy a new custom object in Salesforce.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `label` (string, required): Object Label for tabs, page layouts, and reports
|
||||
- `pluralLabel` (string, required): Plural Label (e.g., "Accounts")
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): A description of the Custom Object
|
||||
- `recordName` (string, required): Record Name that appears in layouts and searches (e.g., "Account Name")
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SALESFORCE_DESCRIBE_ACTION_SCHEMA">
|
||||
**Description:** Get the expected schema for operations on specific object types.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `recordType` (string, required): Record Type to describe
|
||||
- `operation` (string, required): Operation Type (e.g., "CREATE_RECORD" or "UPDATE_RECORD")
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** Use this function first when working with custom objects to understand their schema before performing operations.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Salesforce Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Salesforce tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Salesforce capabilities
|
||||
salesforce_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="CRM Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage customer relationships and sales processes efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in CRM operations and sales automation.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new lead
|
||||
create_lead_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new lead for John Doe from Example Corp with email john.doe@example.com",
|
||||
agent=salesforce_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Lead created successfully with lead ID"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[salesforce_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_lead_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Salesforce Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Salesforce tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["salesforce_create_record_lead", "salesforce_update_record_opportunity", "salesforce_search_records_contact"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
sales_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Sales Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage leads and opportunities in the sales pipeline",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced sales manager who handles lead qualification and opportunity management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage sales pipeline
|
||||
pipeline_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a qualified lead and convert it to an opportunity with $50,000 value",
|
||||
agent=sales_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Lead created and opportunity established successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[sales_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[pipeline_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Contact and Account Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
account_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Account Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage customer accounts and maintain strong relationships",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that specializes in account management and customer relationship building.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage customer accounts
|
||||
account_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Create a new account for TechCorp Inc.
|
||||
2. Add John Doe as the primary contact for this account
|
||||
3. Create a follow-up task for next week to check on their project status
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=account_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Account, contact, and follow-up task created successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[account_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[account_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced SOQL Queries and Reporting
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_analyst = Agent(
|
||||
role="Sales Data Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Generate insights from Salesforce data using SOQL queries",
|
||||
backstory="An analytical AI that excels at extracting meaningful insights from CRM data.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving SOQL queries and data analysis
|
||||
analysis_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Execute a SOQL query to find all opportunities closing this quarter
|
||||
2. Search for contacts at companies with opportunities over $100K
|
||||
3. Create a summary report of the sales pipeline status
|
||||
4. Update high-value opportunities with next steps
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=data_analyst,
|
||||
expected_output="Comprehensive sales pipeline analysis with actionable insights"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[data_analyst],
|
||||
tasks=[analysis_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This comprehensive documentation covers all the Salesforce tools organized by functionality, making it easy for users to find the specific operations they need for their CRM automation tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Salesforce integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
382
docs/enterprise/integrations/shopify.mdx
Normal file
382
docs/enterprise/integrations/shopify.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,382 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Shopify Integration
|
||||
description: "E-commerce and online store management with Shopify integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "shopify"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage e-commerce operations through Shopify. Handle customers, orders, products, inventory, and store analytics to streamline your online business with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Shopify integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Shopify store with appropriate admin permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Shopify store through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/integrations)
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### **Customer Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_GET_CUSTOMERS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a list of customers from your Shopify store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `customerIds` (string, optional): Comma-separated list of customer IDs to filter by (example: "207119551, 207119552")
|
||||
- `createdAtMin` (string, optional): Only return customers created after this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `createdAtMax` (string, optional): Only return customers created before this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `updatedAtMin` (string, optional): Only return customers updated after this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `updatedAtMax` (string, optional): Only return customers updated before this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `limit` (string, optional): Maximum number of customers to return (defaults to 250)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_SEARCH_CUSTOMERS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for customers using advanced filtering criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `filterFormula` (object, optional): Advanced filter in disjunctive normal form with field-specific operators
|
||||
- `limit` (string, optional): Maximum number of customers to return (defaults to 250)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_CREATE_CUSTOMER">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new customer in your Shopify store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `firstName` (string, required): Customer's first name
|
||||
- `lastName` (string, required): Customer's last name
|
||||
- `email` (string, required): Customer's email address
|
||||
- `company` (string, optional): Company name
|
||||
- `streetAddressLine1` (string, optional): Street address
|
||||
- `streetAddressLine2` (string, optional): Street address line 2
|
||||
- `city` (string, optional): City
|
||||
- `state` (string, optional): State or province code
|
||||
- `country` (string, optional): Country
|
||||
- `zipCode` (string, optional): Zip code
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): Phone number
|
||||
- `tags` (string, optional): Tags as array or comma-separated list
|
||||
- `note` (string, optional): Customer note
|
||||
- `sendEmailInvite` (boolean, optional): Whether to send email invitation
|
||||
- `metafields` (object, optional): Additional metafields in JSON format
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_UPDATE_CUSTOMER">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing customer in your Shopify store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `customerId` (string, required): The ID of the customer to update
|
||||
- `firstName` (string, optional): Customer's first name
|
||||
- `lastName` (string, optional): Customer's last name
|
||||
- `email` (string, optional): Customer's email address
|
||||
- `company` (string, optional): Company name
|
||||
- `streetAddressLine1` (string, optional): Street address
|
||||
- `streetAddressLine2` (string, optional): Street address line 2
|
||||
- `city` (string, optional): City
|
||||
- `state` (string, optional): State or province code
|
||||
- `country` (string, optional): Country
|
||||
- `zipCode` (string, optional): Zip code
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): Phone number
|
||||
- `tags` (string, optional): Tags as array or comma-separated list
|
||||
- `note` (string, optional): Customer note
|
||||
- `sendEmailInvite` (boolean, optional): Whether to send email invitation
|
||||
- `metafields` (object, optional): Additional metafields in JSON format
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Order Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_GET_ORDERS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a list of orders from your Shopify store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `orderIds` (string, optional): Comma-separated list of order IDs to filter by (example: "450789469, 450789470")
|
||||
- `createdAtMin` (string, optional): Only return orders created after this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `createdAtMax` (string, optional): Only return orders created before this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `updatedAtMin` (string, optional): Only return orders updated after this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `updatedAtMax` (string, optional): Only return orders updated before this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `limit` (string, optional): Maximum number of orders to return (defaults to 250)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_CREATE_ORDER">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new order in your Shopify store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `email` (string, required): Customer email address
|
||||
- `lineItems` (object, required): Order line items in JSON format with title, price, quantity, and variant_id
|
||||
- `sendReceipt` (boolean, optional): Whether to send order receipt
|
||||
- `fulfillmentStatus` (string, optional): Fulfillment status - Options: fulfilled, null, partial, restocked
|
||||
- `financialStatus` (string, optional): Financial status - Options: pending, authorized, partially_paid, paid, partially_refunded, refunded, voided
|
||||
- `inventoryBehaviour` (string, optional): Inventory behavior - Options: bypass, decrement_ignoring_policy, decrement_obeying_policy
|
||||
- `note` (string, optional): Order note
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_UPDATE_ORDER">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing order in your Shopify store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `orderId` (string, required): The ID of the order to update
|
||||
- `email` (string, optional): Customer email address
|
||||
- `lineItems` (object, optional): Updated order line items in JSON format
|
||||
- `sendReceipt` (boolean, optional): Whether to send order receipt
|
||||
- `fulfillmentStatus` (string, optional): Fulfillment status - Options: fulfilled, null, partial, restocked
|
||||
- `financialStatus` (string, optional): Financial status - Options: pending, authorized, partially_paid, paid, partially_refunded, refunded, voided
|
||||
- `inventoryBehaviour` (string, optional): Inventory behavior - Options: bypass, decrement_ignoring_policy, decrement_obeying_policy
|
||||
- `note` (string, optional): Order note
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_GET_ABANDONED_CARTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve abandoned carts from your Shopify store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `createdWithInLast` (string, optional): Restrict results to checkouts created within specified time
|
||||
- `createdAfterId` (string, optional): Restrict results to after the specified ID
|
||||
- `status` (string, optional): Show checkouts with given status - Options: open, closed (defaults to open)
|
||||
- `createdAtMin` (string, optional): Only return carts created after this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `createdAtMax` (string, optional): Only return carts created before this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `limit` (string, optional): Maximum number of carts to return (defaults to 250)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Product Management (REST API)**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_GET_PRODUCTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a list of products from your Shopify store using REST API.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `productIds` (string, optional): Comma-separated list of product IDs to filter by (example: "632910392, 632910393")
|
||||
- `title` (string, optional): Filter by product title
|
||||
- `productType` (string, optional): Filter by product type
|
||||
- `vendor` (string, optional): Filter by vendor
|
||||
- `status` (string, optional): Filter by status - Options: active, archived, draft
|
||||
- `createdAtMin` (string, optional): Only return products created after this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `createdAtMax` (string, optional): Only return products created before this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `updatedAtMin` (string, optional): Only return products updated after this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `updatedAtMax` (string, optional): Only return products updated before this date (ISO or Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `limit` (string, optional): Maximum number of products to return (defaults to 250)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_CREATE_PRODUCT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new product in your Shopify store using REST API.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `title` (string, required): Product title
|
||||
- `productType` (string, required): Product type/category
|
||||
- `vendor` (string, required): Product vendor
|
||||
- `productDescription` (string, optional): Product description (accepts plain text or HTML)
|
||||
- `tags` (string, optional): Product tags as array or comma-separated list
|
||||
- `price` (string, optional): Product price
|
||||
- `inventoryPolicy` (string, optional): Inventory policy - Options: deny, continue
|
||||
- `imageUrl` (string, optional): Product image URL
|
||||
- `isPublished` (boolean, optional): Whether product is published
|
||||
- `publishToPointToSale` (boolean, optional): Whether to publish to point of sale
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_UPDATE_PRODUCT">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing product in your Shopify store using REST API.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `productId` (string, required): The ID of the product to update
|
||||
- `title` (string, optional): Product title
|
||||
- `productType` (string, optional): Product type/category
|
||||
- `vendor` (string, optional): Product vendor
|
||||
- `productDescription` (string, optional): Product description (accepts plain text or HTML)
|
||||
- `tags` (string, optional): Product tags as array or comma-separated list
|
||||
- `price` (string, optional): Product price
|
||||
- `inventoryPolicy` (string, optional): Inventory policy - Options: deny, continue
|
||||
- `imageUrl` (string, optional): Product image URL
|
||||
- `isPublished` (boolean, optional): Whether product is published
|
||||
- `publishToPointToSale` (boolean, optional): Whether to publish to point of sale
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Product Management (GraphQL)**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_GET_PRODUCTS_GRAPHQL">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve products using advanced GraphQL filtering capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `productFilterFormula` (object, optional): Advanced filter in disjunctive normal form with support for fields like id, title, vendor, status, handle, tag, created_at, updated_at, published_at
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_CREATE_PRODUCT_GRAPHQL">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new product using GraphQL API with enhanced media support.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `title` (string, required): Product title
|
||||
- `productType` (string, required): Product type/category
|
||||
- `vendor` (string, required): Product vendor
|
||||
- `productDescription` (string, optional): Product description (accepts plain text or HTML)
|
||||
- `tags` (string, optional): Product tags as array or comma-separated list
|
||||
- `media` (object, optional): Media objects with alt text, content type, and source URL
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional product fields like status, requiresSellingPlan, giftCard
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SHOPIFY_UPDATE_PRODUCT_GRAPHQL">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing product using GraphQL API with enhanced media support.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `productId` (string, required): The GraphQL ID of the product to update (e.g., "gid://shopify/Product/913144112")
|
||||
- `title` (string, optional): Product title
|
||||
- `productType` (string, optional): Product type/category
|
||||
- `vendor` (string, optional): Product vendor
|
||||
- `productDescription` (string, optional): Product description (accepts plain text or HTML)
|
||||
- `tags` (string, optional): Product tags as array or comma-separated list
|
||||
- `media` (object, optional): Updated media objects with alt text, content type, and source URL
|
||||
- `additionalFields` (object, optional): Additional product fields like status, requiresSellingPlan, giftCard
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Shopify Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Shopify tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Shopify capabilities
|
||||
shopify_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="E-commerce Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage online store operations and customer relationships efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in e-commerce operations and online store management.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new customer
|
||||
create_customer_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new VIP customer Jane Smith with email jane.smith@example.com and phone +1-555-0123",
|
||||
agent=shopify_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Customer created successfully with customer ID"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[shopify_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_customer_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Shopify Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Shopify tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["shopify_create_customer", "shopify_create_order", "shopify_get_products"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
store_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Store Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage customer orders and product catalog",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced store manager who handles customer relationships and inventory management.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage store operations
|
||||
store_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new customer and process their order for 2 Premium Coffee Mugs",
|
||||
agent=store_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Customer created and order processed successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[store_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[store_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Product Management with GraphQL
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
product_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Product Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage product catalog and inventory with advanced GraphQL capabilities",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that specializes in product management and catalog optimization.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage product catalog
|
||||
catalog_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Create a new product "Premium Coffee Mug" from Coffee Co vendor
|
||||
2. Add high-quality product images and descriptions
|
||||
3. Search for similar products from the same vendor
|
||||
4. Update product tags and pricing strategy
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=product_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Product created and catalog optimized successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[product_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[catalog_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Order and Customer Analytics
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
analytics_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="E-commerce Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze customer behavior and order patterns to optimize store performance",
|
||||
backstory="An analytical AI that excels at extracting insights from e-commerce data.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving multiple operations
|
||||
analytics_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Retrieve recent customer data and order history
|
||||
2. Identify abandoned carts from the last 7 days
|
||||
3. Analyze product performance and inventory levels
|
||||
4. Generate recommendations for customer retention
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=analytics_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Comprehensive e-commerce analytics report with actionable insights"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[analytics_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[analytics_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Shopify integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
293
docs/enterprise/integrations/slack.mdx
Normal file
293
docs/enterprise/integrations/slack.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,293 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Slack Integration
|
||||
description: "Team communication and collaboration with Slack integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "slack"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage team communication through Slack. Send messages, search conversations, manage channels, and coordinate team activities to streamline your collaboration workflows with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Slack integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Slack workspace with appropriate permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Slack workspace through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/integrations)
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### **User Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SLACK_LIST_MEMBERS">
|
||||
**Description:** List all members in a Slack channel.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- No parameters required - retrieves all channel members
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SLACK_GET_USER_BY_EMAIL">
|
||||
**Description:** Find a user in your Slack workspace by their email address.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `email` (string, required): The email address of a user in the workspace
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SLACK_GET_USERS_BY_NAME">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for users by their name or display name.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `name` (string, required): User's real name to search for
|
||||
- `displayName` (string, required): User's display name to search for
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings
|
||||
- `pageCursor` (string, optional): Page cursor for pagination
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Channel Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SLACK_LIST_CHANNELS">
|
||||
**Description:** List all channels in your Slack workspace.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- No parameters required - retrieves all accessible channels
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Messaging**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SLACK_SEND_MESSAGE">
|
||||
**Description:** Send a message to a Slack channel.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `channel` (string, required): Channel name or ID - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a channel, or enter a channel name to create a new channel
|
||||
- `message` (string, required): The message text to send
|
||||
- `botName` (string, required): The name of the bot that sends this message
|
||||
- `botIcon` (string, required): Bot icon - Can be either an image URL or an emoji (e.g., ":dog:")
|
||||
- `blocks` (object, optional): Slack Block Kit JSON for rich message formatting with attachments and interactive elements
|
||||
- `authenticatedUser` (boolean, optional): If true, message appears to come from your authenticated Slack user instead of the application (defaults to false)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="SLACK_SEND_DIRECT_MESSAGE">
|
||||
**Description:** Send a direct message to a specific user in Slack.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `memberId` (string, required): Recipient user ID - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a workspace member
|
||||
- `message` (string, required): The message text to send
|
||||
- `botName` (string, required): The name of the bot that sends this message
|
||||
- `botIcon` (string, required): Bot icon - Can be either an image URL or an emoji (e.g., ":dog:")
|
||||
- `blocks` (object, optional): Slack Block Kit JSON for rich message formatting with attachments and interactive elements
|
||||
- `authenticatedUser` (boolean, optional): If true, message appears to come from your authenticated Slack user instead of the application (defaults to false)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Search & Discovery**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="SLACK_SEARCH_MESSAGES">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for messages across your Slack workspace.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `query` (string, required): Search query using Slack search syntax to find messages that match specified criteria
|
||||
|
||||
**Search Query Examples:**
|
||||
- `"project update"` - Search for messages containing "project update"
|
||||
- `from:@john in:#general` - Search for messages from John in the #general channel
|
||||
- `has:link after:2023-01-01` - Search for messages with links after January 1, 2023
|
||||
- `in:@channel before:yesterday` - Search for messages in a specific channel before yesterday
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Block Kit Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Slack's Block Kit allows you to create rich, interactive messages. Here are some examples of how to use the `blocks` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
### Simple Text with Attachment
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "I am a test message",
|
||||
"attachments": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "And here's an attachment!"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rich Formatting with Sections
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "*Project Update*\nStatus: ✅ Complete"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "divider"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "plain_text",
|
||||
"text": "All tasks have been completed successfully."
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Slack Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Slack tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Slack capabilities
|
||||
slack_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Team Communication Manager",
|
||||
goal="Facilitate team communication and coordinate collaboration efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in team communication and workspace coordination.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to send project updates
|
||||
update_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Send a project status update to the #general channel with current progress",
|
||||
agent=slack_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Project update message sent successfully to team channel"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[slack_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[update_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Slack Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Slack tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["slack_send_message", "slack_send_direct_message", "slack_search_messages"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
communication_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Communication Coordinator",
|
||||
goal="Manage team communications and ensure important messages reach the right people",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced communication coordinator who handles team messaging and notifications.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to coordinate team communication
|
||||
coordination_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Send task completion notifications to team members and update project channels",
|
||||
agent=communication_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Team notifications sent and project channels updated successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[communication_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[coordination_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Messaging with Block Kit
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
notification_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Notification Manager",
|
||||
goal="Create rich, interactive notifications and manage workspace communication",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that specializes in creating engaging team notifications and updates.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to send rich notifications
|
||||
notification_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Send a formatted project completion message to #general with progress charts
|
||||
2. Send direct messages to team leads with task summaries
|
||||
3. Create interactive notification with action buttons for team feedback
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=notification_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Rich notifications sent with interactive elements and formatted content"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[notification_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[notification_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Message Search and Analytics
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
analytics_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Communication Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze team communication patterns and extract insights from conversations",
|
||||
backstory="An analytical AI that excels at understanding team dynamics through communication data.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving search and analysis
|
||||
analysis_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for recent project-related messages across all channels
|
||||
2. Find users by email to identify team members
|
||||
3. Analyze communication patterns and response times
|
||||
4. Generate weekly team communication summary
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=analytics_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Comprehensive communication analysis with team insights and recommendations"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[analytics_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[analysis_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Contact Support
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Need Help?" icon="headset" href="mailto:support@crewai.com">
|
||||
Contact our support team for assistance with Slack integration setup or troubleshooting.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
305
docs/enterprise/integrations/stripe.mdx
Normal file
305
docs/enterprise/integrations/stripe.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Stripe Integration
|
||||
description: "Payment processing and subscription management with Stripe integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "stripe"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage payments, subscriptions, and customer billing through Stripe. Handle customer data, process subscriptions, manage products, and track financial transactions to streamline your payment workflows with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Stripe integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Stripe account with appropriate API permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Stripe account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/integrations)
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### **Customer Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_CREATE_CUSTOMER">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new customer in your Stripe account.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `emailCreateCustomer` (string, required): Customer's email address
|
||||
- `name` (string, optional): Customer's full name
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Customer description for internal reference
|
||||
- `metadataCreateCustomer` (object, optional): Additional metadata as key-value pairs (e.g., `{"field1": 1, "field2": 2}`)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_GET_CUSTOMER_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a specific customer by their Stripe customer ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `idGetCustomer` (string, required): The Stripe customer ID to retrieve
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_GET_CUSTOMERS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a list of customers with optional filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `emailGetCustomers` (string, optional): Filter customers by email address
|
||||
- `createdAfter` (string, optional): Filter customers created after this date (Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `createdBefore` (string, optional): Filter customers created before this date (Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `limitGetCustomers` (string, optional): Maximum number of customers to return (defaults to 10)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_UPDATE_CUSTOMER">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing customer's information.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `customerId` (string, required): The ID of the customer to update
|
||||
- `emailUpdateCustomer` (string, optional): Updated email address
|
||||
- `name` (string, optional): Updated customer name
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Updated customer description
|
||||
- `metadataUpdateCustomer` (object, optional): Updated metadata as key-value pairs
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Subscription Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_CREATE_SUBSCRIPTION">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new subscription for a customer.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `customerIdCreateSubscription` (string, required): The customer ID for whom the subscription will be created
|
||||
- `plan` (string, required): The plan ID for the subscription - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select a plan
|
||||
- `metadataCreateSubscription` (object, optional): Additional metadata for the subscription
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_GET_SUBSCRIPTIONS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve subscriptions with optional filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `customerIdGetSubscriptions` (string, optional): Filter subscriptions by customer ID
|
||||
- `subscriptionStatus` (string, optional): Filter by subscription status - Options: incomplete, incomplete_expired, trialing, active, past_due, canceled, unpaid
|
||||
- `limitGetSubscriptions` (string, optional): Maximum number of subscriptions to return (defaults to 10)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Product Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_CREATE_PRODUCT">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new product in your Stripe catalog.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `productName` (string, required): The product name
|
||||
- `description` (string, optional): Product description
|
||||
- `metadataProduct` (object, optional): Additional product metadata as key-value pairs
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_GET_PRODUCT_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a specific product by its Stripe product ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `productId` (string, required): The Stripe product ID to retrieve
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_GET_PRODUCTS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a list of products with optional filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `createdAfter` (string, optional): Filter products created after this date (Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `createdBefore` (string, optional): Filter products created before this date (Unix timestamp)
|
||||
- `limitGetProducts` (string, optional): Maximum number of products to return (defaults to 10)
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Financial Operations**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_GET_BALANCE_TRANSACTIONS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve balance transactions from your Stripe account.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `balanceTransactionType` (string, optional): Filter by transaction type - Options: charge, refund, payment, payment_refund
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings
|
||||
- `pageCursor` (string, optional): Page cursor for pagination
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="STRIPE_GET_PLANS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve subscription plans from your Stripe account.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `isPlanActive` (boolean, optional): Filter by plan status - true for active plans, false for inactive plans
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings
|
||||
- `pageCursor` (string, optional): Page cursor for pagination
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Stripe Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Stripe tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Stripe capabilities
|
||||
stripe_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Payment Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage customer payments, subscriptions, and billing operations efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in payment processing and subscription management.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new customer
|
||||
create_customer_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new premium customer John Doe with email john.doe@example.com",
|
||||
agent=stripe_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Customer created successfully with customer ID"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[stripe_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_customer_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Stripe Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Stripe tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["stripe_create_customer", "stripe_create_subscription", "stripe_get_balance_transactions"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
billing_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Billing Manager",
|
||||
goal="Handle customer billing, subscriptions, and payment processing",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced billing manager who handles subscription lifecycle and payment operations.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage billing operations
|
||||
billing_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a new customer and set up their premium subscription plan",
|
||||
agent=billing_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Customer created and subscription activated successfully"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[billing_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[billing_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Subscription Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
subscription_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Subscription Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage customer subscriptions and optimize recurring revenue",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that specializes in subscription lifecycle management and customer retention.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage subscription operations
|
||||
subscription_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Create a new product "Premium Service Plan" with advanced features
|
||||
2. Set up subscription plans with different tiers
|
||||
3. Create customers and assign them to appropriate plans
|
||||
4. Monitor subscription status and handle billing issues
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=subscription_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Subscription management system configured with customers and active plans"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[subscription_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[subscription_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Financial Analytics and Reporting
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
financial_analyst = Agent(
|
||||
role="Financial Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze payment data and generate financial insights",
|
||||
backstory="An analytical AI that excels at extracting insights from payment and subscription data.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving financial analysis
|
||||
analytics_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Retrieve balance transactions for the current month
|
||||
2. Analyze customer payment patterns and subscription trends
|
||||
3. Identify high-value customers and subscription performance
|
||||
4. Generate monthly financial performance report
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=financial_analyst,
|
||||
expected_output="Comprehensive financial analysis with payment insights and recommendations"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[financial_analyst],
|
||||
tasks=[analytics_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Subscription Status Reference
|
||||
|
||||
Understanding subscription statuses:
|
||||
|
||||
- **incomplete** - Subscription requires payment method or payment confirmation
|
||||
- **incomplete_expired** - Subscription expired before payment was confirmed
|
||||
- **trialing** - Subscription is in trial period
|
||||
- **active** - Subscription is active and current
|
||||
- **past_due** - Payment failed but subscription is still active
|
||||
- **canceled** - Subscription has been canceled
|
||||
- **unpaid** - Payment failed and subscription is no longer active
|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Metadata allows you to store additional information about customers, subscriptions, and products:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"customer_segment": "enterprise",
|
||||
"acquisition_source": "google_ads",
|
||||
"lifetime_value": "high",
|
||||
"custom_field_1": "value1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This integration enables comprehensive payment and subscription management automation, allowing your AI agents to handle billing operations seamlessly within your Stripe ecosystem.
|
||||
343
docs/enterprise/integrations/zendesk.mdx
Normal file
343
docs/enterprise/integrations/zendesk.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Zendesk Integration
|
||||
description: "Customer support and helpdesk management with Zendesk integration for CrewAI."
|
||||
icon: "headset"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Enable your agents to manage customer support operations through Zendesk. Create and update tickets, manage users, track support metrics, and streamline your customer service workflows with AI-powered automation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the Zendesk integration, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- A [CrewAI Enterprise](https://app.crewai.com) account with an active subscription
|
||||
- A Zendesk account with appropriate API permissions
|
||||
- Connected your Zendesk account through the [Integrations page](https://app.crewai.com/integrations)
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### **Ticket Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_CREATE_TICKET">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new support ticket in Zendesk.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `ticketSubject` (string, required): Ticket subject line (e.g., "Help, my printer is on fire!")
|
||||
- `ticketDescription` (string, required): First comment that appears on the ticket (e.g., "The smoke is very colorful.")
|
||||
- `requesterName` (string, required): Name of the user requesting support (e.g., "Jane Customer")
|
||||
- `requesterEmail` (string, required): Email of the user requesting support (e.g., "jane@example.com")
|
||||
- `assigneeId` (string, optional): Zendesk Agent ID assigned to this ticket - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings to allow users to select an assignee
|
||||
- `ticketType` (string, optional): Ticket type - Options: problem, incident, question, task
|
||||
- `ticketPriority` (string, optional): Priority level - Options: urgent, high, normal, low
|
||||
- `ticketStatus` (string, optional): Ticket status - Options: new, open, pending, hold, solved, closed
|
||||
- `ticketDueAt` (string, optional): Due date for task-type tickets (ISO 8601 timestamp)
|
||||
- `ticketTags` (string, optional): Array of tags to apply (e.g., `["enterprise", "other_tag"]`)
|
||||
- `ticketExternalId` (string, optional): External ID to link tickets to local records
|
||||
- `ticketCustomFields` (object, optional): Custom field values in JSON format
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_UPDATE_TICKET">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing support ticket in Zendesk.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `ticketId` (string, required): ID of the ticket to update (e.g., "35436")
|
||||
- `ticketSubject` (string, optional): Updated ticket subject
|
||||
- `requesterName` (string, required): Name of the user who requested this ticket
|
||||
- `requesterEmail` (string, required): Email of the user who requested this ticket
|
||||
- `assigneeId` (string, optional): Updated assignee ID - Use Connect Portal Workflow Settings
|
||||
- `ticketType` (string, optional): Updated ticket type - Options: problem, incident, question, task
|
||||
- `ticketPriority` (string, optional): Updated priority - Options: urgent, high, normal, low
|
||||
- `ticketStatus` (string, optional): Updated status - Options: new, open, pending, hold, solved, closed
|
||||
- `ticketDueAt` (string, optional): Updated due date (ISO 8601 timestamp)
|
||||
- `ticketTags` (string, optional): Updated tags array
|
||||
- `ticketExternalId` (string, optional): Updated external ID
|
||||
- `ticketCustomFields` (object, optional): Updated custom field values
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_GET_TICKET_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a specific ticket by its ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `ticketId` (string, required): The ticket ID to retrieve (e.g., "35436")
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_ADD_COMMENT_TO_TICKET">
|
||||
**Description:** Add a comment or internal note to an existing ticket.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `ticketId` (string, required): ID of the ticket to add comment to (e.g., "35436")
|
||||
- `commentBody` (string, required): Comment message (accepts plain text or HTML, e.g., "Thanks for your help!")
|
||||
- `isInternalNote` (boolean, optional): Set to true for internal notes instead of public replies (defaults to false)
|
||||
- `isPublic` (boolean, optional): True for public comments, false for internal notes
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_SEARCH_TICKETS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for tickets using various filters and criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `ticketSubject` (string, optional): Filter by text in ticket subject
|
||||
- `ticketDescription` (string, optional): Filter by text in ticket description and comments
|
||||
- `ticketStatus` (string, optional): Filter by status - Options: new, open, pending, hold, solved, closed
|
||||
- `ticketType` (string, optional): Filter by type - Options: problem, incident, question, task, no_type
|
||||
- `ticketPriority` (string, optional): Filter by priority - Options: urgent, high, normal, low, no_priority
|
||||
- `requesterId` (string, optional): Filter by requester user ID
|
||||
- `assigneeId` (string, optional): Filter by assigned agent ID
|
||||
- `recipientEmail` (string, optional): Filter by original recipient email address
|
||||
- `ticketTags` (string, optional): Filter by ticket tags
|
||||
- `ticketExternalId` (string, optional): Filter by external ID
|
||||
- `createdDate` (object, optional): Filter by creation date with operator (EQUALS, LESS_THAN_EQUALS, GREATER_THAN_EQUALS) and value
|
||||
- `updatedDate` (object, optional): Filter by update date with operator and value
|
||||
- `dueDate` (object, optional): Filter by due date with operator and value
|
||||
- `sort_by` (string, optional): Sort field - Options: created_at, updated_at, priority, status, ticket_type
|
||||
- `sort_order` (string, optional): Sort direction - Options: asc, desc
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **User Management**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_CREATE_USER">
|
||||
**Description:** Create a new user in Zendesk.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `name` (string, required): User's full name
|
||||
- `email` (string, optional): User's email address (e.g., "jane@example.com")
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): User's phone number
|
||||
- `role` (string, optional): User role - Options: admin, agent, end-user
|
||||
- `externalId` (string, optional): Unique identifier from another system
|
||||
- `details` (string, optional): Additional user details
|
||||
- `notes` (string, optional): Internal notes about the user
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_UPDATE_USER">
|
||||
**Description:** Update an existing user's information.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `userId` (string, required): ID of the user to update
|
||||
- `name` (string, optional): Updated user name
|
||||
- `email` (string, optional): Updated email (adds as secondary email on update)
|
||||
- `phone` (string, optional): Updated phone number
|
||||
- `role` (string, optional): Updated role - Options: admin, agent, end-user
|
||||
- `externalId` (string, optional): Updated external ID
|
||||
- `details` (string, optional): Updated user details
|
||||
- `notes` (string, optional): Updated internal notes
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_GET_USER_BY_ID">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve a specific user by their ID.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `userId` (string, required): The user ID to retrieve
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_SEARCH_USERS">
|
||||
**Description:** Search for users using various criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `name` (string, optional): Filter by user name
|
||||
- `email` (string, optional): Filter by user email (e.g., "jane@example.com")
|
||||
- `role` (string, optional): Filter by role - Options: admin, agent, end-user
|
||||
- `externalId` (string, optional): Filter by external ID
|
||||
- `sort_by` (string, optional): Sort field - Options: created_at, updated_at
|
||||
- `sort_order` (string, optional): Sort direction - Options: asc, desc
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### **Administrative Tools**
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_GET_TICKET_FIELDS">
|
||||
**Description:** Retrieve all standard and custom fields available for tickets.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings
|
||||
- `pageCursor` (string, optional): Page cursor for pagination
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="ZENDESK_GET_TICKET_AUDITS">
|
||||
**Description:** Get audit records (read-only history) for tickets.
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters:**
|
||||
- `ticketId` (string, optional): Get audits for specific ticket (if empty, retrieves audits for all non-archived tickets, e.g., "1234")
|
||||
- `paginationParameters` (object, optional): Pagination settings
|
||||
- `pageCursor` (string, optional): Page cursor for pagination
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom Fields
|
||||
|
||||
Custom fields allow you to store additional information specific to your organization:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{ "id": 27642, "value": "745" },
|
||||
{ "id": 27648, "value": "yes" }
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Ticket Priority Levels
|
||||
|
||||
Understanding priority levels:
|
||||
|
||||
- **urgent** - Critical issues requiring immediate attention
|
||||
- **high** - Important issues that should be addressed quickly
|
||||
- **normal** - Standard priority for most tickets
|
||||
- **low** - Minor issues that can be addressed when convenient
|
||||
|
||||
## Ticket Status Workflow
|
||||
|
||||
Standard ticket status progression:
|
||||
|
||||
- **new** - Recently created, not yet assigned
|
||||
- **open** - Actively being worked on
|
||||
- **pending** - Waiting for customer response or external action
|
||||
- **hold** - Temporarily paused
|
||||
- **solved** - Issue resolved, awaiting customer confirmation
|
||||
- **closed** - Ticket completed and closed
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Zendesk Agent Setup
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get enterprise tools (Zendesk tools will be included)
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an agent with Zendesk capabilities
|
||||
zendesk_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Support Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage customer support tickets and provide excellent customer service",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in customer support operations and ticket management.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to create a new support ticket
|
||||
create_ticket_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a high-priority support ticket for John Smith who is unable to access his account after password reset",
|
||||
agent=zendesk_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Support ticket created successfully with ticket ID"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the task
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[zendesk_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[create_ticket_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering Specific Zendesk Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
# Get only specific Zendesk tools
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token",
|
||||
actions_list=["zendesk_create_ticket", "zendesk_update_ticket", "zendesk_add_comment_to_ticket"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
support_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Customer Support Agent",
|
||||
goal="Handle customer inquiries and resolve support issues efficiently",
|
||||
backstory="An experienced support agent who specializes in ticket resolution and customer communication.",
|
||||
tools=enterprise_tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage support workflow
|
||||
support_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Create a ticket for login issues, add troubleshooting comments, and update status to resolved",
|
||||
agent=support_agent,
|
||||
expected_output="Support ticket managed through complete resolution workflow"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[support_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[support_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Ticket Management
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
ticket_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Ticket Manager",
|
||||
goal="Manage support ticket workflows and ensure timely resolution",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant that specializes in support ticket triage and workflow optimization.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Task to manage ticket lifecycle
|
||||
ticket_workflow = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Create a new support ticket for account access issues
|
||||
2. Add internal notes with troubleshooting steps
|
||||
3. Update ticket priority based on customer tier
|
||||
4. Add resolution comments and close the ticket
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=ticket_manager,
|
||||
expected_output="Complete ticket lifecycle managed from creation to resolution"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[ticket_manager],
|
||||
tasks=[ticket_workflow]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Support Analytics and Reporting
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import CrewaiEnterpriseTools
|
||||
|
||||
enterprise_tools = CrewaiEnterpriseTools(
|
||||
enterprise_token="your_enterprise_token"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
support_analyst = Agent(
|
||||
role="Support Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze support metrics and generate insights for team performance",
|
||||
backstory="An analytical AI that excels at extracting insights from support data and ticket patterns.",
|
||||
tools=[enterprise_tools]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Complex task involving analytics and reporting
|
||||
analytics_task = Task(
|
||||
description="""
|
||||
1. Search for all open tickets from the last 30 days
|
||||
2. Analyze ticket resolution times and customer satisfaction
|
||||
3. Identify common issues and support patterns
|
||||
4. Generate weekly support performance report
|
||||
""",
|
||||
agent=support_analyst,
|
||||
expected_output="Comprehensive support analytics report with performance insights and recommendations"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[support_analyst],
|
||||
tasks=[analytics_task]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew.kickoff()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -277,22 +277,23 @@ This pattern allows you to combine direct data passing with state updates for ma
|
||||
|
||||
One of CrewAI's most powerful features is the ability to persist flow state across executions. This enables workflows that can be paused, resumed, and even recovered after failures.
|
||||
|
||||
### The @persist Decorator
|
||||
### The @persist() Decorator
|
||||
|
||||
The `@persist` decorator automates state persistence, saving your flow's state at key points in execution.
|
||||
The `@persist()` decorator automates state persistence, saving your flow's state at key points in execution.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Class-Level Persistence
|
||||
|
||||
When applied at the class level, `@persist` saves state after every method execution:
|
||||
When applied at the class level, `@persist()` saves state after every method execution:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai.flow.flow import Flow, listen, persist, start
|
||||
from crewai.flow.flow import Flow, listen, start
|
||||
from crewai.flow.persistence import persist
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
class CounterState(BaseModel):
|
||||
value: int = 0
|
||||
|
||||
@persist # Apply to the entire flow class
|
||||
@persist() # Apply to the entire flow class
|
||||
class PersistentCounterFlow(Flow[CounterState]):
|
||||
@start()
|
||||
def increment(self):
|
||||
@@ -319,10 +320,11 @@ print(f"Second run result: {result2}") # Will be higher due to persisted state
|
||||
|
||||
#### Method-Level Persistence
|
||||
|
||||
For more granular control, you can apply `@persist` to specific methods:
|
||||
For more granular control, you can apply `@persist()` to specific methods:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai.flow.flow import Flow, listen, persist, start
|
||||
from crewai.flow.flow import Flow, listen, start
|
||||
from crewai.flow.persistence import persist
|
||||
|
||||
class SelectivePersistFlow(Flow):
|
||||
@start()
|
||||
@@ -330,7 +332,7 @@ class SelectivePersistFlow(Flow):
|
||||
self.state["count"] = 1
|
||||
return "First step"
|
||||
|
||||
@persist # Only persist after this method
|
||||
@persist() # Only persist after this method
|
||||
@listen(first_step)
|
||||
def important_step(self, prev_result):
|
||||
self.state["count"] += 1
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/crew_connectors.png
Normal file
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/crew_connectors.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.2 MiB |
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/enterprise-testing.png
Normal file
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/enterprise-testing.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 288 KiB |
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/enterprise_action_auth_token.png
Normal file
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/enterprise_action_auth_token.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 54 KiB |
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/filtering_enterprise_action_tools.png
Normal file
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/filtering_enterprise_action_tools.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 362 KiB |
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/user_bearer_token.png
Normal file
BIN
docs/images/enterprise/user_bearer_token.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 49 KiB |
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Watch this video tutorial for a step-by-step demonstration of the installation p
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
**Python Version Requirements**
|
||||
|
||||
CrewAI requires `Python >=3.10 and <3.13`. Here's how to check your version:
|
||||
CrewAI requires `Python >=3.10 and <3.14`. Here's how to check your version:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,6 +108,7 @@ crew_2 = Crew(agents=[coding_agent], tasks=[task_2])
|
||||
|
||||
# Async function to kickoff multiple crews asynchronously and wait for all to finish
|
||||
async def async_multiple_crews():
|
||||
# Create coroutines for concurrent execution
|
||||
result_1 = crew_1.kickoff_async(inputs={"ages": [25, 30, 35, 40, 45]})
|
||||
result_2 = crew_2.kickoff_async(inputs={"ages": [20, 22, 24, 28, 30]})
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ icon: brain-circuit
|
||||
CrewAI uses LiteLLM to connect to a wide variety of Language Models (LLMs). This integration provides extensive versatility, allowing you to use models from numerous providers with a simple, unified interface.
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
By default, CrewAI uses the `gpt-4o-mini` model. This is determined by the `OPENAI_MODEL_NAME` environment variable, which defaults to "gpt-4o-mini" if not set.
|
||||
By default, CrewAI uses the `gpt-4o-mini` model. This is determined by the `OPENAI_MODEL_NAME` environment variable, which defaults to "gpt-4o-mini" if not set.
|
||||
You can easily configure your agents to use a different model or provider as described in this guide.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -117,18 +117,27 @@ You can connect to OpenAI-compatible LLMs using either environment variables or
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Using Environment Variables">
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
```python Generic
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-api-key"
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = "https://api.your-provider.com/v1"
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_MODEL_NAME"] = "your-model-name"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python Google
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
# Example using Gemini's OpenAI-compatible API.
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-gemini-key" # Should start with AIza...
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/openai/"
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_MODEL_NAME"] = "openai/gemini-2.0-flash" # Add your Gemini model here, under openai/
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="Using LLM Class Attributes">
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
```python Generic
|
||||
llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="custom-model-name",
|
||||
api_key="your-api-key",
|
||||
@@ -136,6 +145,16 @@ You can connect to OpenAI-compatible LLMs using either environment variables or
|
||||
)
|
||||
agent = Agent(llm=llm, ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python Google
|
||||
# Example using Gemini's OpenAI-compatible API
|
||||
llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="openai/gemini-2.0-flash",
|
||||
base_url="https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/openai/",
|
||||
api_key="your-gemini-key", # Should start with AIza...
|
||||
)
|
||||
agent = Agent(llm=llm, ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
@@ -169,7 +188,7 @@ For local models like those provided by Ollama:
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the base API URL for any LLM provider by setting the `base_url` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
```python Code
|
||||
llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="custom-model-name",
|
||||
base_url="https://api.your-provider.com/v1",
|
||||
|
||||
729
docs/learn/llm-selection-guide.mdx
Normal file
729
docs/learn/llm-selection-guide.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,729 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Strategic LLM Selection Guide'
|
||||
description: 'Strategic framework for choosing the right LLM for your CrewAI AI agents and writing effective task and agent definitions'
|
||||
icon: 'brain-circuit'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## The CrewAI Approach to LLM Selection
|
||||
|
||||
Rather than prescriptive model recommendations, we advocate for a **thinking framework** that helps you make informed decisions based on your specific use case, constraints, and requirements. The LLM landscape evolves rapidly, with new models emerging regularly and existing ones being updated frequently. What matters most is developing a systematic approach to evaluation that remains relevant regardless of which specific models are available.
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
This guide focuses on strategic thinking rather than specific model recommendations, as the LLM landscape evolves rapidly.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Decision Framework
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="Analyze Your Tasks">
|
||||
Begin by deeply understanding what your tasks actually require. Consider the cognitive complexity involved, the depth of reasoning needed, the format of expected outputs, and the amount of context the model will need to process. This foundational analysis will guide every subsequent decision.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Map Model Capabilities">
|
||||
Once you understand your requirements, map them to model strengths. Different model families excel at different types of work; some are optimized for reasoning and analysis, others for creativity and content generation, and others for speed and efficiency.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Consider Constraints">
|
||||
Factor in your real-world operational constraints including budget limitations, latency requirements, data privacy needs, and infrastructure capabilities. The theoretically best model may not be the practically best choice for your situation.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Test and Iterate">
|
||||
Start with reliable, well-understood models and optimize based on actual performance in your specific use case. Real-world results often differ from theoretical benchmarks, so empirical testing is crucial.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
## Core Selection Framework
|
||||
|
||||
### a. Task-First Thinking
|
||||
|
||||
The most critical step in LLM selection is understanding what your task actually demands. Too often, teams select models based on general reputation or benchmark scores without carefully analyzing their specific requirements. This approach leads to either over-engineering simple tasks with expensive, complex models, or under-powering sophisticated work with models that lack the necessary capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Reasoning Complexity">
|
||||
- **Simple Tasks** represent the majority of everyday AI work and include basic instruction following, straightforward data processing, and simple formatting operations. These tasks typically have clear inputs and outputs with minimal ambiguity. The cognitive load is low, and the model primarily needs to follow explicit instructions rather than engage in complex reasoning.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Complex Tasks** require multi-step reasoning, strategic thinking, and the ability to handle ambiguous or incomplete information. These might involve analyzing multiple data sources, developing comprehensive strategies, or solving problems that require breaking down into smaller components. The model needs to maintain context across multiple reasoning steps and often must make inferences that aren't explicitly stated.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Creative Tasks** demand a different type of cognitive capability focused on generating novel, engaging, and contextually appropriate content. This includes storytelling, marketing copy creation, and creative problem-solving. The model needs to understand nuance, tone, and audience while producing content that feels authentic and engaging rather than formulaic.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Output Requirements">
|
||||
- **Structured Data** tasks require precision and consistency in format adherence. When working with JSON, XML, or database formats, the model must reliably produce syntactically correct output that can be programmatically processed. These tasks often have strict validation requirements and little tolerance for format errors, making reliability more important than creativity.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Creative Content** outputs demand a balance of technical competence and creative flair. The model needs to understand audience, tone, and brand voice while producing content that engages readers and achieves specific communication goals. Quality here is often subjective and requires models that can adapt their writing style to different contexts and purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Technical Content** sits between structured data and creative content, requiring both precision and clarity. Documentation, code generation, and technical analysis need to be accurate and comprehensive while remaining accessible to the intended audience. The model must understand complex technical concepts and communicate them effectively.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Context Needs">
|
||||
- **Short Context** scenarios involve focused, immediate tasks where the model needs to process limited information quickly. These are often transactional interactions where speed and efficiency matter more than deep understanding. The model doesn't need to maintain extensive conversation history or process large documents.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Long Context** requirements emerge when working with substantial documents, extended conversations, or complex multi-part tasks. The model needs to maintain coherence across thousands of tokens while referencing earlier information accurately. This capability becomes crucial for document analysis, comprehensive research, and sophisticated dialogue systems.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Very Long Context** scenarios push the boundaries of what's currently possible, involving massive document processing, extensive research synthesis, or complex multi-session interactions. These use cases require models specifically designed for extended context handling and often involve trade-offs between context length and processing speed.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
### b. Model Capability Mapping
|
||||
|
||||
Understanding model capabilities requires looking beyond marketing claims and benchmark scores to understand the fundamental strengths and limitations of different model architectures and training approaches.
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="Reasoning Models" icon="brain">
|
||||
Reasoning models represent a specialized category designed specifically for complex, multi-step thinking tasks. These models excel when problems require careful analysis, strategic planning, or systematic problem decomposition. They typically employ techniques like chain-of-thought reasoning or tree-of-thought processing to work through complex problems step by step.
|
||||
|
||||
The strength of reasoning models lies in their ability to maintain logical consistency across extended reasoning chains and to break down complex problems into manageable components. They're particularly valuable for strategic planning, complex analysis, and situations where the quality of reasoning matters more than speed of response.
|
||||
|
||||
However, reasoning models often come with trade-offs in terms of speed and cost. They may also be less suitable for creative tasks or simple operations where their sophisticated reasoning capabilities aren't needed. Consider these models when your tasks involve genuine complexity that benefits from systematic, step-by-step analysis.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="General Purpose Models" icon="microchip">
|
||||
General purpose models offer the most balanced approach to LLM selection, providing solid performance across a wide range of tasks without extreme specialization in any particular area. These models are trained on diverse datasets and optimized for versatility rather than peak performance in specific domains.
|
||||
|
||||
The primary advantage of general purpose models is their reliability and predictability across different types of work. They handle most standard business tasks competently, from research and analysis to content creation and data processing. This makes them excellent choices for teams that need consistent performance across varied workflows.
|
||||
|
||||
While general purpose models may not achieve the peak performance of specialized alternatives in specific domains, they offer operational simplicity and reduced complexity in model management. They're often the best starting point for new projects, allowing teams to understand their specific needs before potentially optimizing with more specialized models.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Fast & Efficient Models" icon="bolt">
|
||||
Fast and efficient models prioritize speed, cost-effectiveness, and resource efficiency over sophisticated reasoning capabilities. These models are optimized for high-throughput scenarios where quick responses and low operational costs are more important than nuanced understanding or complex reasoning.
|
||||
|
||||
These models excel in scenarios involving routine operations, simple data processing, function calling, and high-volume tasks where the cognitive requirements are relatively straightforward. They're particularly valuable for applications that need to process many requests quickly or operate within tight budget constraints.
|
||||
|
||||
The key consideration with efficient models is ensuring that their capabilities align with your task requirements. While they can handle many routine operations effectively, they may struggle with tasks requiring nuanced understanding, complex reasoning, or sophisticated content generation. They're best used for well-defined, routine operations where speed and cost matter more than sophistication.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Creative Models" icon="pen">
|
||||
Creative models are specifically optimized for content generation, writing quality, and creative thinking tasks. These models typically excel at understanding nuance, tone, and style while producing engaging, contextually appropriate content that feels natural and authentic.
|
||||
|
||||
The strength of creative models lies in their ability to adapt writing style to different audiences, maintain consistent voice and tone, and generate content that engages readers effectively. They often perform better on tasks involving storytelling, marketing copy, brand communications, and other content where creativity and engagement are primary goals.
|
||||
|
||||
When selecting creative models, consider not just their ability to generate text, but their understanding of audience, context, and purpose. The best creative models can adapt their output to match specific brand voices, target different audience segments, and maintain consistency across extended content pieces.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Open Source Models" icon="code">
|
||||
Open source models offer unique advantages in terms of cost control, customization potential, data privacy, and deployment flexibility. These models can be run locally or on private infrastructure, providing complete control over data handling and model behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
The primary benefits of open source models include elimination of per-token costs, ability to fine-tune for specific use cases, complete data privacy, and independence from external API providers. They're particularly valuable for organizations with strict data privacy requirements, budget constraints, or specific customization needs.
|
||||
|
||||
However, open source models require more technical expertise to deploy and maintain effectively. Teams need to consider infrastructure costs, model management complexity, and the ongoing effort required to keep models updated and optimized. The total cost of ownership may be higher than cloud-based alternatives when factoring in technical overhead.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Strategic Configuration Patterns
|
||||
|
||||
### a. Multi-Model Approach
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Use different models for different purposes within the same crew to optimize both performance and cost.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The most sophisticated CrewAI implementations often employ multiple models strategically, assigning different models to different agents based on their specific roles and requirements. This approach allows teams to optimize for both performance and cost by using the most appropriate model for each type of work.
|
||||
|
||||
Planning agents benefit from reasoning models that can handle complex strategic thinking and multi-step analysis. These agents often serve as the "brain" of the operation, developing strategies and coordinating other agents' work. Content agents, on the other hand, perform best with creative models that excel at writing quality and audience engagement. Processing agents handling routine operations can use efficient models that prioritize speed and cost-effectiveness.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example: Research and Analysis Crew**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, LLM
|
||||
|
||||
# High-capability reasoning model for strategic planning
|
||||
manager_llm = LLM(model="gemini-2.5-flash-preview-05-20", temperature=0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Creative model for content generation
|
||||
content_llm = LLM(model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022", temperature=0.7)
|
||||
|
||||
# Efficient model for data processing
|
||||
processing_llm = LLM(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
|
||||
|
||||
research_manager = Agent(
|
||||
role="Research Strategy Manager",
|
||||
goal="Develop comprehensive research strategies and coordinate team efforts",
|
||||
backstory="Expert research strategist with deep analytical capabilities",
|
||||
llm=manager_llm, # High-capability model for complex reasoning
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
content_writer = Agent(
|
||||
role="Research Content Writer",
|
||||
goal="Transform research findings into compelling, well-structured reports",
|
||||
backstory="Skilled writer who excels at making complex topics accessible",
|
||||
llm=content_llm, # Creative model for engaging content
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_processor = Agent(
|
||||
role="Data Analysis Specialist",
|
||||
goal="Extract and organize key data points from research sources",
|
||||
backstory="Detail-oriented analyst focused on accuracy and efficiency",
|
||||
llm=processing_llm, # Fast, cost-effective model for routine tasks
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[research_manager, content_writer, data_processor],
|
||||
tasks=[...], # Your specific tasks
|
||||
manager_llm=manager_llm, # Manager uses the reasoning model
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The key to successful multi-model implementation is understanding how different agents interact and ensuring that model capabilities align with agent responsibilities. This requires careful planning but can result in significant improvements in both output quality and operational efficiency.
|
||||
|
||||
### b. Component-Specific Selection
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Manager LLM">
|
||||
The manager LLM plays a crucial role in hierarchical CrewAI processes, serving as the coordination point for multiple agents and tasks. This model needs to excel at delegation, task prioritization, and maintaining context across multiple concurrent operations.
|
||||
|
||||
Effective manager LLMs require strong reasoning capabilities to make good delegation decisions, consistent performance to ensure predictable coordination, and excellent context management to track the state of multiple agents simultaneously. The model needs to understand the capabilities and limitations of different agents while optimizing task allocation for efficiency and quality.
|
||||
|
||||
Cost considerations are particularly important for manager LLMs since they're involved in every operation. The model needs to provide sufficient capability for effective coordination while remaining cost-effective for frequent use. This often means finding models that offer good reasoning capabilities without the premium pricing of the most sophisticated options.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Function Calling LLM">
|
||||
Function calling LLMs handle tool usage across all agents, making them critical for crews that rely heavily on external tools and APIs. These models need to excel at understanding tool capabilities, extracting parameters accurately, and handling tool responses effectively.
|
||||
|
||||
The most important characteristics for function calling LLMs are precision and reliability rather than creativity or sophisticated reasoning. The model needs to consistently extract the correct parameters from natural language requests and handle tool responses appropriately. Speed is also important since tool usage often involves multiple round trips that can impact overall performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Many teams find that specialized function calling models or general purpose models with strong tool support work better than creative or reasoning-focused models for this role. The key is ensuring that the model can reliably bridge the gap between natural language instructions and structured tool calls.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Agent-Specific Overrides">
|
||||
Individual agents can override crew-level LLM settings when their specific needs differ significantly from the general crew requirements. This capability allows for fine-tuned optimization while maintaining operational simplicity for most agents.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider agent-specific overrides when an agent's role requires capabilities that differ substantially from other crew members. For example, a creative writing agent might benefit from a model optimized for content generation, while a data analysis agent might perform better with a reasoning-focused model.
|
||||
|
||||
The challenge with agent-specific overrides is balancing optimization with operational complexity. Each additional model adds complexity to deployment, monitoring, and cost management. Teams should focus overrides on agents where the performance improvement justifies the additional complexity.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Task Definition Framework
|
||||
|
||||
### a. Focus on Clarity Over Complexity
|
||||
|
||||
Effective task definition is often more important than model selection in determining the quality of CrewAI outputs. Well-defined tasks provide clear direction and context that enable even modest models to perform well, while poorly defined tasks can cause even sophisticated models to produce unsatisfactory results.
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="Effective Task Descriptions" icon="list-check">
|
||||
The best task descriptions strike a balance between providing sufficient detail and maintaining clarity. They should define the specific objective clearly enough that there's no ambiguity about what success looks like, while explaining the approach or methodology in enough detail that the agent understands how to proceed.
|
||||
|
||||
Effective task descriptions include relevant context and constraints that help the agent understand the broader purpose and any limitations they need to work within. They break complex work into focused steps that can be executed systematically, rather than presenting overwhelming, multi-faceted objectives that are difficult to approach systematically.
|
||||
|
||||
Common mistakes include being too vague about objectives, failing to provide necessary context, setting unclear success criteria, or combining multiple unrelated tasks into a single description. The goal is to provide enough information for the agent to succeed while maintaining focus on a single, clear objective.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Expected Output Guidelines" icon="bullseye">
|
||||
Expected output guidelines serve as a contract between the task definition and the agent, clearly specifying what the deliverable should look like and how it will be evaluated. These guidelines should describe both the format and structure needed, as well as the key elements that must be included for the output to be considered complete.
|
||||
|
||||
The best output guidelines provide concrete examples of quality indicators and define completion criteria clearly enough that both the agent and human reviewers can assess whether the task has been completed successfully. This reduces ambiguity and helps ensure consistent results across multiple task executions.
|
||||
|
||||
Avoid generic output descriptions that could apply to any task, missing format specifications that leave agents guessing about structure, unclear quality standards that make evaluation difficult, or failing to provide examples or templates that help agents understand expectations.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### b. Task Sequencing Strategy
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Sequential Dependencies">
|
||||
Sequential task dependencies are essential when tasks build upon previous outputs, information flows from one task to another, or quality depends on the completion of prerequisite work. This approach ensures that each task has access to the information and context it needs to succeed.
|
||||
|
||||
Implementing sequential dependencies effectively requires using the context parameter to chain related tasks, building complexity gradually through task progression, and ensuring that each task produces outputs that serve as meaningful inputs for subsequent tasks. The goal is to maintain logical flow between dependent tasks while avoiding unnecessary bottlenecks.
|
||||
|
||||
Sequential dependencies work best when there's a clear logical progression from one task to another and when the output of one task genuinely improves the quality or feasibility of subsequent tasks. However, they can create bottlenecks if not managed carefully, so it's important to identify which dependencies are truly necessary versus those that are merely convenient.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Parallel Execution">
|
||||
Parallel execution becomes valuable when tasks are independent of each other, time efficiency is important, or different expertise areas are involved that don't require coordination. This approach can significantly reduce overall execution time while allowing specialized agents to work on their areas of strength simultaneously.
|
||||
|
||||
Successful parallel execution requires identifying tasks that can truly run independently, grouping related but separate work streams effectively, and planning for result integration when parallel tasks need to be combined into a final deliverable. The key is ensuring that parallel tasks don't create conflicts or redundancies that reduce overall quality.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider parallel execution when you have multiple independent research streams, different types of analysis that don't depend on each other, or content creation tasks that can be developed simultaneously. However, be mindful of resource allocation and ensure that parallel execution doesn't overwhelm your available model capacity or budget.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimizing Agent Configuration for LLM Performance
|
||||
|
||||
### a. Role-Driven LLM Selection
|
||||
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
Generic agent roles make it impossible to select the right LLM. Specific roles enable targeted model optimization.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
The specificity of your agent roles directly determines which LLM capabilities matter most for optimal performance. This creates a strategic opportunity to match precise model strengths with agent responsibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
**Generic vs. Specific Role Impact on LLM Choice:**
|
||||
|
||||
When defining roles, think about the specific domain knowledge, working style, and decision-making frameworks that would be most valuable for the tasks the agent will handle. The more specific and contextual the role definition, the better the model can embody that role effectively.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# ✅ Specific role - clear LLM requirements
|
||||
specific_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="SaaS Revenue Operations Analyst", # Clear domain expertise needed
|
||||
goal="Analyze recurring revenue metrics and identify growth opportunities",
|
||||
backstory="Specialist in SaaS business models with deep understanding of ARR, churn, and expansion revenue",
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o") # Reasoning model justified for complex analysis
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Role-to-Model Mapping Strategy:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **"Research Analyst"** → Reasoning model (GPT-4o, Claude Sonnet) for complex analysis
|
||||
- **"Content Editor"** → Creative model (Claude, GPT-4o) for writing quality
|
||||
- **"Data Processor"** → Efficient model (GPT-4o-mini, Gemini Flash) for structured tasks
|
||||
- **"API Coordinator"** → Function-calling optimized model (GPT-4o, Claude) for tool usage
|
||||
|
||||
### b. Backstory as Model Context Amplifier
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
Strategic backstories multiply your chosen LLM's effectiveness by providing domain-specific context that generic prompting cannot achieve.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
A well-crafted backstory transforms your LLM choice from generic capability to specialized expertise. This is especially crucial for cost optimization - a well-contextualized efficient model can outperform a premium model without proper context.
|
||||
|
||||
**Context-Driven Performance Example:**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Context amplifies model effectiveness
|
||||
domain_expert = Agent(
|
||||
role="B2B SaaS Marketing Strategist",
|
||||
goal="Develop comprehensive go-to-market strategies for enterprise software",
|
||||
backstory="""
|
||||
You have 10+ years of experience scaling B2B SaaS companies from Series A to IPO.
|
||||
You understand the nuances of enterprise sales cycles, the importance of product-market
|
||||
fit in different verticals, and how to balance growth metrics with unit economics.
|
||||
You've worked with companies like Salesforce, HubSpot, and emerging unicorns, giving
|
||||
you perspective on both established and disruptive go-to-market strategies.
|
||||
""",
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="claude-3-5-sonnet", temperature=0.3) # Balanced creativity with domain knowledge
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# This context enables Claude to perform like a domain expert
|
||||
# Without it, even it would produce generic marketing advice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Backstory Elements That Enhance LLM Performance:**
|
||||
- **Domain Experience**: "10+ years in enterprise SaaS sales"
|
||||
- **Specific Expertise**: "Specializes in technical due diligence for Series B+ rounds"
|
||||
- **Working Style**: "Prefers data-driven decisions with clear documentation"
|
||||
- **Quality Standards**: "Insists on citing sources and showing analytical work"
|
||||
|
||||
### c. Holistic Agent-LLM Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
The most effective agent configurations create synergy between role specificity, backstory depth, and LLM selection. Each element reinforces the others to maximize model performance.
|
||||
|
||||
**Optimization Framework:**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example: Technical Documentation Agent
|
||||
tech_writer = Agent(
|
||||
role="API Documentation Specialist", # Specific role for clear LLM requirements
|
||||
goal="Create comprehensive, developer-friendly API documentation",
|
||||
backstory="""
|
||||
You're a technical writer with 8+ years documenting REST APIs, GraphQL endpoints,
|
||||
and SDK integration guides. You've worked with developer tools companies and
|
||||
understand what developers need: clear examples, comprehensive error handling,
|
||||
and practical use cases. You prioritize accuracy and usability over marketing fluff.
|
||||
""",
|
||||
llm=LLM(
|
||||
model="claude-3-5-sonnet", # Excellent for technical writing
|
||||
temperature=0.1 # Low temperature for accuracy
|
||||
),
|
||||
tools=[code_analyzer_tool, api_scanner_tool],
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Alignment Checklist:**
|
||||
- ✅ **Role Specificity**: Clear domain and responsibilities
|
||||
- ✅ **LLM Match**: Model strengths align with role requirements
|
||||
- ✅ **Backstory Depth**: Provides domain context the LLM can leverage
|
||||
- ✅ **Tool Integration**: Tools support the agent's specialized function
|
||||
- ✅ **Parameter Tuning**: Temperature and settings optimize for role needs
|
||||
|
||||
The key is creating agents where every configuration choice reinforces your LLM selection strategy, maximizing performance while optimizing costs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Practical Implementation Checklist
|
||||
|
||||
Rather than repeating the strategic framework, here's a tactical checklist for implementing your LLM selection decisions in CrewAI:
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="Audit Your Current Setup" icon="clipboard-check">
|
||||
**What to Review:**
|
||||
- Are all agents using the same LLM by default?
|
||||
- Which agents handle the most complex reasoning tasks?
|
||||
- Which agents primarily do data processing or formatting?
|
||||
- Are any agents heavily tool-dependent?
|
||||
|
||||
**Action**: Document current agent roles and identify optimization opportunities.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Implement Crew-Level Strategy" icon="users-gear">
|
||||
**Set Your Baseline:**
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Start with a reliable default for the crew
|
||||
default_crew_llm = LLM(model="gpt-4o-mini") # Cost-effective baseline
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[...],
|
||||
tasks=[...],
|
||||
memory=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Action**: Establish your crew's default LLM before optimizing individual agents.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Optimize High-Impact Agents" icon="star">
|
||||
**Identify and Upgrade Key Agents:**
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Manager or coordination agents
|
||||
manager_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Project Manager",
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="gemini-2.5-flash-preview-05-20"), # Premium for coordination
|
||||
# ... rest of config
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Creative or customer-facing agents
|
||||
content_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Content Creator",
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="claude-3-5-sonnet"), # Best for writing
|
||||
# ... rest of config
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Action**: Upgrade 20% of your agents that handle 80% of the complexity.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Validate with Enterprise Testing" icon="test-tube">
|
||||
**Once you deploy your agents to production:**
|
||||
- Use [CrewAI Enterprise platform](https://app.crewai.com) to A/B test your model selections
|
||||
- Run multiple iterations with real inputs to measure consistency and performance
|
||||
- Compare cost vs. performance across your optimized setup
|
||||
- Share results with your team for collaborative decision-making
|
||||
|
||||
**Action**: Replace guesswork with data-driven validation using the testing platform.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
### When to Use Different Model Types
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Reasoning Models">
|
||||
Reasoning models become essential when tasks require genuine multi-step logical thinking, strategic planning, or high-level decision making that benefits from systematic analysis. These models excel when problems need to be broken down into components and analyzed systematically rather than handled through pattern matching or simple instruction following.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider reasoning models for business strategy development, complex data analysis that requires drawing insights from multiple sources, multi-step problem solving where each step depends on previous analysis, and strategic planning tasks that require considering multiple variables and their interactions.
|
||||
|
||||
However, reasoning models often come with higher costs and slower response times, so they're best reserved for tasks where their sophisticated capabilities provide genuine value rather than being used for simple operations that don't require complex reasoning.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Creative Models">
|
||||
Creative models become valuable when content generation is the primary output and the quality, style, and engagement level of that content directly impact success. These models excel when writing quality and style matter significantly, creative ideation or brainstorming is needed, or brand voice and tone are important considerations.
|
||||
|
||||
Use creative models for blog post writing and article creation, marketing copy that needs to engage and persuade, creative storytelling and narrative development, and brand communications where voice and tone are crucial. These models often understand nuance and context better than general purpose alternatives.
|
||||
|
||||
Creative models may be less suitable for technical or analytical tasks where precision and factual accuracy are more important than engagement and style. They're best used when the creative and communicative aspects of the output are primary success factors.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Efficient Models">
|
||||
Efficient models are ideal for high-frequency, routine operations where speed and cost optimization are priorities. These models work best when tasks have clear, well-defined parameters and don't require sophisticated reasoning or creative capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider efficient models for data processing and transformation tasks, simple formatting and organization operations, function calling and tool usage where precision matters more than sophistication, and high-volume operations where cost per operation is a significant factor.
|
||||
|
||||
The key with efficient models is ensuring that their capabilities align with task requirements. They can handle many routine operations effectively but may struggle with tasks requiring nuanced understanding, complex reasoning, or sophisticated content generation.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Open Source Models">
|
||||
Open source models become attractive when budget constraints are significant, data privacy requirements exist, customization needs are important, or local deployment is required for operational or compliance reasons.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider open source models for internal company tools where data privacy is paramount, privacy-sensitive applications that can't use external APIs, cost-optimized deployments where per-token pricing is prohibitive, and situations requiring custom model modifications or fine-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
However, open source models require more technical expertise to deploy and maintain effectively. Consider the total cost of ownership including infrastructure, technical overhead, and ongoing maintenance when evaluating open source options.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Common CrewAI Model Selection Pitfalls
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="The 'One Model Fits All' Trap" icon="triangle-exclamation">
|
||||
**The Problem**: Using the same LLM for all agents in a crew, regardless of their specific roles and responsibilities. This is often the default approach but rarely optimal.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real Example**: Using GPT-4o for both a strategic planning manager and a data extraction agent. The manager needs reasoning capabilities worth the premium cost, but the data extractor could perform just as well with GPT-4o-mini at a fraction of the price.
|
||||
|
||||
**CrewAI Solution**: Leverage agent-specific LLM configuration to match model capabilities with agent roles:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Strategic agent gets premium model
|
||||
manager = Agent(role="Strategy Manager", llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o"))
|
||||
|
||||
# Processing agent gets efficient model
|
||||
processor = Agent(role="Data Processor", llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o-mini"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Ignoring Crew-Level vs Agent-Level LLM Hierarchy" icon="shuffle">
|
||||
**The Problem**: Not understanding how CrewAI's LLM hierarchy works - crew LLM, manager LLM, and agent LLM settings can conflict or be poorly coordinated.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real Example**: Setting a crew to use Claude, but having agents configured with GPT models, creating inconsistent behavior and unnecessary model switching overhead.
|
||||
|
||||
**CrewAI Solution**: Plan your LLM hierarchy strategically:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[agent1, agent2],
|
||||
tasks=[task1, task2],
|
||||
manager_llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o"), # For crew coordination
|
||||
process=Process.hierarchical # When using manager_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Agents inherit crew LLM unless specifically overridden
|
||||
agent1 = Agent(llm=LLM(model="claude-3-5-sonnet")) # Override for specific needs
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Function Calling Model Mismatch" icon="screwdriver-wrench">
|
||||
**The Problem**: Choosing models based on general capabilities while ignoring function calling performance for tool-heavy CrewAI workflows.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real Example**: Selecting a creative-focused model for an agent that primarily needs to call APIs, search tools, or process structured data. The agent struggles with tool parameter extraction and reliable function calls.
|
||||
|
||||
**CrewAI Solution**: Prioritize function calling capabilities for tool-heavy agents:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# For agents that use many tools
|
||||
tool_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="API Integration Specialist",
|
||||
tools=[search_tool, api_tool, data_tool],
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o"), # Excellent function calling
|
||||
# OR
|
||||
llm=LLM(model="claude-3-5-sonnet") # Also strong with tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Premature Optimization Without Testing" icon="gear">
|
||||
**The Problem**: Making complex model selection decisions based on theoretical performance without validating with actual CrewAI workflows and tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real Example**: Implementing elaborate model switching logic based on task types without testing if the performance gains justify the operational complexity.
|
||||
|
||||
**CrewAI Solution**: Start simple, then optimize based on real performance data:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Start with this
|
||||
crew = Crew(agents=[...], tasks=[...], llm=LLM(model="gpt-4o-mini"))
|
||||
|
||||
# Test performance, then optimize specific agents as needed
|
||||
# Use Enterprise platform testing to validate improvements
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Overlooking Context and Memory Limitations" icon="brain">
|
||||
**The Problem**: Not considering how model context windows interact with CrewAI's memory and context sharing between agents.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real Example**: Using a short-context model for agents that need to maintain conversation history across multiple task iterations, or in crews with extensive agent-to-agent communication.
|
||||
|
||||
**CrewAI Solution**: Match context capabilities to crew communication patterns.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing and Iteration Strategy
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="Start Simple" icon="play">
|
||||
Begin with reliable, general-purpose models that are well-understood and widely supported. This provides a stable foundation for understanding your specific requirements and performance expectations before optimizing for specialized needs.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Measure What Matters" icon="chart-line">
|
||||
Develop metrics that align with your specific use case and business requirements rather than relying solely on general benchmarks. Focus on measuring outcomes that directly impact your success rather than theoretical performance indicators.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Iterate Based on Results" icon="arrows-rotate">
|
||||
Make model changes based on observed performance in your specific context rather than theoretical considerations or general recommendations. Real-world performance often differs significantly from benchmark results or general reputation.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Consider Total Cost" icon="calculator">
|
||||
Evaluate the complete cost of ownership including model costs, development time, maintenance overhead, and operational complexity. The cheapest model per token may not be the most cost-effective choice when considering all factors.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Focus on understanding your requirements first, then select models that best match those needs. The best LLM choice is the one that consistently delivers the results you need within your operational constraints.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Enterprise-Grade Model Validation
|
||||
|
||||
For teams serious about optimizing their LLM selection, the **CrewAI Enterprise platform** provides sophisticated testing capabilities that go far beyond basic CLI testing. The platform enables comprehensive model evaluation that helps you make data-driven decisions about your LLM strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||

|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
**Advanced Testing Features:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **Multi-Model Comparison**: Test multiple LLMs simultaneously across the same tasks and inputs. Compare performance between GPT-4o, Claude, Llama, Groq, Cerebras, and other leading models in parallel to identify the best fit for your specific use case.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Statistical Rigor**: Configure multiple iterations with consistent inputs to measure reliability and performance variance. This helps identify models that not only perform well but do so consistently across runs.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Real-World Validation**: Use your actual crew inputs and scenarios rather than synthetic benchmarks. The platform allows you to test with your specific industry context, company information, and real use cases for more accurate evaluation.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Comprehensive Analytics**: Access detailed performance metrics, execution times, and cost analysis across all tested models. This enables data-driven decision making rather than relying on general model reputation or theoretical capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Team Collaboration**: Share testing results and model performance data across your team, enabling collaborative decision-making and consistent model selection strategies across projects.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to [app.crewai.com](https://app.crewai.com) to get started!
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
The Enterprise platform transforms model selection from guesswork into a data-driven process, enabling you to validate the principles in this guide with your actual use cases and requirements.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Principles Summary
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={2}>
|
||||
<Card title="Task-Driven Selection" icon="bullseye">
|
||||
Choose models based on what the task actually requires, not theoretical capabilities or general reputation.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Capability Matching" icon="puzzle-piece">
|
||||
Align model strengths with agent roles and responsibilities for optimal performance.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Strategic Consistency" icon="link">
|
||||
Maintain coherent model selection strategy across related components and workflows.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Practical Testing" icon="flask">
|
||||
Validate choices through real-world usage rather than benchmarks alone.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Iterative Improvement" icon="arrow-up">
|
||||
Start simple and optimize based on actual performance and needs.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Operational Balance" icon="scale-balanced">
|
||||
Balance performance requirements with cost and complexity constraints.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Check>
|
||||
Remember: The best LLM choice is the one that consistently delivers the results you need within your operational constraints. Focus on understanding your requirements first, then select models that best match those needs.
|
||||
</Check>
|
||||
|
||||
## Current Model Landscape (June 2025)
|
||||
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
**Snapshot in Time**: The following model rankings represent current leaderboard standings as of June 2025, compiled from [LMSys Arena](https://arena.lmsys.org/), [Artificial Analysis](https://artificialanalysis.ai/), and other leading benchmarks. LLM performance, availability, and pricing change rapidly. Always conduct your own evaluations with your specific use cases and data.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
### Leading Models by Category
|
||||
|
||||
The tables below show a representative sample of current top-performing models across different categories, with guidance on their suitability for CrewAI agents:
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
These tables/metrics showcase selected leading models in each category and are not exhaustive. Many excellent models exist beyond those listed here. The goal is to illustrate the types of capabilities to look for rather than provide a complete catalog.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Reasoning & Planning">
|
||||
**Best for Manager LLMs and Complex Analysis**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Intelligence Score | Cost ($/M tokens) | Speed | Best Use in CrewAI |
|
||||
|:------|:------------------|:------------------|:------|:------------------|
|
||||
| **o3** | 70 | $17.50 | Fast | Manager LLM for complex multi-agent coordination |
|
||||
| **Gemini 2.5 Pro** | 69 | $3.44 | Fast | Strategic planning agents, research coordination |
|
||||
| **DeepSeek R1** | 68 | $0.96 | Moderate | Cost-effective reasoning for budget-conscious crews |
|
||||
| **Claude 4 Sonnet** | 53 | $6.00 | Fast | Analysis agents requiring nuanced understanding |
|
||||
| **Qwen3 235B (Reasoning)** | 62 | $2.63 | Moderate | Open-source alternative for reasoning tasks |
|
||||
|
||||
These models excel at multi-step reasoning and are ideal for agents that need to develop strategies, coordinate other agents, or analyze complex information.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Coding & Technical">
|
||||
**Best for Development and Tool-Heavy Workflows**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Coding Performance | Tool Use Score | Cost ($/M tokens) | Best Use in CrewAI |
|
||||
|:------|:------------------|:---------------|:------------------|:------------------|
|
||||
| **Claude 4 Sonnet** | Excellent | 72.7% | $6.00 | Primary coding agent, technical documentation |
|
||||
| **Claude 4 Opus** | Excellent | 72.5% | $30.00 | Complex software architecture, code review |
|
||||
| **DeepSeek V3** | Very Good | High | $0.48 | Cost-effective coding for routine development |
|
||||
| **Qwen2.5 Coder 32B** | Very Good | Medium | $0.15 | Budget-friendly coding agent |
|
||||
| **Llama 3.1 405B** | Good | 81.1% | $3.50 | Function calling LLM for tool-heavy workflows |
|
||||
|
||||
These models are optimized for code generation, debugging, and technical problem-solving, making them ideal for development-focused crews.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Speed & Efficiency">
|
||||
**Best for High-Throughput and Real-Time Applications**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Speed (tokens/s) | Latency (TTFT) | Cost ($/M tokens) | Best Use in CrewAI |
|
||||
|:------|:-----------------|:---------------|:------------------|:------------------|
|
||||
| **Llama 4 Scout** | 2,600 | 0.33s | $0.27 | High-volume processing agents |
|
||||
| **Gemini 2.5 Flash** | 376 | 0.30s | $0.26 | Real-time response agents |
|
||||
| **DeepSeek R1 Distill** | 383 | Variable | $0.04 | Cost-optimized high-speed processing |
|
||||
| **Llama 3.3 70B** | 2,500 | 0.52s | $0.60 | Balanced speed and capability |
|
||||
| **Nova Micro** | High | 0.30s | $0.04 | Simple, fast task execution |
|
||||
|
||||
These models prioritize speed and efficiency, perfect for agents handling routine operations or requiring quick responses. **Pro tip**: Pairing these models with fast inference providers like Groq can achieve even better performance, especially for open-source models like Llama.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Balanced Performance">
|
||||
**Best All-Around Models for General Crews**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Overall Score | Versatility | Cost ($/M tokens) | Best Use in CrewAI |
|
||||
|:------|:--------------|:------------|:------------------|:------------------|
|
||||
| **GPT-4.1** | 53 | Excellent | $3.50 | General-purpose crew LLM |
|
||||
| **Claude 3.7 Sonnet** | 48 | Very Good | $6.00 | Balanced reasoning and creativity |
|
||||
| **Gemini 2.0 Flash** | 48 | Good | $0.17 | Cost-effective general use |
|
||||
| **Llama 4 Maverick** | 51 | Good | $0.37 | Open-source general purpose |
|
||||
| **Qwen3 32B** | 44 | Good | $1.23 | Budget-friendly versatility |
|
||||
|
||||
These models offer good performance across multiple dimensions, suitable for crews with diverse task requirements.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
### Selection Framework for Current Models
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="High-Performance Crews" icon="rocket">
|
||||
**When performance is the priority**: Use top-tier models like **o3**, **Gemini 2.5 Pro**, or **Claude 4 Sonnet** for manager LLMs and critical agents. These models excel at complex reasoning and coordination but come with higher costs.
|
||||
|
||||
**Strategy**: Implement a multi-model approach where premium models handle strategic thinking while efficient models handle routine operations.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Cost-Conscious Crews" icon="dollar-sign">
|
||||
**When budget is a primary constraint**: Focus on models like **DeepSeek R1**, **Llama 4 Scout**, or **Gemini 2.0 Flash**. These provide strong performance at significantly lower costs.
|
||||
|
||||
**Strategy**: Use cost-effective models for most agents, reserving premium models only for the most critical decision-making roles.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Specialized Workflows" icon="screwdriver-wrench">
|
||||
**For specific domain expertise**: Choose models optimized for your primary use case. **Claude 4** series for coding, **Gemini 2.5 Pro** for research, **Llama 405B** for function calling.
|
||||
|
||||
**Strategy**: Select models based on your crew's primary function, ensuring the core capability aligns with model strengths.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Enterprise & Privacy" icon="shield">
|
||||
**For data-sensitive operations**: Consider open-source models like **Llama 4** series, **DeepSeek V3**, or **Qwen3** that can be deployed locally while maintaining competitive performance.
|
||||
|
||||
**Strategy**: Deploy open-source models on private infrastructure, accepting potential performance trade-offs for data control.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### Key Considerations for Model Selection
|
||||
|
||||
- **Performance Trends**: The current landscape shows strong competition between reasoning-focused models (o3, Gemini 2.5 Pro) and balanced models (Claude 4, GPT-4.1). Specialized models like DeepSeek R1 offer excellent cost-performance ratios.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Speed vs. Intelligence Trade-offs**: Models like Llama 4 Scout prioritize speed (2,600 tokens/s) while maintaining reasonable intelligence, whereas models like o3 maximize reasoning capability at the cost of speed and price.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Open Source Viability**: The gap between open-source and proprietary models continues to narrow, with models like Llama 4 Maverick and DeepSeek V3 offering competitive performance at attractive price points. Fast inference providers particularly shine with open-source models, often delivering better speed-to-cost ratios than proprietary alternatives.
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
**Testing is Essential**: Leaderboard rankings provide general guidance, but your specific use case, prompting style, and evaluation criteria may produce different results. Always test candidate models with your actual tasks and data before making final decisions.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
### Practical Implementation Strategy
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="Start with Proven Models">
|
||||
Begin with well-established models like **GPT-4.1**, **Claude 3.7 Sonnet**, or **Gemini 2.0 Flash** that offer good performance across multiple dimensions and have extensive real-world validation.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Identify Specialized Needs">
|
||||
Determine if your crew has specific requirements (coding, reasoning, speed) that would benefit from specialized models like **Claude 4 Sonnet** for development or **o3** for complex analysis. For speed-critical applications, consider fast inference providers like **Groq** alongside model selection.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Implement Multi-Model Strategy">
|
||||
Use different models for different agents based on their roles. High-capability models for managers and complex tasks, efficient models for routine operations.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Monitor and Optimize">
|
||||
Track performance metrics relevant to your use case and be prepared to adjust model selections as new models are released or pricing changes.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
@@ -1,243 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'MCP Servers as Tools in CrewAI'
|
||||
description: 'Learn how to integrate MCP servers as tools in your CrewAI agents using the `crewai-tools` library.'
|
||||
icon: 'plug'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The [Model Context Protocol](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/introduction) (MCP) provides a standardized way for AI agents to provide context to LLMs by communicating with external services, known as MCP Servers.
|
||||
The `crewai-tools` library extends CrewAI's capabilities by allowing you to seamlessly integrate tools from these MCP servers into your agents.
|
||||
This gives your crews access to a vast ecosystem of functionalities. For now, we support **Standard Input/Output** (Stdio) and **Server-Sent Events** (SSE) transport mechanisms.
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
We will also be integrating **Streamable HTTP** transport in the near future.
|
||||
Streamable HTTP is designed for efficient, bi-directional communication over a single HTTP connection.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
## Video Tutorial
|
||||
Watch this video tutorial for a comprehensive guide on MCP integration with CrewAI:
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
width="100%"
|
||||
height="400"
|
||||
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/TpQ45lAZh48"
|
||||
title="CrewAI MCP Integration Guide"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
style={{ borderRadius: '10px' }}
|
||||
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture"
|
||||
allowfullscreen
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Before you start using MCP with `crewai-tools`, you need to install the `mcp` extra `crewai-tools` dependency with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
uv pip install 'crewai-tools[mcp]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Integrating MCP Tools with `MCPServerAdapter`
|
||||
|
||||
The `MCPServerAdapter` class from `crewai-tools` is the primary way to connect to an MCP server and make its tools available to your CrewAI agents.
|
||||
It supports different transport mechanisms, primarily **Stdio** (for local servers) and **SSE** (Server-Sent Events).You have two main options for managing the connection lifecycle:
|
||||
|
||||
### Option 1: Fully Managed Connection (Recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
Using a Python context manager (`with` statement) is the recommended approach. It automatically handles starting and stopping the connection to the MCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
**For a local Stdio-based MCP server:**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
server_params=StdioServerParameters(
|
||||
command="uxv", # Or your python3 executable i.e. "python3"
|
||||
args=["mock_server.py"],
|
||||
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params) as tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available tools from Stdio MCP server: {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: Using the tools from the Stdio MCP server in a CrewAI Agent
|
||||
agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Web Information Retriever",
|
||||
goal="Scrape content from a specified URL.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI that can fetch and process web page data via an MCP tool.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
task = Task(
|
||||
description="Scrape content from a specified URL.",
|
||||
expected_output="Scraped content from the specified URL.",
|
||||
agent=agent,
|
||||
)
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[agent],
|
||||
tasks=[task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**For a remote SSE-based MCP server:**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
|
||||
server_params = {"url": "http://localhost:8000/sse"}
|
||||
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params) as tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available tools from SSE MCP server: {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: Using the tools from the SSE MCP server in a CrewAI Agent
|
||||
agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Web Information Retriever",
|
||||
goal="Scrape content from a specified URL.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI that can fetch and process web page data via an MCP tool.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
task = Task(
|
||||
description="Scrape content from a specified URL.",
|
||||
expected_output="Scraped content from the specified URL.",
|
||||
agent=agent,
|
||||
)
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[agent],
|
||||
tasks=[task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Option 2: More control over the MCP server connection lifecycle
|
||||
|
||||
If you need finer-grained control over the MCP server connection lifecycle, you can instantiate `MCPServerAdapter` directly and manage its `start()` and `stop()` methods.
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
You **MUST** call `mcp_server_adapter.stop()` to ensure the connection is closed and resources are released. Using a `try...finally` block is highly recommended.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Stdio Transport Example (Manual)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
stdio_params = StdioServerParameters(
|
||||
command="uvx", # Or your python3 executable i.e. "python3"
|
||||
args=["--quiet", "your-mcp-server@0.1.3"],
|
||||
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter = MCPServerAdapter(server_params=stdio_params)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.start() # Manually start the connection
|
||||
tools = mcp_server_adapter.tools
|
||||
print(f"Available tools (manual Stdio): {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Use 'tools' with your Agent, Task, Crew setup as in Option 1
|
||||
agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Medical Researcher",
|
||||
goal="Find recent studies on a given topic using PubMed.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in biomedical literature research.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
task = Task(
|
||||
description="Search for recent articles on 'crispr gene editing'.",
|
||||
expected_output="A summary of the top 3 recent articles.",
|
||||
agent=agent
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[agent],
|
||||
tasks=[task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
print("Stopping Stdio MCP server connection (manual)...")
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.stop() # **Crucial: Ensure stop is called**
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### SSE Transport Example (Manual)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
server_params = {"url": "http://localhost:8000/sse"}
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter = MCPServerAdapter(server_params)
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.start()
|
||||
tools = mcp_server_adapter.tools
|
||||
print(f"Available tools (manual SSE): {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Medical Researcher",
|
||||
goal="Find recent studies on a given topic using PubMed.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI assistant specialized in biomedical literature research.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
task = Task(
|
||||
description="Search for recent articles on 'crispr gene editing'.",
|
||||
expected_output="A summary of the top 3 recent articles.",
|
||||
agent=agent
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[agent],
|
||||
tasks=[task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
print("Stopping SSE MCP server connection (manual)...")
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.stop() # **Crucial: Ensure stop is called**
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Staying Safe with MCP
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
Always ensure that you trust an MCP Server before using it.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Security Warning: DNS Rebinding Attacks
|
||||
SSE transports can be vulnerable to DNS rebinding attacks if not properly secured.
|
||||
To prevent this:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Always validate Origin headers** on incoming SSE connections to ensure they come from expected sources
|
||||
2. **Avoid binding servers to all network interfaces** (0.0.0.0) when running locally - bind only to localhost (127.0.0.1) instead
|
||||
3. **Implement proper authentication** for all SSE connections
|
||||
|
||||
Without these protections, attackers could use DNS rebinding to interact with local MCP servers from remote websites.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, see the [MCP Transport Security](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/concepts/transports#security-considerations) documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Limitations
|
||||
* **Supported Primitives**: Currently, `MCPServerAdapter` primarily supports adapting MCP `tools`.
|
||||
Other MCP primitives like `prompts` or `resources` are not directly integrated as CrewAI components through this adapter at this time.
|
||||
* **Output Handling**: The adapter typically processes the primary text output from an MCP tool (e.g., `.content[0].text`). Complex or multi-modal outputs might require custom handling if not fitting this pattern.
|
||||
64
docs/mcp/multiple-servers.mdx
Normal file
64
docs/mcp/multiple-servers.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Connecting to Multiple MCP Servers
|
||||
description: Learn how to use MCPServerAdapter in CrewAI to connect to multiple MCP servers simultaneously and aggregate their tools.
|
||||
icon: layer-group
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
`MCPServerAdapter` in `crewai-tools` allows you to connect to multiple MCP servers concurrently. This is useful when your agents need to access tools distributed across different services or environments. The adapter aggregates tools from all specified servers, making them available to your CrewAI agents.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
To connect to multiple servers, you provide a list of server parameter dictionaries to `MCPServerAdapter`. Each dictionary in the list should define the parameters for one MCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported transport types for each server in the list include `stdio`, `sse`, and `streamable-http`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from mcp import StdioServerParameters # Needed for Stdio example
|
||||
|
||||
# Define parameters for multiple MCP servers
|
||||
server_params_list = [
|
||||
# Streamable HTTP Server
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8001/mcp",
|
||||
"transport": "streamable-http"
|
||||
},
|
||||
# SSE Server
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8000/sse",
|
||||
"transport": "sse"
|
||||
},
|
||||
# StdIO Server
|
||||
StdioServerParameters(
|
||||
command="python3",
|
||||
args=["servers/your_stdio_server.py"],
|
||||
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params_list) as aggregated_tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available aggregated tools: {[tool.name for tool in aggregated_tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
multi_server_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Versatile Assistant",
|
||||
goal="Utilize tools from local Stdio, remote SSE, and remote HTTP MCP servers.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI agent capable of leveraging a diverse set of tools from multiple sources.",
|
||||
tools=aggregated_tools, # All tools are available here
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
... # Your other agent, tasks, and crew code here
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error connecting to or using multiple MCP servers (Managed): {e}")
|
||||
print("Ensure all MCP servers are running and accessible with correct configurations.")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Connection Management
|
||||
|
||||
When using the context manager (`with` statement), `MCPServerAdapter` handles the lifecycle (start and stop) of all connections to the configured MCP servers. This simplifies resource management and ensures that all connections are properly closed when the context is exited.
|
||||
180
docs/mcp/overview.mdx
Normal file
180
docs/mcp/overview.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'MCP Servers as Tools in CrewAI'
|
||||
description: 'Learn how to integrate MCP servers as tools in your CrewAI agents using the `crewai-tools` library.'
|
||||
icon: plug
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The [Model Context Protocol](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/introduction) (MCP) provides a standardized way for AI agents to provide context to LLMs by communicating with external services, known as MCP Servers.
|
||||
The `crewai-tools` library extends CrewAI's capabilities by allowing you to seamlessly integrate tools from these MCP servers into your agents.
|
||||
This gives your crews access to a vast ecosystem of functionalities.
|
||||
|
||||
We currently support the following transport mechanisms:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Stdio**: for local servers (communication via standard input/output between processes on the same machine)
|
||||
- **Server-Sent Events (SSE)**: for remote servers (unidirectional, real-time data streaming from server to client over HTTP)
|
||||
- **Streamable HTTP**: for remote servers (flexible, potentially bi-directional communication over HTTP, often utilizing SSE for server-to-client streams)
|
||||
|
||||
## Video Tutorial
|
||||
Watch this video tutorial for a comprehensive guide on MCP integration with CrewAI:
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
width="100%"
|
||||
height="400"
|
||||
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/TpQ45lAZh48"
|
||||
title="CrewAI MCP Integration Guide"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
style={{ borderRadius: '10px' }}
|
||||
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture"
|
||||
allowfullscreen
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Before you start using MCP with `crewai-tools`, you need to install the `mcp` extra `crewai-tools` dependency with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
uv pip install 'crewai-tools[mcp]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Concepts & Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
The `MCPServerAdapter` class from `crewai-tools` is the primary way to connect to an MCP server and make its tools available to your CrewAI agents. It supports different transport mechanisms and simplifies connection management.
|
||||
|
||||
Using a Python context manager (`with` statement) is the **recommended approach** for `MCPServerAdapter`. It automatically handles starting and stopping the connection to the MCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from mcp import StdioServerParameters # For Stdio Server
|
||||
|
||||
# Example server_params (choose one based on your server type):
|
||||
# 1. Stdio Server:
|
||||
server_params=StdioServerParameters(
|
||||
command="python3",
|
||||
args=["servers/your_server.py"],
|
||||
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. SSE Server:
|
||||
server_params = {
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8000/sse",
|
||||
"transport": "sse"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. Streamable HTTP Server:
|
||||
server_params = {
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8001/mcp",
|
||||
"transport": "streamable-http"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Example usage (uncomment and adapt once server_params is set):
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params) as mcp_tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available tools: {[tool.name for tool in mcp_tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
my_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="MCP Tool User",
|
||||
goal="Utilize tools from an MCP server.",
|
||||
backstory="I can connect to MCP servers and use their tools.",
|
||||
tools=mcp_tools, # Pass the loaded tools to your agent
|
||||
reasoning=True,
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
# ... rest of your crew setup ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
This general pattern shows how to integrate tools. For specific examples tailored to each transport, refer to the detailed guides below.
|
||||
|
||||
## Filtering Tools
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params) as mcp_tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available tools: {[tool.name for tool in mcp_tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
my_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="MCP Tool User",
|
||||
goal="Utilize tools from an MCP server.",
|
||||
backstory="I can connect to MCP servers and use their tools.",
|
||||
tools=mcp_tools["tool_name"], # Pass the loaded tools to your agent
|
||||
reasoning=True,
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
# ... rest of your crew setup ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Explore MCP Integrations
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={2}>
|
||||
<Card
|
||||
title="Stdio Transport"
|
||||
icon="server"
|
||||
href="/mcp/stdio"
|
||||
color="#3B82F6"
|
||||
>
|
||||
Connect to local MCP servers via standard input/output. Ideal for scripts and local executables.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card
|
||||
title="SSE Transport"
|
||||
icon="wifi"
|
||||
href="/mcp/sse"
|
||||
color="#10B981"
|
||||
>
|
||||
Integrate with remote MCP servers using Server-Sent Events for real-time data streaming.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card
|
||||
title="Streamable HTTP Transport"
|
||||
icon="globe"
|
||||
href="/mcp/streamable-http"
|
||||
color="#F59E0B"
|
||||
>
|
||||
Utilize flexible Streamable HTTP for robust communication with remote MCP servers.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card
|
||||
title="Connecting to Multiple Servers"
|
||||
icon="layer-group"
|
||||
href="/mcp/multiple-servers"
|
||||
color="#8B5CF6"
|
||||
>
|
||||
Aggregate tools from several MCP servers simultaneously using a single adapter.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card
|
||||
title="Security Considerations"
|
||||
icon="lock"
|
||||
href="/mcp/security"
|
||||
color="#EF4444"
|
||||
>
|
||||
Review important security best practices for MCP integration to keep your agents safe.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
Checkout this repository for full demos and examples of MCP integration with CrewAI! 👇
|
||||
|
||||
<Card
|
||||
title="GitHub Repository"
|
||||
icon="github"
|
||||
href="https://github.com/tonykipkemboi/crewai-mcp-demo"
|
||||
target="_blank"
|
||||
>
|
||||
CrewAI MCP Demo
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
## Staying Safe with MCP
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
Always ensure that you trust an MCP Server before using it.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Security Warning: DNS Rebinding Attacks
|
||||
SSE transports can be vulnerable to DNS rebinding attacks if not properly secured.
|
||||
To prevent this:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Always validate Origin headers** on incoming SSE connections to ensure they come from expected sources
|
||||
2. **Avoid binding servers to all network interfaces** (0.0.0.0) when running locally - bind only to localhost (127.0.0.1) instead
|
||||
3. **Implement proper authentication** for all SSE connections
|
||||
|
||||
Without these protections, attackers could use DNS rebinding to interact with local MCP servers from remote websites.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, see the [Anthropic's MCP Transport Security docs](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/concepts/transports#security-considerations).
|
||||
|
||||
### Limitations
|
||||
* **Supported Primitives**: Currently, `MCPServerAdapter` primarily supports adapting MCP `tools`.
|
||||
Other MCP primitives like `prompts` or `resources` are not directly integrated as CrewAI components through this adapter at this time.
|
||||
* **Output Handling**: The adapter typically processes the primary text output from an MCP tool (e.g., `.content[0].text`). Complex or multi-modal outputs might require custom handling if not fitting this pattern.
|
||||
166
docs/mcp/security.mdx
Normal file
166
docs/mcp/security.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: MCP Security Considerations
|
||||
description: Learn about important security best practices when integrating MCP servers with your CrewAI agents.
|
||||
icon: lock
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
The most critical aspect of MCP security is **trust**. You should **only** connect your CrewAI agents to MCP servers that you fully trust.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
When integrating external services like MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers into your CrewAI agents, security is paramount.
|
||||
MCP servers can execute code, access data, or interact with other systems based on the tools they expose.
|
||||
It's crucial to understand the implications and follow best practices to protect your applications and data.
|
||||
|
||||
### Risks
|
||||
|
||||
- Execute arbitrary code on the machine where the agent is running (especially with `Stdio` transport if the server can control the command executed).
|
||||
- Expose sensitive data from your agent or its environment.
|
||||
- Manipulate your agent's behavior in unintended ways, including making unauthorized API calls on your behalf.
|
||||
- Hijack your agent's reasoning process through sophisticated prompt injection techniques (see below).
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Trusting MCP Servers
|
||||
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
**Only connect to MCP servers that you trust.**
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
Before configuring `MCPServerAdapter` to connect to an MCP server, ensure you know:
|
||||
- **Who operates the server?** Is it a known, reputable service, or an internal server under your control?
|
||||
- **What tools does it expose?** Understand the capabilities of the tools. Could they be misused if an attacker gained control or if the server itself is malicious?
|
||||
- **What data does it access or process?** Be aware of any sensitive information that might be sent to or handled by the MCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
Avoid connecting to unknown or unverified MCP servers, especially if your agents handle sensitive tasks or data.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Secure Prompt Injection via Tool Metadata: The "Model Control Protocol" Risk
|
||||
|
||||
A significant and subtle risk is the potential for prompt injection through tool metadata. Here's how it works:
|
||||
|
||||
1. When your CrewAI agent connects to an MCP server, it typically requests a list of available tools.
|
||||
2. The MCP server responds with metadata for each tool, including its name, description, and parameter descriptions.
|
||||
3. Your agent's underlying Language Model (LLM) uses this metadata to understand how and when to use the tools. This metadata is often incorporated into the LLM's system prompt or context.
|
||||
4. A malicious MCP server can craft its tool metadata (names, descriptions) to include hidden or overt instructions. These instructions can act as a prompt injection, effectively telling your LLM to behave in a certain way, reveal sensitive information, or perform malicious actions.
|
||||
|
||||
**Crucially, this attack can occur simply by connecting to a malicious server and listing its tools, even if your agent never explicitly decides to *use* any of those tools.** The mere exposure to the malicious metadata can be enough to compromise the agent's behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
**Mitigation:**
|
||||
|
||||
* **Extreme Caution with Untrusted Servers:** Reiterate: *Do not connect to MCP servers you do not fully trust.* The risk of metadata injection makes this paramount.
|
||||
|
||||
### Stdio Transport Security
|
||||
|
||||
Stdio (Standard Input/Output) transport is typically used for local MCP servers running on the same machine as your CrewAI application.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Process Isolation**: While generally safer as it doesn't involve network exposure by default, ensure the script or command run by `StdioServerParameters` is from a trusted source and has appropriate file system permissions. A malicious Stdio server script could still harm your local system.
|
||||
- **Input Sanitization**: If your Stdio server script takes complex inputs derived from agent interactions, ensure the script itself sanitizes these inputs to prevent command injection or other vulnerabilities within the script's logic.
|
||||
- **Resource Limits**: Be mindful that a local Stdio server process consumes local resources (CPU, memory). Ensure it's well-behaved and won't exhaust system resources.
|
||||
|
||||
### Confused Deputy Attacks
|
||||
|
||||
The [Confused Deputy Problem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Confused_deputy_problem) is a classic security vulnerability that can manifest in MCP integrations, especially when an MCP server acts as a proxy to other third-party services (e.g., Google Calendar, GitHub) that use OAuth 2.0 for authorization.
|
||||
|
||||
**Scenario:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. An MCP server (let's call it `MCP-Proxy`) allows your agent to interact with `ThirdPartyAPI`.
|
||||
2. `MCP-Proxy` uses its own single, static `client_id` when talking to `ThirdPartyAPI`'s authorization server.
|
||||
3. You, as the user, legitimately authorize `MCP-Proxy` to access `ThirdPartyAPI` on your behalf. During this, `ThirdPartyAPI`'s auth server might set a cookie in your browser indicating your consent for `MCP-Proxy`'s `client_id`.
|
||||
4. An attacker crafts a malicious link. This link initiates an OAuth flow with `MCP-Proxy`, but is designed to trick `ThirdPartyAPI`'s auth server.
|
||||
5. If you click this link, and `ThirdPartyAPI`'s auth server sees your existing consent cookie for `MCP-Proxy`'s `client_id`, it might *skip* asking for your consent again.
|
||||
6. `MCP-Proxy` might then be tricked into forwarding an authorization code (for `ThirdPartyAPI`) to the attacker, or an MCP authorization code that the attacker can use to impersonate you to `MCP-Proxy`.
|
||||
|
||||
**Mitigation (Primarily for MCP Server Developers):**
|
||||
|
||||
* MCP proxy servers using static client IDs for downstream services **must** obtain explicit user consent for *each client application or agent* connecting to them *before* initiating an OAuth flow with the third-party service. This means `MCP-Proxy` itself should show a consent screen.
|
||||
|
||||
**CrewAI User Implication:**
|
||||
|
||||
* Be cautious if an MCP server redirects you for multiple OAuth authentications, especially if it seems unexpected or if the permissions requested are overly broad.
|
||||
* Prefer MCP servers that clearly delineate their own identity versus the third-party services they might proxy.
|
||||
|
||||
### Remote Transport Security (SSE & Streamable HTTP)
|
||||
|
||||
When connecting to remote MCP servers via Server-Sent Events (SSE) or Streamable HTTP, standard web security practices are essential.
|
||||
|
||||
### SSE Security Considerations
|
||||
|
||||
### a. DNS Rebinding Attacks (Especially for SSE)
|
||||
|
||||
<Critical>
|
||||
**Protect against DNS Rebinding Attacks.**
|
||||
</Critical>
|
||||
|
||||
DNS rebinding allows an attacker-controlled website to bypass the same-origin policy and make requests to servers on the user's local network (e.g., `localhost`) or intranet. This is particularly risky if you run an MCP server locally (e.g., for development) and an agent in a browser-like environment (though less common for typical CrewAI backend setups) or if the MCP server is on an internal network.
|
||||
|
||||
**Mitigation Strategies for MCP Server Implementers:**
|
||||
- **Validate `Origin` and `Host` Headers**: MCP servers (especially SSE ones) should validate the `Origin` and/or `Host` HTTP headers to ensure requests are coming from expected domains/clients.
|
||||
- **Bind to `localhost` (127.0.0.1)**: When running MCP servers locally for development, bind them to `127.0.0.1` instead of `0.0.0.0`. This prevents them from being accessible from other machines on the network.
|
||||
- **Authentication**: Require authentication for all connections to your MCP server if it's not intended for public anonymous access.
|
||||
|
||||
### b. Use HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
- **Encrypt Data in Transit**: Always use HTTPS (HTTP Secure) for the URLs of remote MCP servers. This encrypts the communication between your CrewAI application and the MCP server, protecting against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. `MCPServerAdapter` will respect the scheme (`http` or `https`) provided in the URL.
|
||||
|
||||
### c. Token Passthrough (Anti-Pattern)
|
||||
|
||||
This is primarily a concern for MCP server developers but understanding it helps in choosing secure servers.
|
||||
|
||||
"Token passthrough" is when an MCP server accepts an access token from your CrewAI agent (which might be a token for a *different* service, say `ServiceA`) and simply passes it through to another downstream API (`ServiceB`) without proper validation. Specifically, `ServiceB` (or the MCP server itself) should only accept tokens that were explicitly issued *for them* (i.e., the 'audience' claim in the token matches the server/service).
|
||||
|
||||
**Risks:**
|
||||
|
||||
* Bypasses security controls (like rate limiting or fine-grained permissions) on the MCP server or the downstream API.
|
||||
* Breaks audit trails and accountability.
|
||||
* Allows misuse of stolen tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
**Mitigation (For MCP Server Developers):**
|
||||
|
||||
* MCP servers **MUST NOT** accept tokens that were not explicitly issued for them. They must validate the token's audience claim.
|
||||
|
||||
**CrewAI User Implication:**
|
||||
|
||||
* While not directly controllable by the user, this highlights the importance of connecting to well-designed MCP servers that adhere to security best practices.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Authentication and Authorization
|
||||
|
||||
- **Verify Identity**: If the MCP server provides sensitive tools or access to private data, it MUST implement strong authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of the client (your CrewAI application). This could involve API keys, OAuth tokens, or other standard methods.
|
||||
- **Principle of Least Privilege**: Ensure the credentials used by `MCPServerAdapter` (if any) have only the necessary permissions to access the required tools.
|
||||
|
||||
### d. Input Validation and Sanitization
|
||||
|
||||
- **Input Validation is Critical**: MCP servers **must** rigorously validate all inputs received from agents *before* processing them or passing them to tools. This is a primary defense against many common vulnerabilities:
|
||||
- **Command Injection:** If a tool constructs shell commands, SQL queries, or other interpreted language statements based on input, the server must meticulously sanitize this input to prevent malicious commands from being injected and executed.
|
||||
- **Path Traversal:** If a tool accesses files based on input parameters, the server must validate and sanitize these paths to prevent access to unauthorized files or directories (e.g., by blocking `../` sequences).
|
||||
- **Data Type & Range Checks:** Servers must ensure that input data conforms to the expected data types (e.g., string, number, boolean) and falls within acceptable ranges or adheres to defined formats (e.g., regex for URLs).
|
||||
- **JSON Schema Validation:** All tool parameters should be strictly validated against their defined JSON schema. This helps catch malformed requests early.
|
||||
- **Client-Side Awareness**: While server-side validation is paramount, as a CrewAI user, be mindful of the data your agents are constructed to send to MCP tools, especially if interacting with less-trusted or new MCP servers.
|
||||
|
||||
### e. Rate Limiting and Resource Management
|
||||
|
||||
- **Prevent Abuse**: MCP servers should implement rate limiting to prevent abuse, whether intentional (Denial of Service attacks) or unintentional (e.g., a misconfigured agent making too many requests).
|
||||
- **Client-Side Retries**: Implement sensible retry logic in your CrewAI tasks if transient network issues or server rate limits are expected, but avoid aggressive retries that could exacerbate server load.
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. Secure MCP Server Implementation Advice (For Developers)
|
||||
|
||||
If you are developing an MCP server that CrewAI agents might connect to, consider these best practices in addition to the points above:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Follow Secure Coding Practices**: Adhere to standard secure coding principles for your chosen language and framework (e.g., OWASP Top 10).
|
||||
- **Principle of Least Privilege**: Ensure the process running the MCP server (especially for `Stdio`) has only the minimum necessary permissions. Tools themselves should also operate with the least privilege required to perform their function.
|
||||
- **Dependency Management**: Keep all server-side dependencies, including operating system packages, language runtimes, and third-party libraries, up-to-date to patch known vulnerabilities. Use tools to scan for vulnerable dependencies.
|
||||
- **Secure Defaults**: Design your server and its tools to be secure by default. For example, features that could be risky should be off by default or require explicit opt-in with clear warnings.
|
||||
- **Access Control for Tools**: Implement robust mechanisms to control which authenticated and authorized agents or users can access specific tools, especially those that are powerful, sensitive, or incur costs.
|
||||
- **Secure Error Handling**: Servers should not expose detailed internal error messages, stack traces, or debugging information to the client, as these can reveal internal workings or potential vulnerabilities. Log errors comprehensively on the server-side for diagnostics.
|
||||
- **Comprehensive Logging and Monitoring**: Implement detailed logging of security-relevant events (e.g., authentication attempts, tool invocations, errors, authorization changes). Monitor these logs for suspicious activity or abuse patterns.
|
||||
- **Adherence to MCP Authorization Spec**: If implementing authentication and authorization, strictly follow the [MCP Authorization specification](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/draft/basic/authorization) and relevant [OAuth 2.0 security best practices](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc9700).
|
||||
- **Regular Security Audits**: If your MCP server handles sensitive data, performs critical operations, or is publicly exposed, consider periodic security audits by qualified professionals.
|
||||
|
||||
## 5. Further Reading
|
||||
|
||||
For more detailed information on MCP security, refer to the official documentation:
|
||||
- **[MCP Transport Security](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/concepts/transports#security-considerations)**
|
||||
|
||||
By understanding these security considerations and implementing best practices, you can safely leverage the power of MCP servers in your CrewAI projects.
|
||||
These are by no means exhaustive, but they cover the most common and critical security concerns.
|
||||
The threats will continue to evolve, so it's important to stay informed and adapt your security measures accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
150
docs/mcp/sse.mdx
Normal file
150
docs/mcp/sse.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: SSE Transport
|
||||
description: Learn how to connect CrewAI to remote MCP servers using Server-Sent Events (SSE) for real-time communication.
|
||||
icon: wifi
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Server-Sent Events (SSE) provide a standard way for a web server to send updates to a client over a single, long-lived HTTP connection. In the context of MCP, SSE is used for remote servers to stream data (like tool responses) to your CrewAI application in real-time.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Concepts
|
||||
|
||||
- **Remote Servers**: SSE is suitable for MCP servers hosted remotely.
|
||||
- **Unidirectional Stream**: Typically, SSE is a one-way communication channel from server to client.
|
||||
- **`MCPServerAdapter` Configuration**: For SSE, you'll provide the server's URL and specify the transport type.
|
||||
|
||||
## Connecting via SSE
|
||||
|
||||
You can connect to an SSE-based MCP server using two main approaches for managing the connection lifecycle:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Fully Managed Connection (Recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
Using a Python context manager (`with` statement) is the recommended approach. It automatically handles establishing and closing the connection to the SSE MCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
|
||||
server_params = {
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8000/sse", # Replace with your actual SSE server URL
|
||||
"transport": "sse"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Using MCPServerAdapter with a context manager
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params) as tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available tools from SSE MCP server: {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: Using a tool from the SSE MCP server
|
||||
sse_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Remote Service User",
|
||||
goal="Utilize a tool provided by a remote SSE MCP server.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI agent that connects to external services via SSE.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
reasoning=True,
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
sse_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Fetch real-time stock updates for 'AAPL' using an SSE tool.",
|
||||
expected_output="The latest stock price for AAPL.",
|
||||
agent=sse_agent,
|
||||
markdown=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
sse_crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[sse_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[sse_task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if tools: # Only kickoff if tools were loaded
|
||||
result = sse_crew.kickoff() # Add inputs={'stock_symbol': 'AAPL'} if tool requires it
|
||||
print("\nCrew Task Result (SSE - Managed):\n", result)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Skipping crew kickoff as tools were not loaded (check server connection).")
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error connecting to or using SSE MCP server (Managed): {e}")
|
||||
print("Ensure the SSE MCP server is running and accessible at the specified URL.")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
Replace `"http://localhost:8000/sse"` with the actual URL of your SSE MCP server.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Manual Connection Lifecycle
|
||||
|
||||
If you need finer-grained control, you can manage the `MCPServerAdapter` connection lifecycle manually.
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
You **MUST** call `mcp_server_adapter.stop()` to ensure the connection is closed and resources are released. Using a `try...finally` block is highly recommended.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
|
||||
server_params = {
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8000/sse", # Replace with your actual SSE server URL
|
||||
"transport": "sse"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter = None
|
||||
try:
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter = MCPServerAdapter(server_params)
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.start()
|
||||
tools = mcp_server_adapter.tools
|
||||
print(f"Available tools (manual SSE): {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
manual_sse_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Remote Data Analyst",
|
||||
goal="Analyze data fetched from a remote SSE MCP server using manual connection management.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI skilled in handling SSE connections explicitly.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
analysis_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Fetch and analyze the latest user activity trends from the SSE server.",
|
||||
expected_output="A summary report of user activity trends.",
|
||||
agent=manual_sse_agent
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
analysis_crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[manual_sse_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[analysis_task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = analysis_crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print("\nCrew Task Result (SSE - Manual):\n", result)
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"An error occurred during manual SSE MCP integration: {e}")
|
||||
print("Ensure the SSE MCP server is running and accessible.")
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
if mcp_server_adapter and mcp_server_adapter.is_connected:
|
||||
print("Stopping SSE MCP server connection (manual)...")
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.stop() # **Crucial: Ensure stop is called**
|
||||
elif mcp_server_adapter:
|
||||
print("SSE MCP server adapter was not connected. No stop needed or start failed.")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Security Considerations for SSE
|
||||
|
||||
<Warning>
|
||||
**DNS Rebinding Attacks**: SSE transports can be vulnerable to DNS rebinding attacks if the MCP server is not properly secured. This could allow malicious websites to interact with local or intranet-based MCP servers.
|
||||
</Warning>
|
||||
|
||||
To mitigate this risk:
|
||||
- MCP server implementations should **validate `Origin` headers** on incoming SSE connections.
|
||||
- When running local SSE MCP servers for development, **bind only to `localhost` (`127.0.0.1`)** rather than all network interfaces (`0.0.0.0`).
|
||||
- Implement **proper authentication** for all SSE connections if they expose sensitive tools or data.
|
||||
|
||||
For a comprehensive overview of security best practices, please refer to our [Security Considerations](./security.mdx) page and the official [MCP Transport Security documentation](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/concepts/transports#security-considerations).
|
||||
134
docs/mcp/stdio.mdx
Normal file
134
docs/mcp/stdio.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Stdio Transport
|
||||
description: Learn how to connect CrewAI to local MCP servers using the Stdio (Standard Input/Output) transport mechanism.
|
||||
icon: server
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The Stdio (Standard Input/Output) transport is designed for connecting `MCPServerAdapter` to local MCP servers that communicate over their standard input and output streams. This is typically used when the MCP server is a script or executable running on the same machine as your CrewAI application.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Concepts
|
||||
|
||||
- **Local Execution**: Stdio transport manages a locally running process for the MCP server.
|
||||
- **`StdioServerParameters`**: This class from the `mcp` library is used to configure the command, arguments, and environment variables for launching the Stdio server.
|
||||
|
||||
## Connecting via Stdio
|
||||
|
||||
You can connect to an Stdio-based MCP server using two main approaches for managing the connection lifecycle:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Fully Managed Connection (Recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
Using a Python context manager (`with` statement) is the recommended approach. It automatically handles starting the MCP server process and stopping it when the context is exited.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a StdioServerParameters object
|
||||
server_params=StdioServerParameters(
|
||||
command="python3",
|
||||
args=["servers/your_stdio_server.py"],
|
||||
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params) as tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available tools from Stdio MCP server: {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: Using the tools from the Stdio MCP server in a CrewAI Agent
|
||||
research_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Local Data Processor",
|
||||
goal="Process data using a local Stdio-based tool.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI that leverages local scripts via MCP for specialized tasks.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
reasoning=True,
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
processing_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Process the input data file 'data.txt' and summarize its contents.",
|
||||
expected_output="A summary of the processed data.",
|
||||
agent=research_agent,
|
||||
markdown=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[research_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[processing_task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = data_crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print("\nCrew Task Result (Stdio - Managed):\n", result)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Manual Connection Lifecycle
|
||||
|
||||
If you need finer-grained control over when the Stdio MCP server process is started and stopped, you can manage the `MCPServerAdapter` lifecycle manually.
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
You **MUST** call `mcp_server_adapter.stop()` to ensure the server process is terminated and resources are released. Using a `try...finally` block is highly recommended.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
from mcp import StdioServerParameters
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a StdioServerParameters object
|
||||
stdio_params=StdioServerParameters(
|
||||
command="python3",
|
||||
args=["servers/your_stdio_server.py"],
|
||||
env={"UV_PYTHON": "3.12", **os.environ},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter = MCPServerAdapter(server_params=stdio_params)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.start() # Manually start the connection and server process
|
||||
tools = mcp_server_adapter.tools
|
||||
print(f"Available tools (manual Stdio): {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: Using the tools with your Agent, Task, Crew setup
|
||||
manual_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Local Task Executor",
|
||||
goal="Execute a specific local task using a manually managed Stdio tool.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI proficient in controlling local processes via MCP.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
manual_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Execute the 'perform_analysis' command via the Stdio tool.",
|
||||
expected_output="Results of the analysis.",
|
||||
agent=manual_agent
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
manual_crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[manual_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[manual_task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
result = manual_crew.kickoff() # Actual inputs depend on your tool
|
||||
print("\nCrew Task Result (Stdio - Manual):\n", result)
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"An error occurred during manual Stdio MCP integration: {e}")
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
if mcp_server_adapter and mcp_server_adapter.is_connected: # Check if connected before stopping
|
||||
print("Stopping Stdio MCP server connection (manual)...")
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.stop() # **Crucial: Ensure stop is called**
|
||||
elif mcp_server_adapter: # If adapter exists but not connected (e.g. start failed)
|
||||
print("Stdio MCP server adapter was not connected. No stop needed or start failed.")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to replace placeholder paths and commands with your actual Stdio server details. The `env` parameter in `StdioServerParameters` can
|
||||
be used to set environment variables for the server process, which can be useful for configuring its behavior or providing necessary paths (like `PYTHONPATH`).
|
||||
135
docs/mcp/streamable-http.mdx
Normal file
135
docs/mcp/streamable-http.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Streamable HTTP Transport
|
||||
description: Learn how to connect CrewAI to remote MCP servers using the flexible Streamable HTTP transport.
|
||||
icon: globe
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Streamable HTTP transport provides a flexible way to connect to remote MCP servers. It's often built upon HTTP and can support various communication patterns, including request-response and streaming, sometimes utilizing Server-Sent Events (SSE) for server-to-client streams within a broader HTTP interaction.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Concepts
|
||||
|
||||
- **Remote Servers**: Designed for MCP servers hosted remotely.
|
||||
- **Flexibility**: Can support more complex interaction patterns than plain SSE, potentially including bi-directional communication if the server implements it.
|
||||
- **`MCPServerAdapter` Configuration**: You'll need to provide the server's base URL for MCP communication and specify `"streamable-http"` as the transport type.
|
||||
|
||||
## Connecting via Streamable HTTP
|
||||
|
||||
You have two primary methods for managing the connection lifecycle with a Streamable HTTP MCP server:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Fully Managed Connection (Recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
The recommended approach is to use a Python context manager (`with` statement), which handles the connection's setup and teardown automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
|
||||
server_params = {
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8001/mcp", # Replace with your actual Streamable HTTP server URL
|
||||
"transport": "streamable-http"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with MCPServerAdapter(server_params) as tools:
|
||||
print(f"Available tools from Streamable HTTP MCP server: {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
http_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="HTTP Service Integrator",
|
||||
goal="Utilize tools from a remote MCP server via Streamable HTTP.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI agent adept at interacting with complex web services.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
http_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Perform a complex data query using a tool from the Streamable HTTP server.",
|
||||
expected_output="The result of the complex data query.",
|
||||
agent=http_agent,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
http_crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[http_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[http_task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = http_crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print("\nCrew Task Result (Streamable HTTP - Managed):\n", result)
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error connecting to or using Streamable HTTP MCP server (Managed): {e}")
|
||||
print("Ensure the Streamable HTTP MCP server is running and accessible at the specified URL.")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Note:** Replace `"http://localhost:8001/mcp"` with the actual URL of your Streamable HTTP MCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Manual Connection Lifecycle
|
||||
|
||||
For scenarios requiring more explicit control, you can manage the `MCPServerAdapter` connection manually.
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
It is **critical** to call `mcp_server_adapter.stop()` when you are done to close the connection and free up resources. A `try...finally` block is the safest way to ensure this.
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from crewai_tools import MCPServerAdapter
|
||||
|
||||
server_params = {
|
||||
"url": "http://localhost:8001/mcp", # Replace with your actual Streamable HTTP server URL
|
||||
"transport": "streamable-http"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter = None
|
||||
try:
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter = MCPServerAdapter(server_params)
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.start()
|
||||
tools = mcp_server_adapter.tools
|
||||
print(f"Available tools (manual Streamable HTTP): {[tool.name for tool in tools]}")
|
||||
|
||||
manual_http_agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Advanced Web Service User",
|
||||
goal="Interact with an MCP server using manually managed Streamable HTTP connections.",
|
||||
backstory="An AI specialist in fine-tuning HTTP-based service integrations.",
|
||||
tools=tools,
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_processing_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Submit data for processing and retrieve results via Streamable HTTP.",
|
||||
expected_output="Processed data or confirmation.",
|
||||
agent=manual_http_agent
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
data_crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[manual_http_agent],
|
||||
tasks=[data_processing_task],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
process=Process.sequential
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = data_crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print("\nCrew Task Result (Streamable HTTP - Manual):\n", result)
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"An error occurred during manual Streamable HTTP MCP integration: {e}")
|
||||
print("Ensure the Streamable HTTP MCP server is running and accessible.")
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
if mcp_server_adapter and mcp_server_adapter.is_connected:
|
||||
print("Stopping Streamable HTTP MCP server connection (manual)...")
|
||||
mcp_server_adapter.stop() # **Crucial: Ensure stop is called**
|
||||
elif mcp_server_adapter:
|
||||
print("Streamable HTTP MCP server adapter was not connected. No stop needed or start failed.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Security Considerations
|
||||
|
||||
When using Streamable HTTP transport, general web security best practices are paramount:
|
||||
- **Use HTTPS**: Always prefer HTTPS (HTTP Secure) for your MCP server URLs to encrypt data in transit.
|
||||
- **Authentication**: Implement robust authentication mechanisms if your MCP server exposes sensitive tools or data.
|
||||
- **Input Validation**: Ensure your MCP server validates all incoming requests and parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
For a comprehensive guide on securing your MCP integrations, please refer to our [Security Considerations](./security.mdx) page and the official [MCP Transport Security documentation](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/concepts/transports#security-considerations).
|
||||
@@ -30,18 +30,29 @@ Set your Langfuse API keys and configure OpenTelemetry export settings to send t
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import base64
|
||||
|
||||
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
|
||||
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
|
||||
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
|
||||
os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
|
||||
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Your OpenAI key
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse client. get_client() initializes the Langfuse client using the credentials provided in the environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY="pk-lf-..."
|
||||
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY="sk-lf-..."
|
||||
LANGFUSE_AUTH=base64.b64encode(f"{LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY}:{LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY}".encode()).decode()
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel" # EU data region
|
||||
# os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel" # US data region
|
||||
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"
|
||||
|
||||
# your openai key
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-..."
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langfuse import get_client
|
||||
|
||||
langfuse = get_client()
|
||||
|
||||
# Verify connection
|
||||
if langfuse.auth_check():
|
||||
print("Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Authentication failed. Please check your credentials and host.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Initialize OpenLit
|
||||
|
||||
152
docs/observability/maxim.mdx
Normal file
152
docs/observability/maxim.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Maxim Integration
|
||||
description: Start Agent monitoring, evaluation, and observability
|
||||
icon: bars-staggered
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Maxim Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Maxim AI provides comprehensive agent monitoring, evaluation, and observability for your CrewAI applications. With Maxim's one-line integration, you can easily trace and analyse agent interactions, performance metrics, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Features: One Line Integration
|
||||
|
||||
- **End-to-End Agent Tracing**: Monitor the complete lifecycle of your agents
|
||||
- **Performance Analytics**: Track latency, tokens consumed, and costs
|
||||
- **Hyperparameter Monitoring**: View the configuration details of your agent runs
|
||||
- **Tool Call Tracking**: Observe when and how agents use their tools
|
||||
- **Advanced Visualisation**: Understand agent trajectories through intuitive dashboards
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
- Python version >=3.10
|
||||
- A Maxim account ([sign up here](https://getmaxim.ai/))
|
||||
- A CrewAI project
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install the Maxim SDK via pip:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pip install maxim-py>=3.6.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or add it to your `requirements.txt`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
maxim-py>=3.6.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Setup
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Set up environment variables
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
### Environment Variables Setup
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a `.env` file in your project root:
|
||||
|
||||
# Maxim API Configuration
|
||||
MAXIM_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
|
||||
MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID=your_repo_id_here
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Import the required packages
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
|
||||
from maxim import Maxim
|
||||
from maxim.logger.crewai import instrument_crewai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Initialise Maxim with your API key
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Initialize Maxim logger
|
||||
logger = Maxim().logger()
|
||||
|
||||
# Instrument CrewAI with just one line
|
||||
instrument_crewai(logger)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Create and run your CrewAI application as usual
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
# Create your agent
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role='Senior Research Analyst',
|
||||
goal='Uncover cutting-edge developments in AI',
|
||||
backstory="You are an expert researcher at a tech think tank...",
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Define the task
|
||||
research_task = Task(
|
||||
description="Research the latest AI advancements...",
|
||||
expected_output="",
|
||||
agent=researcher
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure and run the crew
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[researcher],
|
||||
tasks=[research_task],
|
||||
verbose=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
maxim.cleanup() # Ensure cleanup happens even if errors occur
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That's it! All your CrewAI agent interactions will now be logged and available in your Maxim dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
Check this Google Colab Notebook for a quick reference - [Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1ZKIZWsmgQQ46n8TH9zLsT1negKkJA6K8?usp=sharing)
|
||||
|
||||
## Viewing Your Traces
|
||||
|
||||
After running your CrewAI application:
|
||||
|
||||
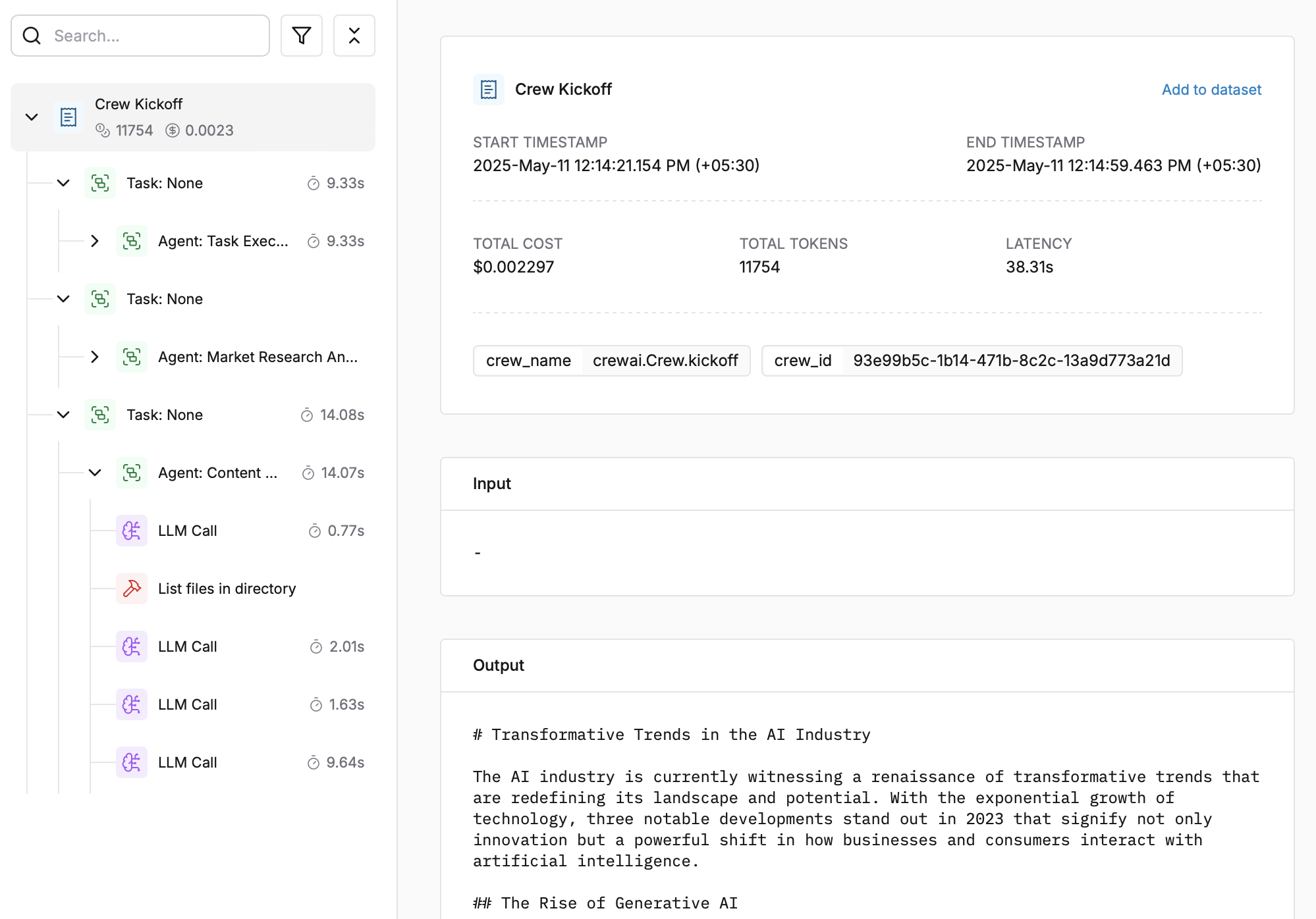
|
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to your [Maxim Dashboard](https://getmaxim.ai/dashboard)
|
||||
2. Navigate to your repository
|
||||
3. View detailed agent traces, including:
|
||||
- Agent conversations
|
||||
- Tool usage patterns
|
||||
- Performance metrics
|
||||
- Cost analytics
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues
|
||||
|
||||
- **No traces appearing**: Ensure your API key and repository ID are correc
|
||||
- Ensure you've **called `instrument_crewai()`** ***before*** running your crew. This initializes logging hooks correctly.
|
||||
- Set `debug=True` in your `instrument_crewai()` call to surface any internal errors:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
instrument_crewai(logger, debug=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Configure your agents with `verbose=True` to capture detailed logs:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CrewAgent(..., verbose=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Double-check that `instrument_crewai()` is called **before** creating or executing agents. This might be obvious, but it's a common oversight.
|
||||
|
||||
### Support
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter any issues:
|
||||
|
||||
- Check the [Maxim Documentation](https://getmaxim.ai/docs)
|
||||
- Maxim Github [Link](https://github.com/maximhq)
|
||||
@@ -7,196 +7,818 @@ icon: key
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/main/Portkey-CrewAI.png" alt="Portkey CrewAI Header Image" width="70%" />
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Portkey](https://portkey.ai/?utm_source=crewai&utm_medium=crewai&utm_campaign=crewai) is a 2-line upgrade to make your CrewAI agents reliable, cost-efficient, and fast.
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey adds 4 core production capabilities to any CrewAI agent:
|
||||
1. Routing to **200+ LLMs**
|
||||
2. Making each LLM call more robust
|
||||
3. Full-stack tracing & cost, performance analytics
|
||||
4. Real-time guardrails to enforce behavior
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting Started
|
||||
Portkey enhances CrewAI with production-readiness features, turning your experimental agent crews into robust systems by providing:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Complete observability** of every agent step, tool use, and interaction
|
||||
- **Built-in reliability** with fallbacks, retries, and load balancing
|
||||
- **Cost tracking and optimization** to manage your AI spend
|
||||
- **Access to 200+ LLMs** through a single integration
|
||||
- **Guardrails** to keep agent behavior safe and compliant
|
||||
- **Version-controlled prompts** for consistent agent performance
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation & Setup
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="Install CrewAI and Portkey">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -qU crewai portkey-ai
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Configure the LLM Client">
|
||||
To build CrewAI Agents with Portkey, you'll need two keys:
|
||||
- **Portkey API Key**: Sign up on the [Portkey app](https://app.portkey.ai/?utm_source=crewai&utm_medium=crewai&utm_campaign=crewai) and copy your API key
|
||||
- **Virtual Key**: Virtual Keys securely manage your LLM API keys in one place. Store your LLM provider API keys securely in Portkey's vault
|
||||
<Step title="Install the required packages">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U crewai portkey-ai
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
<Step title="Generate API Key" icon="lock">
|
||||
Create a Portkey API key with optional budget/rate limits from the [Portkey dashboard](https://app.portkey.ai/). You can also attach configurations for reliability, caching, and more to this key. More on this later.
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
gpt_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy", # We are using Virtual key
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_VIRTUAL_KEY", # Enter your Virtual key from Portkey
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="Create and Run Your First Agent">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
|
||||
|
||||
# Define your agents with roles and goals
|
||||
coder = Agent(
|
||||
role='Software developer',
|
||||
goal='Write clear, concise code on demand',
|
||||
backstory='An expert coder with a keen eye for software trends.',
|
||||
llm=gpt_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create tasks for your agents
|
||||
task1 = Task(
|
||||
description="Define the HTML for making a simple website with heading- Hello World! Portkey is working!",
|
||||
expected_output="A clear and concise HTML code",
|
||||
agent=coder
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiate your crew
|
||||
crew = Crew(
|
||||
agents=[coder],
|
||||
tasks=[task1],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
|:--------|:------------|
|
||||
| 🌐 Multi-LLM Support | Access OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Azure, and 250+ providers through a unified interface |
|
||||
| 🛡️ Production Reliability | Implement retries, timeouts, load balancing, and fallbacks |
|
||||
| 📊 Advanced Observability | Track 40+ metrics including costs, tokens, latency, and custom metadata |
|
||||
| 🔍 Comprehensive Logging | Debug with detailed execution traces and function call logs |
|
||||
| 🚧 Security Controls | Set budget limits and implement role-based access control |
|
||||
| 🔄 Performance Analytics | Capture and analyze feedback for continuous improvement |
|
||||
| 💾 Intelligent Caching | Reduce costs and latency with semantic or simple caching |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Production Features with Portkey Configs
|
||||
|
||||
All features mentioned below are through Portkey's Config system. Portkey's Config system allows you to define routing strategies using simple JSON objects in your LLM API calls. You can create and manage Configs directly in your code or through the Portkey Dashboard. Each Config has a unique ID for easy reference.
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Portkey-AI/docs-core/refs/heads/main/images/libraries/libraries-3.avif"/>
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Use 250+ LLMs
|
||||
Access various LLMs like Anthropic, Gemini, Mistral, Azure OpenAI, and more with minimal code changes. Switch between providers or use them together seamlessly. [Learn more about Universal API](https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/universal-api)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Easily switch between different LLM providers:
|
||||
<Step title="Configure CrewAI with Portkey">
|
||||
The integration is simple - you just need to update the LLM configuration in your CrewAI setup:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Anthropic Configuration
|
||||
anthropic_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-latest",
|
||||
from crewai import LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an LLM instance with Portkey integration
|
||||
gpt_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
api_key="dummy", # We are using a Virtual key, so this is a placeholder
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_ANTHROPIC_VIRTUAL_KEY", #You don't need provider when using Virtual keys
|
||||
trace_id="anthropic_agent"
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_LLM_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
trace_id="unique-trace-id", # Optional, for request tracing
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Azure OpenAI Configuration
|
||||
azure_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4",
|
||||
#Use them in your Crew Agents like this:
|
||||
|
||||
@agent
|
||||
def lead_market_analyst(self) -> Agent:
|
||||
return Agent(
|
||||
config=self.agents_config['lead_market_analyst'],
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
memory=False,
|
||||
llm=gpt_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
**What are Virtual Keys?** Virtual keys in Portkey securely store your LLM provider API keys (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) in an encrypted vault. They allow for easier key rotation and budget management. [Learn more about virtual keys here](https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/virtual-keys).
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
## Production Features
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Enhanced Observability
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey provides comprehensive observability for your CrewAI agents, helping you understand exactly what's happening during each execution.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Traces">
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/CrewAI%20Product%2011.1.webp"/>
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
Traces provide a hierarchical view of your crew's execution, showing the sequence of LLM calls, tool invocations, and state transitions.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Add trace_id to enable hierarchical tracing in Portkey
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_AZURE_VIRTUAL_KEY", #You don't need provider when using Virtual keys
|
||||
trace_id="azure_agent"
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
trace_id="unique-session-id" # Add unique trace ID
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Logs">
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/CrewAI%20Portkey%20Docs%20Metadata.png"/>
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey logs every interaction with LLMs, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete request and response payloads
|
||||
- Latency and token usage metrics
|
||||
- Cost calculations
|
||||
- Tool calls and function executions
|
||||
|
||||
All logs can be filtered by metadata, trace IDs, models, and more, making it easy to debug specific crew runs.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Metrics & Dashboards">
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/CrewAI%20Dashboard.png"/>
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey provides built-in dashboards that help you:
|
||||
|
||||
- Track cost and token usage across all crew runs
|
||||
- Analyze performance metrics like latency and success rates
|
||||
- Identify bottlenecks in your agent workflows
|
||||
- Compare different crew configurations and LLMs
|
||||
|
||||
You can filter and segment all metrics by custom metadata to analyze specific crew types, user groups, or use cases.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Metadata Filtering">
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/Metadata%20Filters%20from%20CrewAI.png" alt="Analytics with metadata filters" />
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
Add custom metadata to your CrewAI LLM configuration to enable powerful filtering and segmentation:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"crew_type": "research_crew",
|
||||
"environment": "production",
|
||||
"_user": "user_123", # Special _user field for user analytics
|
||||
"request_source": "mobile_app"
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This metadata can be used to filter logs, traces, and metrics on the Portkey dashboard, allowing you to analyze specific crew runs, users, or environments.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Caching
|
||||
Improve response times and reduce costs with two powerful caching modes:
|
||||
- **Simple Cache**: Perfect for exact matches
|
||||
- **Semantic Cache**: Matches responses for requests that are semantically similar
|
||||
[Learn more about Caching](https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/cache-simple-and-semantic)
|
||||
### 2. Reliability - Keep Your Crews Running Smoothly
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"cache": {
|
||||
"mode": "semantic", # or "simple" for exact matching
|
||||
When running crews in production, things can go wrong - API rate limits, network issues, or provider outages. Portkey's reliability features ensure your agents keep running smoothly even when problems occur.
|
||||
|
||||
It's simple to enable fallback in your CrewAI setup by using a Portkey Config:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Create LLM with fallback configuration
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
max_tokens=1000,
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"strategy": {
|
||||
"mode": "fallback"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"targets": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"provider": "openai",
|
||||
"api_key": "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY",
|
||||
"override_params": {"model": "gpt-4o"}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"provider": "anthropic",
|
||||
"api_key": "YOUR_ANTHROPIC_API_KEY",
|
||||
"override_params": {"model": "claude-3-opus-20240229"}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Use this LLM configuration with your agents
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This configuration will automatically try Claude if the GPT-4o request fails, ensuring your crew can continue operating.
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols="2">
|
||||
<Card title="Automatic Retries" icon="rotate" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/automatic-retries">
|
||||
Handles temporary failures automatically. If an LLM call fails, Portkey will retry the same request for the specified number of times - perfect for rate limits or network blips.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Request Timeouts" icon="clock" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/request-timeouts">
|
||||
Prevent your agents from hanging. Set timeouts to ensure you get responses (or can fail gracefully) within your required timeframes.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Conditional Routing" icon="route" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/conditional-routing">
|
||||
Send different requests to different providers. Route complex reasoning to GPT-4, creative tasks to Claude, and quick responses to Gemini based on your needs.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Fallbacks" icon="shield" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/fallbacks">
|
||||
Keep running even if your primary provider fails. Automatically switch to backup providers to maintain availability.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Load Balancing" icon="scale-balanced" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/load-balancing">
|
||||
Spread requests across multiple API keys or providers. Great for high-volume crew operations and staying within rate limits.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Prompting in CrewAI
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey's Prompt Engineering Studio helps you create, manage, and optimize the prompts used in your CrewAI agents. Instead of hardcoding prompts or instructions, use Portkey's prompt rendering API to dynamically fetch and apply your versioned prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame caption="Manage prompts in Portkey's Prompt Library">
|
||||
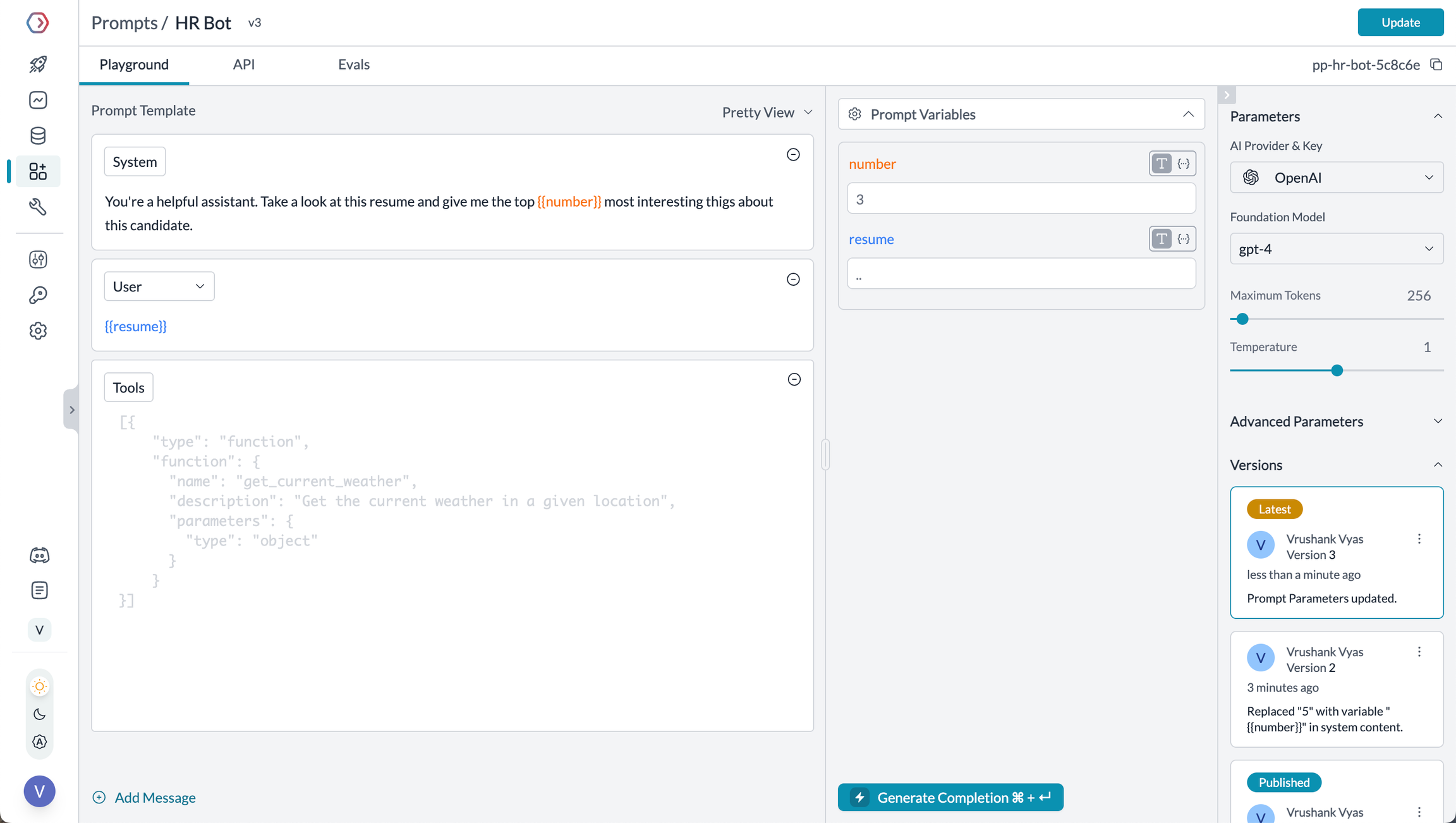
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Prompt Playground">
|
||||
Prompt Playground is a place to compare, test and deploy perfect prompts for your AI application. It's where you experiment with different models, test variables, compare outputs, and refine your prompt engineering strategy before deploying to production. It allows you to:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Iteratively develop prompts before using them in your agents
|
||||
2. Test prompts with different variables and models
|
||||
3. Compare outputs between different prompt versions
|
||||
4. Collaborate with team members on prompt development
|
||||
|
||||
This visual environment makes it easier to craft effective prompts for each step in your CrewAI agents' workflow.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Using Prompt Templates">
|
||||
The Prompt Render API retrieves your prompt templates with all parameters configured:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL, Portkey
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize Portkey admin client
|
||||
portkey_admin = Portkey(api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY")
|
||||
|
||||
# Retrieve prompt using the render API
|
||||
prompt_data = portkey_client.prompts.render(
|
||||
prompt_id="YOUR_PROMPT_ID",
|
||||
variables={
|
||||
"agent_role": "Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
backstory_agent_prompt=prompt_data.data.messages[0]["content"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up LLM with Portkey integration
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY"
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create agent using the rendered prompt
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role="Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
goal="Discover groundbreaking insights about the assigned topic",
|
||||
backstory=backstory_agent, # Use the rendered prompt
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=portkey_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Prompt Versioning">
|
||||
You can:
|
||||
- Create multiple versions of the same prompt
|
||||
- Compare performance between versions
|
||||
- Roll back to previous versions if needed
|
||||
- Specify which version to use in your code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Use a specific prompt version
|
||||
prompt_data = portkey_admin.prompts.render(
|
||||
prompt_id="YOUR_PROMPT_ID@version_number",
|
||||
variables={
|
||||
"agent_role": "Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
"agent_goal": "Discover groundbreaking insights"
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Mustache Templating for variables">
|
||||
Portkey prompts use Mustache-style templating for easy variable substitution:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
You are a {{agent_role}} with expertise in {{domain}}.
|
||||
|
||||
Your mission is to {{agent_goal}} by leveraging your knowledge
|
||||
and experience in the field.
|
||||
|
||||
Always maintain a {{tone}} tone and focus on providing {{focus_area}}.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When rendering, simply pass the variables:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt_data = portkey_admin.prompts.render(
|
||||
prompt_id="YOUR_PROMPT_ID",
|
||||
variables={
|
||||
"agent_role": "Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
"domain": "artificial intelligence",
|
||||
"agent_goal": "discover groundbreaking insights",
|
||||
"tone": "professional",
|
||||
"focus_area": "practical applications"
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Prompt Engineering Studio" icon="wand-magic-sparkles" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/prompt-library">
|
||||
Learn more about Portkey's prompt management features
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Guardrails for Safe Crews
|
||||
|
||||
Guardrails ensure your CrewAI agents operate safely and respond appropriately in all situations.
|
||||
|
||||
**Why Use Guardrails?**
|
||||
|
||||
CrewAI agents can experience various failure modes:
|
||||
- Generating harmful or inappropriate content
|
||||
- Leaking sensitive information like PII
|
||||
- Hallucinating incorrect information
|
||||
- Generating outputs in incorrect formats
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey's guardrails add protections for both inputs and outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
**Implementing Guardrails**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Create LLM with guardrails
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"input_guardrails": ["guardrails-id-xxx", "guardrails-id-yyy"],
|
||||
"output_guardrails": ["guardrails-id-zzz"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create agent with guardrailed LLM
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role="Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
goal="Discover groundbreaking insights about the assigned topic",
|
||||
backstory="You are an expert researcher with deep domain knowledge.",
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=portkey_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey's guardrails can:
|
||||
- Detect and redact PII in both inputs and outputs
|
||||
- Filter harmful or inappropriate content
|
||||
- Validate response formats against schemas
|
||||
- Check for hallucinations against ground truth
|
||||
- Apply custom business logic and rules
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Learn More About Guardrails" icon="shield-check" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/guardrails">
|
||||
Explore Portkey's guardrail features to enhance agent safety
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. User Tracking with Metadata
|
||||
|
||||
Track individual users through your CrewAI agents using Portkey's metadata system.
|
||||
|
||||
**What is Metadata in Portkey?**
|
||||
|
||||
Metadata allows you to associate custom data with each request, enabling filtering, segmentation, and analytics. The special `_user` field is specifically designed for user tracking.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure LLM with user tracking
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"_user": "user_123", # Special _user field for user analytics
|
||||
"user_tier": "premium",
|
||||
"user_company": "Acme Corp",
|
||||
"session_id": "abc-123"
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create agent with tracked LLM
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role="Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
goal="Discover groundbreaking insights about the assigned topic",
|
||||
backstory="You are an expert researcher with deep domain knowledge.",
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=portkey_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Filter Analytics by User**
|
||||
|
||||
With metadata in place, you can filter analytics by user and analyze performance metrics on a per-user basis:
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame caption="Filter analytics by user">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/Metadata%20Filters%20from%20CrewAI.png"/>
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
This enables:
|
||||
- Per-user cost tracking and budgeting
|
||||
- Personalized user analytics
|
||||
- Team or organization-level metrics
|
||||
- Environment-specific monitoring (staging vs. production)
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Learn More About Metadata" icon="tags" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/product/observability/metadata">
|
||||
Explore how to use custom metadata to enhance your analytics
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Caching for Efficient Crews
|
||||
|
||||
Implement caching to make your CrewAI agents more efficient and cost-effective:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="Simple Caching">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure LLM with simple caching
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"cache": {
|
||||
"mode": "simple"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create agent with cached LLM
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role="Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
goal="Discover groundbreaking insights about the assigned topic",
|
||||
backstory="You are an expert researcher with deep domain knowledge.",
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=portkey_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Simple caching performs exact matches on input prompts, caching identical requests to avoid redundant model executions.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tab title="Semantic Caching">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure LLM with semantic caching
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"cache": {
|
||||
"mode": "semantic"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create agent with semantically cached LLM
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role="Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
goal="Discover groundbreaking insights about the assigned topic",
|
||||
backstory="You are an expert researcher with deep domain knowledge.",
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=portkey_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Semantic caching considers the contextual similarity between input requests, caching responses for semantically similar inputs.
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Model Interoperability
|
||||
|
||||
CrewAI supports multiple LLM providers, and Portkey extends this capability by providing access to over 200 LLMs through a unified interface. You can easily switch between different models without changing your core agent logic:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import createHeaders, PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up LLMs with different providers
|
||||
openai_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY"
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
anthropic_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-latest",
|
||||
max_tokens=1000,
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="dummy",
|
||||
extra_headers=createHeaders(
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY",
|
||||
virtual_key="YOUR_ANTHROPIC_VIRTUAL_KEY"
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose which LLM to use for each agent based on your needs
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role="Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
goal="Discover groundbreaking insights about the assigned topic",
|
||||
backstory="You are an expert researcher with deep domain knowledge.",
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=openai_llm # Use anthropic_llm for Anthropic
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey provides access to LLMs from providers including:
|
||||
|
||||
- OpenAI (GPT-4o, GPT-4 Turbo, etc.)
|
||||
- Anthropic (Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Claude 3 Opus, etc.)
|
||||
- Mistral AI (Mistral Large, Mistral Medium, etc.)
|
||||
- Google Vertex AI (Gemini 1.5 Pro, etc.)
|
||||
- Cohere (Command, Command-R, etc.)
|
||||
- AWS Bedrock (Claude, Titan, etc.)
|
||||
- Local/Private Models
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Supported Providers" icon="server" href="https://portkey.ai/docs/integrations/llms">
|
||||
See the full list of LLM providers supported by Portkey
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
## Set Up Enterprise Governance for CrewAI
|
||||
|
||||
**Why Enterprise Governance?**
|
||||
If you are using CrewAI inside your organization, you need to consider several governance aspects:
|
||||
- **Cost Management**: Controlling and tracking AI spending across teams
|
||||
- **Access Control**: Managing which teams can use specific models
|
||||
- **Usage Analytics**: Understanding how AI is being used across the organization
|
||||
- **Security & Compliance**: Maintaining enterprise security standards
|
||||
- **Reliability**: Ensuring consistent service across all users
|
||||
|
||||
Portkey adds a comprehensive governance layer to address these enterprise needs. Let's implement these controls step by step.
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="Create Virtual Key">
|
||||
Virtual Keys are Portkey's secure way to manage your LLM provider API keys. They provide essential controls like:
|
||||
- Budget limits for API usage
|
||||
- Rate limiting capabilities
|
||||
- Secure API key storage
|
||||
|
||||
To create a virtual key:
|
||||
Go to [Virtual Keys](https://app.portkey.ai/virtual-keys) in the Portkey App. Save and copy the virtual key ID
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/Virtual%20Key%20from%20Portkey%20Docs.png" width="500"/>
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
Save your virtual key ID - you'll need it for the next step.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Create Default Config">
|
||||
Configs in Portkey define how your requests are routed, with features like advanced routing, fallbacks, and retries.
|
||||
|
||||
To create your config:
|
||||
1. Go to [Configs](https://app.portkey.ai/configs) in Portkey dashboard
|
||||
2. Create new config with:
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"virtual_key": "YOUR_VIRTUAL_KEY_FROM_STEP1",
|
||||
"override_params": {
|
||||
"model": "gpt-4o" // Your preferred model name
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. Save and note the Config name for the next step
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/CrewAI%20Portkey%20Docs%20Config.png" width="500"/>
|
||||
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Configure Portkey API Key">
|
||||
Now create a Portkey API key and attach the config you created in Step 2:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to [API Keys](https://app.portkey.ai/api-keys) in Portkey and Create new API key
|
||||
2. Select your config from `Step 2`
|
||||
3. Generate and save your API key
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/CrewAI%20API%20Key.png" width="500"/>
|
||||
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
|
||||
<Step title="Connect to CrewAI">
|
||||
After setting up your Portkey API key with the attached config, connect it to your CrewAI agents:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai import Agent, LLM
|
||||
from portkey_ai import PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure LLM with your API key
|
||||
portkey_llm = LLM(
|
||||
model="gpt-4o",
|
||||
base_url=PORTKEY_GATEWAY_URL,
|
||||
api_key="YOUR_PORTKEY_API_KEY"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create agent with Portkey-enabled LLM
|
||||
researcher = Agent(
|
||||
role="Senior Research Scientist",
|
||||
goal="Discover groundbreaking insights about the assigned topic",
|
||||
backstory="You are an expert researcher with deep domain knowledge.",
|
||||
verbose=True,
|
||||
llm=portkey_llm
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="Step 1: Implement Budget Controls & Rate Limits">
|
||||
### Step 1: Implement Budget Controls & Rate Limits
|
||||
|
||||
Virtual Keys enable granular control over LLM access at the team/department level. This helps you:
|
||||
- Set up [budget limits](https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/virtual-keys/budget-limits)
|
||||
- Prevent unexpected usage spikes using Rate limits
|
||||
- Track departmental spending
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setting Up Department-Specific Controls:
|
||||
1. Navigate to [Virtual Keys](https://app.portkey.ai/virtual-keys) in Portkey dashboard
|
||||
2. Create new Virtual Key for each department with budget limits and rate limits
|
||||
3. Configure department-specific limits
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/refs/heads/main/Virtual%20Key%20from%20Portkey%20Docs.png" width="500"/>
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Step 2: Define Model Access Rules">
|
||||
### Step 2: Define Model Access Rules
|
||||
|
||||
As your AI usage scales, controlling which teams can access specific models becomes crucial. Portkey Configs provide this control layer with features like:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Access Control Features:
|
||||
- **Model Restrictions**: Limit access to specific models
|
||||
- **Data Protection**: Implement guardrails for sensitive data
|
||||
- **Reliability Controls**: Add fallbacks and retry logic
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example Configuration:
|
||||
Here's a basic configuration to route requests to OpenAI, specifically using GPT-4o:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"strategy": {
|
||||
"mode": "single"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"targets": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"virtual_key": "YOUR_OPENAI_VIRTUAL_KEY",
|
||||
"override_params": {
|
||||
"model": "gpt-4o"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Production Reliability
|
||||
Portkey provides comprehensive reliability features:
|
||||
- **Automatic Retries**: Handle temporary failures gracefully
|
||||
- **Request Timeouts**: Prevent hanging operations
|
||||
- **Conditional Routing**: Route requests based on specific conditions
|
||||
- **Fallbacks**: Set up automatic provider failovers
|
||||
- **Load Balancing**: Distribute requests efficiently
|
||||
Create your config on the [Configs page](https://app.portkey.ai/configs) in your Portkey dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
[Learn more about Reliability Features](https://portkey.ai/docs/product/ai-gateway/)
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
Configs can be updated anytime to adjust controls without affecting running applications.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Step 3: Implement Access Controls">
|
||||
### Step 3: Implement Access Controls
|
||||
|
||||
Create User-specific API keys that automatically:
|
||||
- Track usage per user/team with the help of virtual keys
|
||||
- Apply appropriate configs to route requests
|
||||
- Collect relevant metadata to filter logs
|
||||
- Enforce access permissions
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Metrics
|
||||
Create API keys through:
|
||||
- [Portkey App](https://app.portkey.ai/)
|
||||
- [API Key Management API](/api-reference/admin-api/control-plane/api-keys/create-api-key)
|
||||
|
||||
Agent runs are complex. Portkey automatically logs **40+ comprehensive metrics** for your AI agents, including cost, tokens used, latency, etc. Whether you need a broad overview or granular insights into your agent runs, Portkey's customizable filters provide the metrics you need.
|
||||
Example using Python SDK:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from portkey_ai import Portkey
|
||||
|
||||
portkey = Portkey(api_key="YOUR_ADMIN_API_KEY")
|
||||
|
||||
- Cost per agent interaction
|
||||
- Response times and latency
|
||||
- Token usage and efficiency
|
||||
- Success/failure rates
|
||||
- Cache hit rates
|
||||
api_key = portkey.api_keys.create(
|
||||
name="engineering-team",
|
||||
type="organisation",
|
||||
workspace_id="YOUR_WORKSPACE_ID",
|
||||
defaults={
|
||||
"config_id": "your-config-id",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"environment": "production",
|
||||
"department": "engineering"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
scopes=["logs.view", "configs.read"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/blob/main/Portkey-Dashboard.png?raw=true" width="70%" alt="Portkey Dashboard" />
|
||||
For detailed key management instructions, see our [API Keys documentation](/api-reference/admin-api/control-plane/api-keys/create-api-key).
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Detailed Logging
|
||||
Logs are essential for understanding agent behavior, diagnosing issues, and improving performance. They provide a detailed record of agent activities and tool use, which is crucial for debugging and optimizing processes.
|
||||
<Accordion title="Step 4: Deploy & Monitor">
|
||||
### Step 4: Deploy & Monitor
|
||||
After distributing API keys to your team members, your enterprise-ready CrewAI setup is ready to go. Each team member can now use their designated API keys with appropriate access levels and budget controls.
|
||||
|
||||
Monitor usage in Portkey dashboard:
|
||||
- Cost tracking by department
|
||||
- Model usage patterns
|
||||
- Request volumes
|
||||
- Error rates
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
Access a dedicated section to view records of agent executions, including parameters, outcomes, function calls, and errors. Filter logs based on multiple parameters such as trace ID, model, tokens used, and metadata.
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary><b>Traces</b></summary>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/main/Portkey-Traces.png" alt="Portkey Traces" width="70%" />
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
### Enterprise Features Now Available
|
||||
**Your CrewAI integration now has:**
|
||||
- Departmental budget controls
|
||||
- Model access governance
|
||||
- Usage tracking & attribution
|
||||
- Security guardrails
|
||||
- Reliability features
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary><b>Logs</b></summary>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddharthsambharia-portkey/Portkey-Product-Images/main/Portkey-Logs.png" alt="Portkey Logs" width="70%" />
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
## Frequently Asked Questions
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Enterprise Security Features
|
||||
- Set budget limit and rate limts per Virtual Key (disposable API keys)
|
||||
- Implement role-based access control
|
||||
- Track system changes with audit logs
|
||||
- Configure data retention policies
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="How does Portkey enhance CrewAI?">
|
||||
Portkey adds production-readiness to CrewAI through comprehensive observability (traces, logs, metrics), reliability features (fallbacks, retries, caching), and access to 200+ LLMs through a unified interface. This makes it easier to debug, optimize, and scale your agent applications.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Can I use Portkey with existing CrewAI applications?">
|
||||
Yes! Portkey integrates seamlessly with existing CrewAI applications. You just need to update your LLM configuration code with the Portkey-enabled version. The rest of your agent and crew code remains unchanged.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Does Portkey work with all CrewAI features?">
|
||||
Portkey supports all CrewAI features, including agents, tools, human-in-the-loop workflows, and all task process types (sequential, hierarchical, etc.). It adds observability and reliability without limiting any of the framework's functionality.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed information on creating and managing Configs, visit the [Portkey documentation](https://docs.portkey.ai/product/ai-gateway/configs).
|
||||
<Accordion title="Can I track usage across multiple agents in a crew?">
|
||||
Yes, Portkey allows you to use a consistent `trace_id` across multiple agents in a crew to track the entire workflow. This is especially useful for complex crews where you want to understand the full execution path across multiple agents.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="How do I filter logs and traces for specific crew runs?">
|
||||
Portkey allows you to add custom metadata to your LLM configuration, which you can then use for filtering. Add fields like `crew_name`, `crew_type`, or `session_id` to easily find and analyze specific crew executions.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Can I use my own API keys with Portkey?">
|
||||
Yes! Portkey uses your own API keys for the various LLM providers. It securely stores them as virtual keys, allowing you to easily manage and rotate keys without changing your code.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
- [📘 Portkey Documentation](https://docs.portkey.ai)
|
||||
- [📊 Portkey Dashboard](https://app.portkey.ai/?utm_source=crewai&utm_medium=crewai&utm_campaign=crewai)
|
||||
- [🐦 Twitter](https://twitter.com/portkeyai)
|
||||
- [💬 Discord Community](https://discord.gg/DD7vgKK299)
|
||||
<CardGroup cols="3">
|
||||
<Card title="CrewAI Docs" icon="book" href="https://docs.crewai.com/">
|
||||
<p>Official CrewAI documentation</p>
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Book a Demo" icon="calendar" href="https://calendly.com/portkey-ai">
|
||||
<p>Get personalized guidance on implementing this integration</p>
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
@@ -212,7 +212,7 @@ Follow the steps below to get Crewing! 🚣♂️
|
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to your CrewAI Enterprise account (create a free account at [app.crewai.com](https://app.crewai.com))
|
||||
2. Open Crew Studio
|
||||
3. Type what is the automation you're tryign to build
|
||||
3. Type what is the automation you're trying to build
|
||||
4. Create your tasks visually and connect them in sequence
|
||||
5. Configure your inputs and click "Download Code" or "Deploy"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
47
docs/style.css
Normal file
47
docs/style.css
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
/* Fix for Frame component width issue in installation docs */
|
||||
/* Ensures file structure displays with proper width */
|
||||
|
||||
/* CSS Custom Properties for maintainability */
|
||||
:root {
|
||||
--frame-min-width: 300px;
|
||||
--frame-width: 100%;
|
||||
--frame-pre-min-width: 280px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Consolidated Frame component selectors */
|
||||
.frame-container,
|
||||
[data-component="frame"],
|
||||
.frame,
|
||||
div[class*="frame"] {
|
||||
min-width: var(--frame-min-width);
|
||||
width: var(--frame-width);
|
||||
overflow-x: auto;
|
||||
-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch; /* Smooth scrolling on iOS */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Pre elements within Frame components */
|
||||
.frame-container pre,
|
||||
[data-component="frame"] pre,
|
||||
.frame pre,
|
||||
div[class*="frame"] pre {
|
||||
min-width: var(--frame-pre-min-width);
|
||||
white-space: pre;
|
||||
overflow-x: auto;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Responsive design for smaller screens */
|
||||
@media screen and (max-width: 768px) {
|
||||
.frame-container,
|
||||
[data-component="frame"],
|
||||
.frame,
|
||||
div[class*="frame"] {
|
||||
min-width: 100%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.frame-container pre,
|
||||
[data-component="frame"] pre,
|
||||
.frame pre,
|
||||
div[class*="frame"] pre {
|
||||
min-width: 100%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -56,6 +56,10 @@ These tools enable your agents to interact with the web, extract data from websi
|
||||
<Card title="Stagehand Tool" icon="hand" href="/tools/web-scraping/stagehandtool">
|
||||
Intelligent browser automation with natural language commands.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Oxylabs Scraper Tool" icon="globe" href="/tools/web-scraping/oxylabsscraperstool">
|
||||
Access web data at scale with Oxylabs.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## **Common Use Cases**
|
||||
@@ -100,4 +104,4 @@ agent = Agent(
|
||||
- **JavaScript-Heavy Sites**: Use `SeleniumScrapingTool` for dynamic content
|
||||
- **Scale & Performance**: Use `FirecrawlScrapeWebsiteTool` for high-volume scraping
|
||||
- **Cloud Infrastructure**: Use `BrowserBaseLoadTool` for scalable browser automation
|
||||
- **Complex Workflows**: Use `StagehandTool` for intelligent browser interactions
|
||||
- **Complex Workflows**: Use `StagehandTool` for intelligent browser interactions
|
||||
|
||||
236
docs/tools/web-scraping/oxylabsscraperstool.mdx
Normal file
236
docs/tools/web-scraping/oxylabsscraperstool.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Oxylabs Scrapers
|
||||
description: >
|
||||
Oxylabs Scrapers allow to easily access the information from the respective sources. Please see the list of available sources below:
|
||||
- `Amazon Product`
|
||||
- `Amazon Search`
|
||||
- `Google Seach`
|
||||
- `Universal`
|
||||
icon: globe
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Get the credentials by creating an Oxylabs Account [here](https://oxylabs.io).
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install 'crewai[tools]' oxylabs
|
||||
```
|
||||
Check [Oxylabs Documentation](https://developers.oxylabs.io/scraping-solutions/web-scraper-api/targets) to get more information about API parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
# `OxylabsAmazonProductScraperTool`
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsAmazonProductScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsAmazonProductScraperTool()
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(query="AAAAABBBBCC")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
- `query` - 10-symbol ASIN code.
|
||||
- `domain` - domain localization for Amazon.
|
||||
- `geo_location` - the _Deliver to_ location.
|
||||
- `user_agent_type` - device type and browser.
|
||||
- `render` - enables JavaScript rendering when set to `html`.
|
||||
- `callback_url` - URL to your callback endpoint.
|
||||
- `context` - Additional advanced settings and controls for specialized requirements.
|
||||
- `parse` - returns parsed data when set to true.
|
||||
- `parsing_instructions` - define your own parsing and data transformation logic that will be executed on an HTML scraping result.
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsAmazonProductScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsAmazonProductScraperTool(
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"domain": "com",
|
||||
"parse": True,
|
||||
"context": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "autoselect_variant",
|
||||
"value": True
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(query="AAAAABBBBCC")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# `OxylabsAmazonSearchScraperTool`
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsAmazonSearchScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsAmazonSearchScraperTool()
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(query="headsets")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
- `query` - Amazon search term.
|
||||
- `domain` - Domain localization for Bestbuy.
|
||||
- `start_page` - starting page number.
|
||||
- `pages` - number of pages to retrieve.
|
||||
- `geo_location` - the _Deliver to_ location.
|
||||
- `user_agent_type` - device type and browser.
|
||||
- `render` - enables JavaScript rendering when set to `html`.
|
||||
- `callback_url` - URL to your callback endpoint.
|
||||
- `context` - Additional advanced settings and controls for specialized requirements.
|
||||
- `parse` - returns parsed data when set to true.
|
||||
- `parsing_instructions` - define your own parsing and data transformation logic that will be executed on an HTML scraping result.
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsAmazonSearchScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsAmazonSearchScraperTool(
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"domain": 'nl',
|
||||
"start_page": 2,
|
||||
"pages": 2,
|
||||
"parse": True,
|
||||
"context": [
|
||||
{'key': 'category_id', 'value': 16391693031}
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(query='nirvana tshirt')
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# `OxylabsGoogleSearchScraperTool`
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsGoogleSearchScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsGoogleSearchScraperTool()
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(query="iPhone 16")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
- `query` - search keyword.
|
||||
- `domain` - domain localization for Google.
|
||||
- `start_page` - starting page number.
|
||||
- `pages` - number of pages to retrieve.
|
||||
- `limit` - number of results to retrieve in each page.
|
||||
- `locale` - `Accept-Language` header value which changes your Google search page web interface language.
|
||||
- `geo_location` - the geographical location that the result should be adapted for. Using this parameter correctly is extremely important to get the right data.
|
||||
- `user_agent_type` - device type and browser.
|
||||
- `render` - enables JavaScript rendering when set to `html`.
|
||||
- `callback_url` - URL to your callback endpoint.
|
||||
- `context` - Additional advanced settings and controls for specialized requirements.
|
||||
- `parse` - returns parsed data when set to true.
|
||||
- `parsing_instructions` - define your own parsing and data transformation logic that will be executed on an HTML scraping result.
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsGoogleSearchScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsGoogleSearchScraperTool(
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"parse": True,
|
||||
"geo_location": "Paris, France",
|
||||
"user_agent_type": "tablet",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(query="iPhone 16")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# `OxylabsUniversalScraperTool`
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsUniversalScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsUniversalScraperTool()
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(url="https://ip.oxylabs.io")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
- `url` - website url to scrape.
|
||||
- `user_agent_type` - device type and browser.
|
||||
- `geo_location` - sets the proxy's geolocation to retrieve data.
|
||||
- `render` - enables JavaScript rendering when set to `html`.
|
||||
- `callback_url` - URL to your callback endpoint.
|
||||
- `context` - Additional advanced settings and controls for specialized requirements.
|
||||
- `parse` - returns parsed data when set to `true`, as long as a dedicated parser exists for the submitted URL's page type.
|
||||
- `parsing_instructions` - define your own parsing and data transformation logic that will be executed on an HTML scraping result.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from crewai_tools import OxylabsUniversalScraperTool
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure OXYLABS_USERNAME and OXYLABS_PASSWORD variables are set
|
||||
tool = OxylabsUniversalScraperTool(
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"render": "html",
|
||||
"user_agent_type": "mobile",
|
||||
"context": [
|
||||
{"key": "force_headers", "value": True},
|
||||
{"key": "force_cookies", "value": True},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "headers",
|
||||
"value": {
|
||||
"Custom-Header-Name": "custom header content",
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "cookies",
|
||||
"value": [
|
||||
{"key": "NID", "value": "1234567890"},
|
||||
{"key": "1P JAR", "value": "0987654321"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"key": "http_method", "value": "get"},
|
||||
{"key": "follow_redirects", "value": True},
|
||||
{"key": "successful_status_codes", "value": [808, 909]},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = tool.run(url="https://ip.oxylabs.io")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
216
mkdocs.yml
216
mkdocs.yml
@@ -1,216 +0,0 @@
|
||||
site_name: crewAI
|
||||
site_author: crewAI, Inc
|
||||
site_description: Cutting-edge framework for orchestrating role-playing, autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks.
|
||||
repo_name: crewAI
|
||||
repo_url: https://github.com/crewAIInc/crewAI
|
||||
site_url: https://docs.crewai.com
|
||||
edit_uri: edit/main/docs/
|
||||
copyright: Copyright © 2024 crewAI, Inc
|
||||
|
||||
markdown_extensions:
|
||||
- abbr
|
||||
- admonition
|
||||
- pymdownx.details
|
||||
- attr_list
|
||||
- def_list
|
||||
- footnotes
|
||||
- md_in_html
|
||||
- toc:
|
||||
permalink: true
|
||||
- pymdownx.arithmatex:
|
||||
generic: true
|
||||
- pymdownx.betterem:
|
||||
smart_enable: all
|
||||
- pymdownx.caret
|
||||
- pymdownx.emoji:
|
||||
emoji_generator: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.to_svg
|
||||
emoji_index: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.twemoji
|
||||
- pymdownx.highlight:
|
||||
anchor_linenums: true
|
||||
line_spans: __span
|
||||
pygments_lang_class: true
|
||||
- pymdownx.inlinehilite
|
||||
- pymdownx.keys
|
||||
- pymdownx.magiclink:
|
||||
normalize_issue_symbols: true
|
||||
repo_url_shorthand: true
|
||||
user: joaomdmoura
|
||||
repo: crewAI
|
||||
- pymdownx.mark
|
||||
- pymdownx.smartsymbols
|
||||
- pymdownx.snippets:
|
||||
auto_append:
|
||||
- includes/mkdocs.md
|
||||
- pymdownx.superfences:
|
||||
custom_fences:
|
||||
- name: mermaid
|
||||
class: mermaid
|
||||
format: !!python/name:pymdownx.superfences.fence_code_format
|
||||
- pymdownx.tabbed:
|
||||
alternate_style: true
|
||||
combine_header_slug: true
|
||||
slugify: !!python/object/apply:pymdownx.slugs.slugify
|
||||
kwds:
|
||||
case: lower
|
||||
- pymdownx.tasklist:
|
||||
custom_checkbox: true
|
||||
- pymdownx.tilde
|
||||
theme:
|
||||
name: material
|
||||
language: en
|
||||
icon:
|
||||
repo: fontawesome/brands/github
|
||||
edit: material/pencil
|
||||
view: material/eye
|
||||
admonition:
|
||||
note: octicons/light-bulb-16
|
||||
abstract: octicons/checklist-16
|
||||
info: octicons/info-16
|
||||
tip: octicons/squirrel-16
|
||||
success: octicons/check-16
|
||||
question: octicons/question-16
|
||||
warning: octicons/alert-16
|
||||
failure: octicons/x-circle-16
|
||||
danger: octicons/zap-16
|
||||
bug: octicons/bug-16
|
||||
example: octicons/beaker-16
|
||||
quote: octicons/quote-16
|
||||
|
||||
palette:
|
||||
- scheme: default
|
||||
primary: deep orange
|
||||
accent: deep orange
|
||||
toggle:
|
||||
icon: material/brightness-7
|
||||
name: Switch to dark mode
|
||||
- scheme: slate
|
||||
primary: deep orange
|
||||
accent: deep orange
|
||||
toggle:
|
||||
icon: material/brightness-4
|
||||
name: Switch to light mode
|
||||
features:
|
||||
- announce.dismiss
|
||||
- content.action.edit
|
||||
- content.action.view
|
||||
- content.code.annotate
|
||||
- content.code.copy
|
||||
- content.code.select
|
||||
- content.tabs.link
|
||||
- content.tooltips
|
||||
- header.autohide
|
||||
- navigation.footer
|
||||
- navigation.indexes
|
||||
# - navigation.prune
|
||||
# - navigation.sections
|
||||
# - navigation.tabs
|
||||
- search.suggest
|
||||
- navigation.instant
|
||||
- navigation.instant.progress
|
||||
- navigation.instant.prefetch
|
||||
- navigation.tracking
|
||||
# - navigation.expand
|
||||
- navigation.path
|
||||
- navigation.top
|
||||
- toc.follow
|
||||
- toc.integrate
|
||||
- search.highlight
|
||||
- search.share
|
||||
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- Home: '/'
|
||||
- Getting Started:
|
||||
- Installing CrewAI: 'getting-started/Installing-CrewAI.md'
|
||||
- Starting a new CrewAI project: 'getting-started/Start-a-New-CrewAI-Project-Template-Method.md'
|
||||
- Core Concepts:
|
||||
- Agents: 'core-concepts/Agents.md'
|
||||
- Tasks: 'core-concepts/Tasks.md'
|
||||
- Tools: 'core-concepts/Tools.md'
|
||||
- Processes: 'core-concepts/Processes.md'
|
||||
- Crews: 'core-concepts/Crews.md'
|
||||
- Collaboration: 'core-concepts/Collaboration.md'
|
||||
- Training: 'core-concepts/Training-Crew.md'
|
||||
- Memory: 'core-concepts/Memory.md'
|
||||
- Planning: 'core-concepts/Planning.md'
|
||||
- Testing: 'core-concepts/Testing.md'
|
||||
- Using LangChain Tools: 'core-concepts/Using-LangChain-Tools.md'
|
||||
- Using LlamaIndex Tools: 'core-concepts/Using-LlamaIndex-Tools.md'
|
||||
- How to Guides:
|
||||
- Create Custom Tools: 'how-to/Create-Custom-Tools.md'
|
||||
- Using Sequential Process: 'how-to/Sequential.md'
|
||||
- Using Hierarchical Process: 'how-to/Hierarchical.md'
|
||||
- Create your own Manager Agent: 'how-to/Your-Own-Manager-Agent.md'
|
||||
- Connecting to any LLM: 'how-to/LLM-Connections.md'
|
||||
- Customizing Agents: 'how-to/Customizing-Agents.md'
|
||||
- Coding Agents: 'how-to/Coding-Agents.md'
|
||||
- Forcing Tool Output as Result: 'how-to/Force-Tool-Ouput-as-Result.md'
|
||||
- Human Input on Execution: 'how-to/Human-Input-on-Execution.md'
|
||||
- Kickoff a Crew Asynchronously: 'how-to/Kickoff-async.md'
|
||||
- Kickoff a Crew for a List: 'how-to/Kickoff-for-each.md'
|
||||
- Replay from a specific task from a kickoff: 'how-to/Replay-tasks-from-latest-Crew-Kickoff.md'
|
||||
- Conditional Tasks: 'how-to/Conditional-Tasks.md'
|
||||
- Agent Monitoring with AgentOps: 'how-to/AgentOps-Observability.md'
|
||||
- Agent Monitoring with LangTrace: 'how-to/Langtrace-Observability.md'
|
||||
- Agent Monitoring with OpenLIT: 'how-to/openlit-Observability.md'
|
||||
- Agent Monitoring with MLflow: 'how-to/mlflow-Observability.md'
|
||||
- Tools Docs:
|
||||
- Browserbase Web Loader: 'tools/BrowserbaseLoadTool.md'
|
||||
- Code Docs RAG Search: 'tools/CodeDocsSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Code Interpreter: 'tools/CodeInterpreterTool.md'
|
||||
- Composio Tools: 'tools/ComposioTool.md'
|
||||
- CSV RAG Search: 'tools/CSVSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- DALL-E Tool: 'tools/DALL-ETool.md'
|
||||
- Directory RAG Search: 'tools/DirectorySearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Directory Read: 'tools/DirectoryReadTool.md'
|
||||
- Docx Rag Search: 'tools/DOCXSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- EXA Search Web Loader: 'tools/EXASearchTool.md'
|
||||
- File Read: 'tools/FileReadTool.md'
|
||||
- File Write: 'tools/FileWriteTool.md'
|
||||
- Firecrawl Crawl Website Tool: 'tools/FirecrawlCrawlWebsiteTool.md'
|
||||
- Firecrawl Scrape Website Tool: 'tools/FirecrawlScrapeWebsiteTool.md'
|
||||
- Firecrawl Search Tool: 'tools/FirecrgstawlSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Github RAG Search: 'tools/GitHubSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Google Serper Search: 'tools/SerperDevTool.md'
|
||||
- JSON RAG Search: 'tools/JSONSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- MDX RAG Search: 'tools/MDXSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- MySQL Tool: 'tools/MySQLTool.md'
|
||||
- NL2SQL Tool: 'tools/NL2SQLTool.md'
|
||||
- PDF RAG Search: 'tools/PDFSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- PG RAG Search: 'tools/PGSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Scrape Website: 'tools/ScrapeWebsiteTool.md'
|
||||
- Selenium Scraper: 'tools/SeleniumScrapingTool.md'
|
||||
- Spider Scraper: 'tools/SpiderTool.md'
|
||||
- TXT RAG Search: 'tools/TXTSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Vision Tool: 'tools/VisionTool.md'
|
||||
- Website RAG Search: 'tools/WebsiteSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- XML RAG Search: 'tools/XMLSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Youtube Channel RAG Search: 'tools/YoutubeChannelSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Youtube Video RAG Search: 'tools/YoutubeVideoSearchTool.md'
|
||||
- Examples:
|
||||
- Trip Planner Crew: https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI-examples/tree/main/trip_planner"
|
||||
- Create Instagram Post: https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI-examples/tree/main/instagram_post"
|
||||
- Stock Analysis: https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI-examples/tree/main/stock_analysis"
|
||||
- Game Generator: https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI-examples/tree/main/game-builder-crew"
|
||||
- Drafting emails with LangGraph: https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI-examples/tree/main/CrewAI-LangGraph"
|
||||
- Landing Page Generator: https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI-examples/tree/main/landing_page_generator"
|
||||
- Prepare for meetings: https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI-examples/tree/main/prep-for-a-meeting"
|
||||
- Telemetry: 'telemetry/Telemetry.md'
|
||||
- Change Log: 'https://github.com/crewAIInc/crewAI/releases'
|
||||
|
||||
extra_css:
|
||||
- stylesheets/output.css
|
||||
- stylesheets/extra.css
|
||||
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- social
|
||||
- search
|
||||
|
||||
extra:
|
||||
analytics:
|
||||
provider: google
|
||||
property: G-N3Q505TMQ6
|
||||
social:
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/brands/x-twitter
|
||||
link: https://x.com/crewAIInc
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/brands/github
|
||||
link: https://github.com/crewAIInc/crewAI
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
||||
[project]
|
||||
name = "crewai"
|
||||
version = "0.121.0"
|
||||
version = "0.130.0"
|
||||
description = "Cutting-edge framework for orchestrating role-playing, autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks."
|
||||
readme = "README.md"
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.13"
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.14"
|
||||
authors = [
|
||||
{ name = "Joao Moura", email = "joao@crewai.com" }
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ dependencies = [
|
||||
# Core Dependencies
|
||||
"pydantic>=2.4.2",
|
||||
"openai>=1.13.3",
|
||||
"litellm==1.68.0",
|
||||
"litellm==1.72.0",
|
||||
"instructor>=1.3.3",
|
||||
# Text Processing
|
||||
"pdfplumber>=0.11.4",
|
||||
@@ -22,6 +22,8 @@ dependencies = [
|
||||
"opentelemetry-exporter-otlp-proto-http>=1.30.0",
|
||||
# Data Handling
|
||||
"chromadb>=0.5.23",
|
||||
"tokenizers>=0.20.3",
|
||||
"onnxruntime==1.22.0",
|
||||
"openpyxl>=3.1.5",
|
||||
"pyvis>=0.3.2",
|
||||
# Authentication and Security
|
||||
@@ -45,12 +47,11 @@ Documentation = "https://docs.crewai.com"
|
||||
Repository = "https://github.com/crewAIInc/crewAI"
|
||||
|
||||
[project.optional-dependencies]
|
||||
tools = ["crewai-tools~=0.45.0"]
|
||||
tools = ["crewai-tools~=0.47.1"]
|
||||
embeddings = [
|
||||
"tiktoken~=0.7.0"
|
||||
"tiktoken~=0.8.0"
|
||||
]
|
||||
agentops = ["agentops>=0.3.0"]
|
||||
fastembed = ["fastembed>=0.4.1"]
|
||||
pdfplumber = [
|
||||
"pdfplumber>=0.11.4",
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -73,11 +74,6 @@ dev-dependencies = [
|
||||
"ruff>=0.8.2",
|
||||
"mypy>=1.10.0",
|
||||
"pre-commit>=3.6.0",
|
||||
"mkdocs>=1.4.3",
|
||||
"mkdocstrings>=0.22.0",
|
||||
"mkdocstrings-python>=1.1.2",
|
||||
"mkdocs-material>=9.5.7",
|
||||
"mkdocs-material-extensions>=1.3.1",
|
||||
"pillow>=10.2.0",
|
||||
"cairosvg>=2.7.1",
|
||||
"pytest>=8.0.0",
|
||||
@@ -100,6 +96,27 @@ exclude = ["cli/templates"]
|
||||
[tool.bandit]
|
||||
exclude_dirs = ["src/crewai/cli/templates"]
|
||||
|
||||
# PyTorch index configuration, since torch 2.5.0 is not compatible with python 3.13
|
||||
[[tool.uv.index]]
|
||||
name = "pytorch-nightly"
|
||||
url = "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cpu"
|
||||
explicit = true
|
||||
|
||||
[[tool.uv.index]]
|
||||
name = "pytorch"
|
||||
url = "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu"
|
||||
explicit = true
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.uv.sources]
|
||||
torch = [
|
||||
{ index = "pytorch-nightly", marker = "python_version >= '3.13'" },
|
||||
{ index = "pytorch", marker = "python_version < '3.13'" },
|
||||
]
|
||||
torchvision = [
|
||||
{ index = "pytorch-nightly", marker = "python_version >= '3.13'" },
|
||||
{ index = "pytorch", marker = "python_version < '3.13'" },
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[build-system]
|
||||
requires = ["hatchling"]
|
||||
build-backend = "hatchling.build"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ warnings.filterwarnings(
|
||||
category=UserWarning,
|
||||
module="pydantic.main",
|
||||
)
|
||||
__version__ = "0.121.0"
|
||||
__version__ = "0.130.0"
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
"Agent",
|
||||
"Crew",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Literal, Optional, Sequence, Type, Union
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Literal, Optional, Sequence, Tuple, Type, Union
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import Field, InstanceOf, PrivateAttr, model_validator
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -155,6 +155,13 @@ class Agent(BaseAgent):
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
description="The Agent's role to be used from your repository.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
guardrail: Optional[Union[Callable[[Any], Tuple[bool, Any]], str]] = Field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
description="Function or string description of a guardrail to validate agent output"
|
||||
)
|
||||
guardrail_max_retries: int = Field(
|
||||
default=3, description="Maximum number of retries when guardrail fails"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@model_validator(mode="before")
|
||||
def validate_from_repository(cls, v):
|
||||
@@ -200,6 +207,7 @@ class Agent(BaseAgent):
|
||||
collection_name=self.role,
|
||||
storage=self.knowledge_storage or None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.knowledge.add_sources()
|
||||
except (TypeError, ValueError) as e:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Invalid Knowledge Configuration: {str(e)}")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -243,21 +251,28 @@ class Agent(BaseAgent):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.reasoning:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.reasoning_handler import AgentReasoning, AgentReasoningOutput
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.reasoning_handler import (
|
||||
AgentReasoning,
|
||||
AgentReasoningOutput,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
reasoning_handler = AgentReasoning(task=task, agent=self)
|
||||
reasoning_output: AgentReasoningOutput = reasoning_handler.handle_agent_reasoning()
|
||||
|
||||
reasoning_output: AgentReasoningOutput = (
|
||||
reasoning_handler.handle_agent_reasoning()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the reasoning plan to the task description
|
||||
task.description += f"\n\nReasoning Plan:\n{reasoning_output.plan.plan}"
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
if hasattr(self, '_logger'):
|
||||
self._logger.log("error", f"Error during reasoning process: {str(e)}")
|
||||
if hasattr(self, "_logger"):
|
||||
self._logger.log(
|
||||
"error", f"Error during reasoning process: {str(e)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(f"Error during reasoning process: {str(e)}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
self._inject_date_to_task(task)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if self.tools_handler:
|
||||
self.tools_handler.last_used_tool = {} # type: ignore # Incompatible types in assignment (expression has type "dict[Never, Never]", variable has type "ToolCalling")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -622,22 +637,33 @@ class Agent(BaseAgent):
|
||||
"""Inject the current date into the task description if inject_date is enabled."""
|
||||
if self.inject_date:
|
||||
from datetime import datetime
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
valid_format_codes = ['%Y', '%m', '%d', '%H', '%M', '%S', '%B', '%b', '%A', '%a']
|
||||
valid_format_codes = [
|
||||
"%Y",
|
||||
"%m",
|
||||
"%d",
|
||||
"%H",
|
||||
"%M",
|
||||
"%S",
|
||||
"%B",
|
||||
"%b",
|
||||
"%A",
|
||||
"%a",
|
||||
]
|
||||
is_valid = any(code in self.date_format for code in valid_format_codes)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if not is_valid:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Invalid date format: {self.date_format}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
current_date: str = datetime.now().strftime(self.date_format)
|
||||
task.description += f"\n\nCurrent Date: {current_date}"
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
if hasattr(self, '_logger'):
|
||||
if hasattr(self, "_logger"):
|
||||
self._logger.log("warning", f"Failed to inject date: {str(e)}")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(f"Warning: Failed to inject date: {str(e)}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _validate_docker_installation(self) -> None:
|
||||
"""Check if Docker is installed and running."""
|
||||
if not shutil.which("docker"):
|
||||
@@ -761,6 +787,8 @@ class Agent(BaseAgent):
|
||||
response_format=response_format,
|
||||
i18n=self.i18n,
|
||||
original_agent=self,
|
||||
guardrail=self.guardrail,
|
||||
guardrail_max_retries=self.guardrail_max_retries,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return lite_agent.kickoff(messages)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@ from crewai.utilities import I18N
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.converter import ConverterError
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.evaluators.task_evaluator import TaskEvaluator
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.printer import Printer
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events.event_listener import event_listener
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from crewai.agents.agent_builder.base_agent import BaseAgent
|
||||
@@ -125,33 +126,38 @@ class CrewAgentExecutorMixin:
|
||||
|
||||
def _ask_human_input(self, final_answer: str) -> str:
|
||||
"""Prompt human input with mode-appropriate messaging."""
|
||||
self._printer.print(
|
||||
content=f"\033[1m\033[95m ## Final Result:\033[00m \033[92m{final_answer}\033[00m"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Training mode prompt (single iteration)
|
||||
if self.crew and getattr(self.crew, "_train", False):
|
||||
prompt = (
|
||||
"\n\n=====\n"
|
||||
"## TRAINING MODE: Provide feedback to improve the agent's performance.\n"
|
||||
"This will be used to train better versions of the agent.\n"
|
||||
"Please provide detailed feedback about the result quality and reasoning process.\n"
|
||||
"=====\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Regular human-in-the-loop prompt (multiple iterations)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
prompt = (
|
||||
"\n\n=====\n"
|
||||
"## HUMAN FEEDBACK: Provide feedback on the Final Result and Agent's actions.\n"
|
||||
"Please follow these guidelines:\n"
|
||||
" - If you are happy with the result, simply hit Enter without typing anything.\n"
|
||||
" - Otherwise, provide specific improvement requests.\n"
|
||||
" - You can provide multiple rounds of feedback until satisfied.\n"
|
||||
"=====\n"
|
||||
event_listener.formatter.pause_live_updates()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self._printer.print(
|
||||
content=f"\033[1m\033[95m ## Final Result:\033[00m \033[92m{final_answer}\033[00m"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self._printer.print(content=prompt, color="bold_yellow")
|
||||
response = input()
|
||||
if response.strip() != "":
|
||||
self._printer.print(content="\nProcessing your feedback...", color="cyan")
|
||||
return response
|
||||
# Training mode prompt (single iteration)
|
||||
if self.crew and getattr(self.crew, "_train", False):
|
||||
prompt = (
|
||||
"\n\n=====\n"
|
||||
"## TRAINING MODE: Provide feedback to improve the agent's performance.\n"
|
||||
"This will be used to train better versions of the agent.\n"
|
||||
"Please provide detailed feedback about the result quality and reasoning process.\n"
|
||||
"=====\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Regular human-in-the-loop prompt (multiple iterations)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
prompt = (
|
||||
"\n\n=====\n"
|
||||
"## HUMAN FEEDBACK: Provide feedback on the Final Result and Agent's actions.\n"
|
||||
"Please follow these guidelines:\n"
|
||||
" - If you are happy with the result, simply hit Enter without typing anything.\n"
|
||||
" - Otherwise, provide specific improvement requests.\n"
|
||||
" - You can provide multiple rounds of feedback until satisfied.\n"
|
||||
"=====\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self._printer.print(content=prompt, color="bold_yellow")
|
||||
response = input()
|
||||
if response.strip() != "":
|
||||
self._printer.print(content="\nProcessing your feedback...", color="cyan")
|
||||
return response
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
event_listener.formatter.resume_live_updates()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,12 +25,16 @@ from crewai.utilities.agent_utils import (
|
||||
has_reached_max_iterations,
|
||||
is_context_length_exceeded,
|
||||
process_llm_response,
|
||||
show_agent_logs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.constants import MAX_LLM_RETRY, TRAINING_DATA_FILE
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.logger import Logger
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.tool_utils import execute_tool_and_check_finality
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.training_handler import CrewTrainingHandler
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events.agent_events import (
|
||||
AgentLogsStartedEvent,
|
||||
AgentLogsExecutionEvent,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events.crewai_event_bus import crewai_event_bus
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CrewAgentExecutor(CrewAgentExecutorMixin):
|
||||
@@ -263,26 +267,32 @@ class CrewAgentExecutor(CrewAgentExecutorMixin):
|
||||
"""Show logs for the start of agent execution."""
|
||||
if self.agent is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Agent cannot be None")
|
||||
show_agent_logs(
|
||||
printer=self._printer,
|
||||
agent_role=self.agent.role,
|
||||
task_description=(
|
||||
getattr(self.task, "description") if self.task else "Not Found"
|
||||
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self.agent,
|
||||
AgentLogsStartedEvent(
|
||||
agent_role=self.agent.role,
|
||||
task_description=(
|
||||
getattr(self.task, "description") if self.task else "Not Found"
|
||||
),
|
||||
verbose=self.agent.verbose
|
||||
or (hasattr(self, "crew") and getattr(self.crew, "verbose", False)),
|
||||
),
|
||||
verbose=self.agent.verbose
|
||||
or (hasattr(self, "crew") and getattr(self.crew, "verbose", False)),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _show_logs(self, formatted_answer: Union[AgentAction, AgentFinish]):
|
||||
"""Show logs for the agent's execution."""
|
||||
if self.agent is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Agent cannot be None")
|
||||
show_agent_logs(
|
||||
printer=self._printer,
|
||||
agent_role=self.agent.role,
|
||||
formatted_answer=formatted_answer,
|
||||
verbose=self.agent.verbose
|
||||
or (hasattr(self, "crew") and getattr(self.crew, "verbose", False)),
|
||||
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self.agent,
|
||||
AgentLogsExecutionEvent(
|
||||
agent_role=self.agent.role,
|
||||
formatted_answer=formatted_answer,
|
||||
verbose=self.agent.verbose
|
||||
or (hasattr(self, "crew") and getattr(self.crew, "verbose", False)),
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _summarize_messages(self) -> None:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@ from .deploy.main import DeployCommand
|
||||
from .evaluate_crew import evaluate_crew
|
||||
from .install_crew import install_crew
|
||||
from .kickoff_flow import kickoff_flow
|
||||
from .organization.main import OrganizationCommand
|
||||
from .plot_flow import plot_flow
|
||||
from .replay_from_task import replay_task_command
|
||||
from .reset_memories_command import reset_memories_command
|
||||
@@ -353,5 +354,33 @@ def chat():
|
||||
run_chat()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai.group(invoke_without_command=True)
|
||||
def org():
|
||||
"""Organization management commands."""
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@org.command()
|
||||
def list():
|
||||
"""List available organizations."""
|
||||
org_command = OrganizationCommand()
|
||||
org_command.list()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@org.command()
|
||||
@click.argument("id")
|
||||
def switch(id):
|
||||
"""Switch to a specific organization."""
|
||||
org_command = OrganizationCommand()
|
||||
org_command.switch(id)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@org.command()
|
||||
def current():
|
||||
"""Show current organization when 'crewai org' is called without subcommands."""
|
||||
org_command = OrganizationCommand()
|
||||
org_command.current()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
crewai()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,6 +14,12 @@ class Settings(BaseModel):
|
||||
tool_repository_password: Optional[str] = Field(
|
||||
None, description="Password for interacting with the Tool Repository"
|
||||
)
|
||||
org_name: Optional[str] = Field(
|
||||
None, description="Name of the currently active organization"
|
||||
)
|
||||
org_uuid: Optional[str] = Field(
|
||||
None, description="UUID of the currently active organization"
|
||||
)
|
||||
config_path: Path = Field(default=DEFAULT_CONFIG_PATH, exclude=True)
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config_path: Path = DEFAULT_CONFIG_PATH, **data):
|
||||
|
||||
1
src/crewai/cli/organization/__init__.py
Normal file
1
src/crewai/cli/organization/__init__.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
|
||||
76
src/crewai/cli/organization/main.py
Normal file
76
src/crewai/cli/organization/main.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
from rich.console import Console
|
||||
from rich.table import Table
|
||||
|
||||
from requests import HTTPError
|
||||
from crewai.cli.command import BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin
|
||||
from crewai.cli.config import Settings
|
||||
|
||||
console = Console()
|
||||
|
||||
class OrganizationCommand(BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
BaseCommand.__init__(self)
|
||||
PlusAPIMixin.__init__(self, telemetry=self._telemetry)
|
||||
|
||||
def list(self):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
response = self.plus_api_client.get_organizations()
|
||||
response.raise_for_status()
|
||||
orgs = response.json()
|
||||
|
||||
if not orgs:
|
||||
console.print("You don't belong to any organizations yet.", style="yellow")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
table = Table(title="Your Organizations")
|
||||
table.add_column("Name", style="cyan")
|
||||
table.add_column("ID", style="green")
|
||||
for org in orgs:
|
||||
table.add_row(org["name"], org["uuid"])
|
||||
|
||||
console.print(table)
|
||||
except HTTPError as e:
|
||||
if e.response.status_code == 401:
|
||||
console.print("You are not logged in to any organization. Use 'crewai login' to login.", style="bold red")
|
||||
return
|
||||
console.print(f"Failed to retrieve organization list: {str(e)}", style="bold red")
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
console.print(f"Failed to retrieve organization list: {str(e)}", style="bold red")
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def switch(self, org_id):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
response = self.plus_api_client.get_organizations()
|
||||
response.raise_for_status()
|
||||
orgs = response.json()
|
||||
|
||||
org = next((o for o in orgs if o["uuid"] == org_id), None)
|
||||
if not org:
|
||||
console.print(f"Organization with id '{org_id}' not found.", style="bold red")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
settings = Settings()
|
||||
settings.org_name = org["name"]
|
||||
settings.org_uuid = org["uuid"]
|
||||
settings.dump()
|
||||
|
||||
console.print(f"Successfully switched to {org['name']} ({org['uuid']})", style="bold green")
|
||||
except HTTPError as e:
|
||||
if e.response.status_code == 401:
|
||||
console.print("You are not logged in to any organization. Use 'crewai login' to login.", style="bold red")
|
||||
return
|
||||
console.print(f"Failed to retrieve organization list: {str(e)}", style="bold red")
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
console.print(f"Failed to switch organization: {str(e)}", style="bold red")
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def current(self):
|
||||
settings = Settings()
|
||||
if settings.org_uuid:
|
||||
console.print(f"Currently logged in to organization {settings.org_name} ({settings.org_uuid})", style="bold green")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
console.print("You're not currently logged in to any organization.", style="yellow")
|
||||
console.print("Use 'crewai org list' to see available organizations.", style="yellow")
|
||||
console.print("Use 'crewai org switch <id>' to switch to an organization.", style="yellow")
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
from os import getenv
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional
|
||||
from urllib.parse import urljoin
|
||||
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.cli.config import Settings
|
||||
from crewai.cli.version import get_crewai_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,6 +14,7 @@ class PlusAPI:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
TOOLS_RESOURCE = "/crewai_plus/api/v1/tools"
|
||||
ORGANIZATIONS_RESOURCE = "/crewai_plus/api/v1/me/organizations"
|
||||
CREWS_RESOURCE = "/crewai_plus/api/v1/crews"
|
||||
AGENTS_RESOURCE = "/crewai_plus/api/v1/agents"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,6 +26,9 @@ class PlusAPI:
|
||||
"User-Agent": f"CrewAI-CLI/{get_crewai_version()}",
|
||||
"X-Crewai-Version": get_crewai_version(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
settings = Settings()
|
||||
if settings.org_uuid:
|
||||
self.headers["X-Crewai-Organization-Id"] = settings.org_uuid
|
||||
self.base_url = getenv("CREWAI_BASE_URL", "https://app.crewai.com")
|
||||
|
||||
def _make_request(self, method: str, endpoint: str, **kwargs) -> requests.Response:
|
||||
@@ -48,6 +53,7 @@ class PlusAPI:
|
||||
version: str,
|
||||
description: Optional[str],
|
||||
encoded_file: str,
|
||||
available_exports: Optional[List[str]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
params = {
|
||||
"handle": handle,
|
||||
@@ -55,6 +61,7 @@ class PlusAPI:
|
||||
"version": version,
|
||||
"file": encoded_file,
|
||||
"description": description,
|
||||
"available_exports": available_exports,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return self._make_request("POST", f"{self.TOOLS_RESOURCE}", json=params)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -101,3 +108,7 @@ class PlusAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
def create_crew(self, payload) -> requests.Response:
|
||||
return self._make_request("POST", self.CREWS_RESOURCE, json=payload)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_organizations(self) -> requests.Response:
|
||||
return self._make_request("GET", self.ORGANIZATIONS_RESOURCE)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import certifi
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
@@ -163,8 +165,10 @@ def fetch_provider_data(cache_file):
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
- dict or None: The fetched provider data or None if the operation fails.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
ssl_config = os.environ['SSL_CERT_FILE'] = certifi.where()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
response = requests.get(JSON_URL, stream=True, timeout=60)
|
||||
response = requests.get(JSON_URL, stream=True, timeout=60, verify=ssl_config)
|
||||
response.raise_for_status()
|
||||
data = download_data(response)
|
||||
with open(cache_file, "w") as f:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ Welcome to the {{crew_name}} Crew project, powered by [crewAI](https://crewai.co
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.13 installed on your system. This project uses [UV](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for dependency management and package handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.14 installed on your system. This project uses [UV](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for dependency management and package handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
|
||||
|
||||
First, if you haven't already, install uv:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,9 +3,9 @@ name = "{{folder_name}}"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
description = "{{name}} using crewAI"
|
||||
authors = [{ name = "Your Name", email = "you@example.com" }]
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.13"
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.14"
|
||||
dependencies = [
|
||||
"crewai[tools]>=0.121.0,<1.0.0"
|
||||
"crewai[tools]>=0.130.0,<1.0.0"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[project.scripts]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ Welcome to the {{crew_name}} Crew project, powered by [crewAI](https://crewai.co
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.13 installed on your system. This project uses [UV](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for dependency management and package handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.14 installed on your system. This project uses [UV](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for dependency management and package handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
|
||||
|
||||
First, if you haven't already, install uv:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,9 +3,9 @@ name = "{{folder_name}}"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
description = "{{name}} using crewAI"
|
||||
authors = [{ name = "Your Name", email = "you@example.com" }]
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.13"
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.14"
|
||||
dependencies = [
|
||||
"crewai[tools]>=0.121.0,<1.0.0",
|
||||
"crewai[tools]>=0.130.0,<1.0.0",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[project.scripts]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ custom tools to power up your crews.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.13 installed on your system. This project
|
||||
Ensure you have Python >=3.10 <3.14 installed on your system. This project
|
||||
uses [UV](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for dependency management and package
|
||||
handling, offering a seamless setup and execution experience.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,9 +3,9 @@ name = "{{folder_name}}"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
description = "Power up your crews with {{folder_name}}"
|
||||
readme = "README.md"
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.13"
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.14"
|
||||
dependencies = [
|
||||
"crewai[tools]>=0.121.0"
|
||||
"crewai[tools]>=0.130.0"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.crewai]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
from .tool import {{class_name}}
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["{{class_name}}"]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@ import os
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import Any
|
||||
|
||||
import click
|
||||
from rich.console import Console
|
||||
@@ -11,6 +12,7 @@ from crewai.cli import git
|
||||
from crewai.cli.command import BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin
|
||||
from crewai.cli.config import Settings
|
||||
from crewai.cli.utils import (
|
||||
extract_available_exports,
|
||||
get_project_description,
|
||||
get_project_name,
|
||||
get_project_version,
|
||||
@@ -82,6 +84,15 @@ class ToolCommand(BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin):
|
||||
project_description = get_project_description(require=False)
|
||||
encoded_tarball = None
|
||||
|
||||
console.print("[bold blue]Discovering tools from your project...[/bold blue]")
|
||||
available_exports = extract_available_exports()
|
||||
|
||||
if available_exports:
|
||||
console.print(
|
||||
f"[green]Found these tools to publish: {', '.join([e['name'] for e in available_exports])}[/green]"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._print_current_organization()
|
||||
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as temp_build_dir:
|
||||
subprocess.run(
|
||||
["uv", "build", "--sdist", "--out-dir", temp_build_dir],
|
||||
@@ -105,12 +116,14 @@ class ToolCommand(BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin):
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_tarball = base64.b64encode(tarball_contents).decode("utf-8")
|
||||
|
||||
console.print("[bold blue]Publishing tool to repository...[/bold blue]")
|
||||
publish_response = self.plus_api_client.publish_tool(
|
||||
handle=project_name,
|
||||
is_public=is_public,
|
||||
version=project_version,
|
||||
description=project_description,
|
||||
encoded_file=f"data:application/x-gzip;base64,{encoded_tarball}",
|
||||
available_exports=available_exports,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self._validate_response(publish_response)
|
||||
@@ -124,6 +137,7 @@ class ToolCommand(BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def install(self, handle: str):
|
||||
self._print_current_organization()
|
||||
get_response = self.plus_api_client.get_tool(handle)
|
||||
|
||||
if get_response.status_code == 404:
|
||||
@@ -161,13 +175,20 @@ class ToolCommand(BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin):
|
||||
settings.tool_repository_password = login_response_json["credential"][
|
||||
"password"
|
||||
]
|
||||
settings.org_uuid = login_response_json["current_organization"][
|
||||
"uuid"
|
||||
]
|
||||
settings.org_name = login_response_json["current_organization"][
|
||||
"name"
|
||||
]
|
||||
settings.dump()
|
||||
|
||||
console.print(
|
||||
"Successfully authenticated to the tool repository.", style="bold green"
|
||||
f"Successfully authenticated to the tool repository as {settings.org_name} ({settings.org_uuid}).", style="bold green"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _add_package(self, tool_details):
|
||||
def _add_package(self, tool_details: dict[str, Any]):
|
||||
is_from_pypi = tool_details.get("source", None) == "pypi"
|
||||
tool_handle = tool_details["handle"]
|
||||
repository_handle = tool_details["repository"]["handle"]
|
||||
repository_url = tool_details["repository"]["url"]
|
||||
@@ -176,10 +197,13 @@ class ToolCommand(BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin):
|
||||
add_package_command = [
|
||||
"uv",
|
||||
"add",
|
||||
"--index",
|
||||
index,
|
||||
tool_handle,
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if is_from_pypi:
|
||||
add_package_command.append(tool_handle)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
add_package_command.extend(["--index", index, tool_handle])
|
||||
|
||||
add_package_result = subprocess.run(
|
||||
add_package_command,
|
||||
capture_output=False,
|
||||
@@ -218,3 +242,10 @@ class ToolCommand(BaseCommand, PlusAPIMixin):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return env
|
||||
|
||||
def _print_current_organization(self):
|
||||
settings = Settings()
|
||||
if settings.org_uuid:
|
||||
console.print(f"Current organization: {settings.org_name} ({settings.org_uuid})", style="bold blue")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
console.print("No organization currently set. We recommend setting one before using: `crewai org switch <org_id>` command.", style="yellow")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,8 +1,10 @@
|
||||
import importlib.util
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from functools import reduce
|
||||
from inspect import isfunction, ismethod
|
||||
from inspect import getmro, isclass, isfunction, ismethod
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, get_type_hints
|
||||
|
||||
import click
|
||||
@@ -339,3 +341,112 @@ def fetch_crews(module_attr) -> list[Crew]:
|
||||
if crew_instance := get_crew_instance(attr):
|
||||
crew_instances.append(crew_instance)
|
||||
return crew_instances
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_valid_tool(obj):
|
||||
from crewai.tools.base_tool import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
if isclass(obj):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return any(base.__name__ == "BaseTool" for base in getmro(obj))
|
||||
except (TypeError, AttributeError):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
return isinstance(obj, Tool)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def extract_available_exports(dir_path: str = "src"):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Extract available tool classes from the project's __init__.py files.
|
||||
Only includes classes that inherit from BaseTool or functions decorated with @tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
list: A list of valid tool class names or ["BaseTool"] if none found
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
init_files = Path(dir_path).glob("**/__init__.py")
|
||||
available_exports = []
|
||||
|
||||
for init_file in init_files:
|
||||
tools = _load_tools_from_init(init_file)
|
||||
available_exports.extend(tools)
|
||||
|
||||
if not available_exports:
|
||||
_print_no_tools_warning()
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
return available_exports
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
console.print(f"[red]Error: Could not extract tool classes: {str(e)}[/red]")
|
||||
console.print(
|
||||
"Please ensure your project contains valid tools (classes inheriting from BaseTool or functions with @tool decorator)."
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _load_tools_from_init(init_file: Path) -> list[dict[str, Any]]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Load and validate tools from a given __init__.py file.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("temp_module", init_file)
|
||||
|
||||
if not spec or not spec.loader:
|
||||
return []
|
||||
|
||||
module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
|
||||
sys.modules["temp_module"] = module
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
spec.loader.exec_module(module)
|
||||
|
||||
if not hasattr(module, "__all__"):
|
||||
console.print(
|
||||
f"[bold yellow]Warning: No __all__ defined in {init_file}[/bold yellow]"
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
return [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": name,
|
||||
}
|
||||
for name in module.__all__
|
||||
if hasattr(module, name) and is_valid_tool(getattr(module, name))
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
console.print(f"[red]Warning: Could not load {init_file}: {str(e)}[/red]")
|
||||
raise SystemExit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
sys.modules.pop("temp_module", None)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _print_no_tools_warning():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Display warning and usage instructions if no tools were found.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
console.print(
|
||||
"\n[bold yellow]Warning: No valid tools were exposed in your __init__.py file![/bold yellow]"
|
||||
)
|
||||
console.print(
|
||||
"Your __init__.py file must contain all classes that inherit from [bold]BaseTool[/bold] "
|
||||
"or functions decorated with [bold]@tool[/bold]."
|
||||
)
|
||||
console.print(
|
||||
"\nExample:\n[dim]# In your __init__.py file[/dim]\n"
|
||||
"[green]__all__ = ['YourTool', 'your_tool_function'][/green]\n\n"
|
||||
"[dim]# In your tool.py file[/dim]\n"
|
||||
"[green]from crewai.tools import BaseTool, tool\n\n"
|
||||
"# Tool class example\n"
|
||||
"class YourTool(BaseTool):\n"
|
||||
' name = "your_tool"\n'
|
||||
' description = "Your tool description"\n'
|
||||
" # ... rest of implementation\n\n"
|
||||
"# Decorated function example\n"
|
||||
"@tool\n"
|
||||
"def your_tool_function(text: str) -> str:\n"
|
||||
' """Your tool description"""\n'
|
||||
" # ... implementation\n"
|
||||
" return result\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -655,8 +655,6 @@ class Crew(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
if self.planning:
|
||||
self._handle_crew_planning()
|
||||
|
||||
metrics: List[UsageMetrics] = []
|
||||
|
||||
if self.process == Process.sequential:
|
||||
result = self._run_sequential_process()
|
||||
elif self.process == Process.hierarchical:
|
||||
@@ -669,11 +667,8 @@ class Crew(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
for after_callback in self.after_kickoff_callbacks:
|
||||
result = after_callback(result)
|
||||
|
||||
metrics += [agent._token_process.get_summary() for agent in self.agents]
|
||||
self.usage_metrics = self.calculate_usage_metrics()
|
||||
|
||||
self.usage_metrics = UsageMetrics()
|
||||
for metric in metrics:
|
||||
self.usage_metrics.add_usage_metrics(metric)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,8 @@ class FlowTrackable(BaseModel):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@model_validator(mode="after")
|
||||
def _set_parent_flow(self, max_depth: int = 5) -> "FlowTrackable":
|
||||
def _set_parent_flow(self) -> "FlowTrackable":
|
||||
max_depth = 5
|
||||
frame = inspect.currentframe()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Example
|
||||
|
||||
import ast
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils import (
|
||||
build_ancestor_dict,
|
||||
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ def compute_positions(
|
||||
flow: Any,
|
||||
node_levels: Dict[str, int],
|
||||
y_spacing: float = 150,
|
||||
x_spacing: float = 150
|
||||
x_spacing: float = 300
|
||||
) -> Dict[str, Tuple[float, float]]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Compute the (x, y) positions for each node in the flow graph.
|
||||
@@ -154,7 +154,7 @@ def compute_positions(
|
||||
y_spacing : float, optional
|
||||
Vertical spacing between levels, by default 150.
|
||||
x_spacing : float, optional
|
||||
Horizontal spacing between nodes, by default 150.
|
||||
Horizontal spacing between nodes, by default 300.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from .base_embedder import BaseEmbedder
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from fastembed_gpu import TextEmbedding # type: ignore
|
||||
|
||||
FASTEMBED_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from fastembed import TextEmbedding
|
||||
|
||||
FASTEMBED_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
FASTEMBED_AVAILABLE = False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FastEmbed(BaseEmbedder):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A wrapper class for text embedding models using FastEmbed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model_name: str = "BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5",
|
||||
cache_dir: Optional[Union[str, Path]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Initialize the embedding model
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
model_name: Name of the model to use
|
||||
cache_dir: Directory to cache the model
|
||||
gpu: Whether to use GPU acceleration
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not FASTEMBED_AVAILABLE:
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
"FastEmbed is not installed. Please install it with: "
|
||||
"uv pip install fastembed or uv pip install fastembed-gpu for GPU support"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.model = TextEmbedding(
|
||||
model_name=model_name,
|
||||
cache_dir=str(cache_dir) if cache_dir else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def embed_chunks(self, chunks: List[str]) -> List[np.ndarray]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generate embeddings for a list of text chunks
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
chunks: List of text chunks to embed
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
List of embeddings
|
||||
"""
|
||||
embeddings = list(self.model.embed(chunks))
|
||||
return embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
def embed_texts(self, texts: List[str]) -> List[np.ndarray]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generate embeddings for a list of texts
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
texts: List of texts to embed
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
List of embeddings
|
||||
"""
|
||||
embeddings = list(self.model.embed(texts))
|
||||
return embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
def embed_text(self, text: str) -> np.ndarray:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generate embedding for a single text
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
text: Text to embed
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Embedding array
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.embed_texts([text])[0]
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def dimension(self) -> int:
|
||||
"""Get the dimension of the embeddings"""
|
||||
# Generate a test embedding to get dimensions
|
||||
test_embed = self.embed_text("test")
|
||||
return len(test_embed)
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,33 @@
|
||||
import asyncio
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
import uuid
|
||||
from datetime import datetime
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Optional, Type, Union, cast
|
||||
from typing import (
|
||||
Any,
|
||||
Callable,
|
||||
Dict,
|
||||
List,
|
||||
Optional,
|
||||
Tuple,
|
||||
Type,
|
||||
Union,
|
||||
cast,
|
||||
get_args,
|
||||
get_origin,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field, InstanceOf, PrivateAttr, model_validator
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from typing import Self
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
from typing_extensions import Self
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import (
|
||||
BaseModel,
|
||||
Field,
|
||||
InstanceOf,
|
||||
PrivateAttr,
|
||||
model_validator,
|
||||
field_validator,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.agents.agent_builder.base_agent import BaseAgent
|
||||
from crewai.agents.agent_builder.utilities.base_token_process import TokenProcess
|
||||
@@ -18,6 +42,7 @@ from crewai.llm import LLM
|
||||
from crewai.tools.base_tool import BaseTool
|
||||
from crewai.tools.structured_tool import CrewStructuredTool
|
||||
from crewai.utilities import I18N
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.guardrail import process_guardrail
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.agent_utils import (
|
||||
enforce_rpm_limit,
|
||||
format_message_for_llm,
|
||||
@@ -33,10 +58,10 @@ from crewai.utilities.agent_utils import (
|
||||
parse_tools,
|
||||
process_llm_response,
|
||||
render_text_description_and_args,
|
||||
show_agent_logs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.converter import convert_to_model, generate_model_description
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.converter import generate_model_description
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events.agent_events import (
|
||||
AgentLogsExecutionEvent,
|
||||
LiteAgentExecutionCompletedEvent,
|
||||
LiteAgentExecutionErrorEvent,
|
||||
LiteAgentExecutionStartedEvent,
|
||||
@@ -146,6 +171,17 @@ class LiteAgent(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
default=[], description="Callbacks to be used for the agent"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Guardrail Properties
|
||||
guardrail: Optional[Union[Callable[[LiteAgentOutput], Tuple[bool, Any]], str]] = (
|
||||
Field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
description="Function or string description of a guardrail to validate agent output",
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
guardrail_max_retries: int = Field(
|
||||
default=3, description="Maximum number of retries when guardrail fails"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# State and Results
|
||||
tools_results: List[Dict[str, Any]] = Field(
|
||||
default=[], description="Results of the tools used by the agent."
|
||||
@@ -163,6 +199,8 @@ class LiteAgent(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
_messages: List[Dict[str, str]] = PrivateAttr(default_factory=list)
|
||||
_iterations: int = PrivateAttr(default=0)
|
||||
_printer: Printer = PrivateAttr(default_factory=Printer)
|
||||
_guardrail: Optional[Callable] = PrivateAttr(default=None)
|
||||
_guardrail_retry_count: int = PrivateAttr(default=0)
|
||||
|
||||
@model_validator(mode="after")
|
||||
def setup_llm(self):
|
||||
@@ -184,6 +222,61 @@ class LiteAgent(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
@model_validator(mode="after")
|
||||
def ensure_guardrail_is_callable(self) -> Self:
|
||||
if callable(self.guardrail):
|
||||
self._guardrail = self.guardrail
|
||||
elif isinstance(self.guardrail, str):
|
||||
from crewai.tasks.llm_guardrail import LLMGuardrail
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(self.llm, LLM)
|
||||
|
||||
self._guardrail = LLMGuardrail(description=self.guardrail, llm=self.llm)
|
||||
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
@field_validator("guardrail", mode="before")
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def validate_guardrail_function(
|
||||
cls, v: Optional[Union[Callable, str]]
|
||||
) -> Optional[Union[Callable, str]]:
|
||||
"""Validate that the guardrail function has the correct signature.
|
||||
|
||||
If v is a callable, validate that it has the correct signature.
|
||||
If v is a string, return it as is.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
v: The guardrail function to validate or a string describing the guardrail task
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
The validated guardrail function or a string describing the guardrail task
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if v is None or isinstance(v, str):
|
||||
return v
|
||||
|
||||
# Check function signature
|
||||
sig = inspect.signature(v)
|
||||
if len(sig.parameters) != 1:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Guardrail function must accept exactly 1 parameter (LiteAgentOutput), "
|
||||
f"but it accepts {len(sig.parameters)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check return annotation if present
|
||||
if sig.return_annotation is not sig.empty:
|
||||
if sig.return_annotation == Tuple[bool, Any]:
|
||||
return v
|
||||
|
||||
origin = get_origin(sig.return_annotation)
|
||||
args = get_args(sig.return_annotation)
|
||||
|
||||
if origin is not tuple or len(args) != 2 or args[0] is not bool:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"If return type is annotated, it must be Tuple[bool, Any]"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return v
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def key(self) -> str:
|
||||
"""Get the unique key for this agent instance."""
|
||||
@@ -223,54 +316,7 @@ class LiteAgent(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
# Format messages for the LLM
|
||||
self._messages = self._format_messages(messages)
|
||||
|
||||
# Emit event for agent execution start
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=LiteAgentExecutionStartedEvent(
|
||||
agent_info=agent_info,
|
||||
tools=self._parsed_tools,
|
||||
messages=messages,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Execute the agent using invoke loop
|
||||
agent_finish = self._invoke_loop()
|
||||
formatted_result: Optional[BaseModel] = None
|
||||
if self.response_format:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Cast to BaseModel to ensure type safety
|
||||
result = self.response_format.model_validate_json(
|
||||
agent_finish.output
|
||||
)
|
||||
if isinstance(result, BaseModel):
|
||||
formatted_result = result
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
self._printer.print(
|
||||
content=f"Failed to parse output into response format: {str(e)}",
|
||||
color="yellow",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Calculate token usage metrics
|
||||
usage_metrics = self._token_process.get_summary()
|
||||
|
||||
# Create output
|
||||
output = LiteAgentOutput(
|
||||
raw=agent_finish.output,
|
||||
pydantic=formatted_result,
|
||||
agent_role=self.role,
|
||||
usage_metrics=usage_metrics.model_dump() if usage_metrics else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Emit completion event
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=LiteAgentExecutionCompletedEvent(
|
||||
agent_info=agent_info,
|
||||
output=agent_finish.output,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return output
|
||||
return self._execute_core(agent_info=agent_info)
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
self._printer.print(
|
||||
@@ -288,6 +334,95 @@ class LiteAgent(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
|
||||
def _execute_core(self, agent_info: Dict[str, Any]) -> LiteAgentOutput:
|
||||
# Emit event for agent execution start
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=LiteAgentExecutionStartedEvent(
|
||||
agent_info=agent_info,
|
||||
tools=self._parsed_tools,
|
||||
messages=self._messages,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Execute the agent using invoke loop
|
||||
agent_finish = self._invoke_loop()
|
||||
formatted_result: Optional[BaseModel] = None
|
||||
if self.response_format:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Cast to BaseModel to ensure type safety
|
||||
result = self.response_format.model_validate_json(agent_finish.output)
|
||||
if isinstance(result, BaseModel):
|
||||
formatted_result = result
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
self._printer.print(
|
||||
content=f"Failed to parse output into response format: {str(e)}",
|
||||
color="yellow",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Calculate token usage metrics
|
||||
usage_metrics = self._token_process.get_summary()
|
||||
|
||||
# Create output
|
||||
output = LiteAgentOutput(
|
||||
raw=agent_finish.output,
|
||||
pydantic=formatted_result,
|
||||
agent_role=self.role,
|
||||
usage_metrics=usage_metrics.model_dump() if usage_metrics else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Process guardrail if set
|
||||
if self._guardrail is not None:
|
||||
guardrail_result = process_guardrail(
|
||||
output=output,
|
||||
guardrail=self._guardrail,
|
||||
retry_count=self._guardrail_retry_count,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not guardrail_result.success:
|
||||
if self._guardrail_retry_count >= self.guardrail_max_retries:
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
f"Agent's guardrail failed validation after {self.guardrail_max_retries} retries. "
|
||||
f"Last error: {guardrail_result.error}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._guardrail_retry_count += 1
|
||||
if self.verbose:
|
||||
self._printer.print(
|
||||
f"Guardrail failed. Retrying ({self._guardrail_retry_count}/{self.guardrail_max_retries})..."
|
||||
f"\n{guardrail_result.error}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self._messages.append(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": guardrail_result.error
|
||||
or "Guardrail validation failed",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return self._execute_core(agent_info=agent_info)
|
||||
|
||||
# Apply guardrail result if available
|
||||
if guardrail_result.result is not None:
|
||||
if isinstance(guardrail_result.result, str):
|
||||
output.raw = guardrail_result.result
|
||||
elif isinstance(guardrail_result.result, BaseModel):
|
||||
output.pydantic = guardrail_result.result
|
||||
|
||||
usage_metrics = self._token_process.get_summary()
|
||||
output.usage_metrics = usage_metrics.model_dump() if usage_metrics else None
|
||||
|
||||
# Emit completion event
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=LiteAgentExecutionCompletedEvent(
|
||||
agent_info=agent_info,
|
||||
output=agent_finish.output,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return output
|
||||
|
||||
async def kickoff_async(
|
||||
self, messages: Union[str, List[Dict[str, str]]]
|
||||
) -> LiteAgentOutput:
|
||||
@@ -467,11 +602,13 @@ class LiteAgent(FlowTrackable, BaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
def _show_logs(self, formatted_answer: Union[AgentAction, AgentFinish]):
|
||||
"""Show logs for the agent's execution."""
|
||||
show_agent_logs(
|
||||
printer=self._printer,
|
||||
agent_role=self.role,
|
||||
formatted_answer=formatted_answer,
|
||||
verbose=self.verbose,
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
AgentLogsExecutionEvent(
|
||||
agent_role=self.role,
|
||||
formatted_answer=formatted_answer,
|
||||
verbose=self.verbose,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _append_message(self, text: str, role: str = "assistant") -> None:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ import sys
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager, redirect_stderr, redirect_stdout
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from typing import (
|
||||
Any,
|
||||
DefaultDict,
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ from typing import (
|
||||
Union,
|
||||
cast,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from datetime import datetime
|
||||
from dotenv import load_dotenv
|
||||
from litellm.types.utils import ChatCompletionDeltaToolCall
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
|
||||
@@ -30,6 +30,11 @@ from crewai.utilities.events.llm_events import (
|
||||
LLMCallType,
|
||||
LLMStreamChunkEvent,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events.tool_usage_events import (
|
||||
ToolUsageStartedEvent,
|
||||
ToolUsageFinishedEvent,
|
||||
ToolUsageErrorEvent,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings():
|
||||
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", UserWarning)
|
||||
@@ -833,7 +838,26 @@ class LLM(BaseLLM):
|
||||
fn = available_functions[function_name]
|
||||
|
||||
# --- 3.2) Execute function
|
||||
assert hasattr(crewai_event_bus, "emit")
|
||||
started_at = datetime.now()
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=ToolUsageStartedEvent(
|
||||
tool_name=function_name,
|
||||
tool_args=function_args,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
result = fn(**function_args)
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=ToolUsageFinishedEvent(
|
||||
output=result,
|
||||
tool_name=function_name,
|
||||
tool_args=function_args,
|
||||
started_at=started_at,
|
||||
finished_at=datetime.now(),
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# --- 3.3) Emit success event
|
||||
self._handle_emit_call_events(result, LLMCallType.TOOL_CALL)
|
||||
@@ -849,6 +873,14 @@ class LLM(BaseLLM):
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=LLMCallFailedEvent(error=f"Tool execution error: {str(e)}"),
|
||||
)
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
event=ToolUsageErrorEvent(
|
||||
tool_name=function_name,
|
||||
tool_args=function_args,
|
||||
error=f"Tool execution error: {str(e)}"
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
def call(
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,6 +4,9 @@ from typing import Any, Dict, List
|
||||
from mem0 import Memory, MemoryClient
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.memory.storage.interface import Storage
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.chromadb import sanitize_collection_name
|
||||
|
||||
MAX_AGENT_ID_LENGTH_MEM0 = 255
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Mem0Storage(Storage):
|
||||
@@ -134,7 +137,7 @@ class Mem0Storage(Storage):
|
||||
agents = self.crew.agents
|
||||
agents = [self._sanitize_role(agent.role) for agent in agents]
|
||||
agents = "_".join(agents)
|
||||
return agents
|
||||
return sanitize_collection_name(name=agents,max_collection_length=MAX_AGENT_ID_LENGTH_MEM0)
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_config(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
|
||||
return self.config or getattr(self, "memory_config", {}).get("config", {}) or {}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,12 +35,12 @@ from pydantic_core import PydanticCustomError
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.agents.agent_builder.base_agent import BaseAgent
|
||||
from crewai.security import Fingerprint, SecurityConfig
|
||||
from crewai.tasks.guardrail_result import GuardrailResult
|
||||
from crewai.tasks.output_format import OutputFormat
|
||||
from crewai.tasks.task_output import TaskOutput
|
||||
from crewai.tools.base_tool import BaseTool
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.config import process_config
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.constants import NOT_SPECIFIED
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.constants import NOT_SPECIFIED, _NotSpecified
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.guardrail import process_guardrail, GuardrailResult
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.converter import Converter, convert_to_model
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events import (
|
||||
TaskCompletedEvent,
|
||||
@@ -95,9 +95,9 @@ class Task(BaseModel):
|
||||
agent: Optional[BaseAgent] = Field(
|
||||
description="Agent responsible for execution the task.", default=None
|
||||
)
|
||||
context: Optional[List["Task"]] = Field(
|
||||
context: Union[List["Task"], None, _NotSpecified] = Field(
|
||||
description="Other tasks that will have their output used as context for this task.",
|
||||
default=NOT_SPECIFIED,
|
||||
default=NOT_SPECIFIED
|
||||
)
|
||||
async_execution: Optional[bool] = Field(
|
||||
description="Whether the task should be executed asynchronously or not.",
|
||||
@@ -158,6 +158,9 @@ class Task(BaseModel):
|
||||
end_time: Optional[datetime.datetime] = Field(
|
||||
default=None, description="End time of the task execution"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_config = {
|
||||
"arbitrary_types_allowed": True
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@field_validator("guardrail")
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
@@ -431,7 +434,11 @@ class Task(BaseModel):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if self._guardrail:
|
||||
guardrail_result = self._process_guardrail(task_output)
|
||||
guardrail_result = process_guardrail(
|
||||
output=task_output,
|
||||
guardrail=self._guardrail,
|
||||
retry_count=self.retry_count
|
||||
)
|
||||
if not guardrail_result.success:
|
||||
if self.retry_count >= self.max_retries:
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
@@ -527,10 +534,10 @@ class Task(BaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
def prompt(self) -> str:
|
||||
"""Generates the task prompt with optional markdown formatting.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When the markdown attribute is True, instructions for formatting the
|
||||
response in Markdown syntax will be added to the prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
str: The formatted prompt string containing the task description,
|
||||
expected output, and optional markdown formatting instructions.
|
||||
@@ -541,7 +548,7 @@ class Task(BaseModel):
|
||||
expected_output=self.expected_output
|
||||
)
|
||||
tasks_slices = [self.description, output]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if self.markdown:
|
||||
markdown_instruction = """Your final answer MUST be formatted in Markdown syntax.
|
||||
Follow these guidelines:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ import platform
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from importlib.metadata import version
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any, Optional
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any, Callable, Optional
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
|
||||
from opentelemetry import trace
|
||||
@@ -73,11 +73,16 @@ class Telemetry:
|
||||
with cls._lock:
|
||||
if cls._instance is None:
|
||||
cls._instance = super(Telemetry, cls).__new__(cls)
|
||||
cls._instance._initialized = False
|
||||
return cls._instance
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self) -> None:
|
||||
if hasattr(self, '_initialized') and self._initialized:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
self.ready: bool = False
|
||||
self.trace_set: bool = False
|
||||
self._initialized: bool = True
|
||||
|
||||
if self._is_telemetry_disabled():
|
||||
return
|
||||
@@ -113,6 +118,10 @@ class Telemetry:
|
||||
or os.getenv("CREWAI_DISABLE_TELEMETRY", "false").lower() == "true"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _should_execute_telemetry(self) -> bool:
|
||||
"""Check if telemetry operations should be executed."""
|
||||
return self.ready and not self._is_telemetry_disabled()
|
||||
|
||||
def set_tracer(self):
|
||||
if self.ready and not self.trace_set:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
@@ -123,8 +132,9 @@ class Telemetry:
|
||||
self.ready = False
|
||||
self.trace_set = False
|
||||
|
||||
def _safe_telemetry_operation(self, operation):
|
||||
if not self.ready:
|
||||
def _safe_telemetry_operation(self, operation: Callable[[], None]) -> None:
|
||||
"""Execute telemetry operation safely, checking both readiness and environment variables."""
|
||||
if not self._should_execute_telemetry():
|
||||
return
|
||||
try:
|
||||
operation()
|
||||
@@ -423,7 +433,8 @@ class Telemetry:
|
||||
|
||||
return span
|
||||
|
||||
return self._safe_telemetry_operation(operation)
|
||||
self._safe_telemetry_operation(operation)
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
def task_ended(self, span: Span, task: Task, crew: Crew):
|
||||
"""Records the completion of a task execution in a crew.
|
||||
@@ -773,7 +784,8 @@ class Telemetry:
|
||||
return span
|
||||
|
||||
if crew.share_crew:
|
||||
return self._safe_telemetry_operation(operation)
|
||||
self._safe_telemetry_operation(operation)
|
||||
return operation()
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
def end_crew(self, crew, final_string_output):
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1 +1,7 @@
|
||||
from .base_tool import BaseTool, tool
|
||||
from .base_tool import BaseTool, tool, EnvVar
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
"BaseTool",
|
||||
"tool",
|
||||
"EnvVar",
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
import asyncio
|
||||
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
|
||||
from inspect import signature
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Type, get_args, get_origin
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Type, get_args, get_origin, Optional, List
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import (
|
||||
BaseModel,
|
||||
@@ -14,6 +14,11 @@ from pydantic import BaseModel as PydanticBaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.tools.structured_tool import CrewStructuredTool
|
||||
|
||||
class EnvVar(BaseModel):
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
description: str
|
||||
required: bool = True
|
||||
default: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
|
||||
class BaseTool(BaseModel, ABC):
|
||||
class _ArgsSchemaPlaceholder(PydanticBaseModel):
|
||||
@@ -25,6 +30,8 @@ class BaseTool(BaseModel, ABC):
|
||||
"""The unique name of the tool that clearly communicates its purpose."""
|
||||
description: str
|
||||
"""Used to tell the model how/when/why to use the tool."""
|
||||
env_vars: List[EnvVar] = []
|
||||
"""List of environment variables used by the tool."""
|
||||
args_schema: Type[PydanticBaseModel] = Field(
|
||||
default_factory=_ArgsSchemaPlaceholder, validate_default=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +64,7 @@ class BaseTool(BaseModel, ABC):
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@field_validator("max_usage_count", mode="before")
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def validate_max_usage_count(cls, v: int | None) -> int | None:
|
||||
@@ -81,11 +88,11 @@ class BaseTool(BaseModel, ABC):
|
||||
# If _run is async, we safely run it
|
||||
if asyncio.iscoroutine(result):
|
||||
result = asyncio.run(result)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
self.current_usage_count += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reset_usage_count(self) -> None:
|
||||
"""Reset the current usage count to zero."""
|
||||
self.current_usage_count = 0
|
||||
@@ -272,7 +279,7 @@ def to_langchain(
|
||||
def tool(*args, result_as_answer: bool = False, max_usage_count: int | None = None) -> Callable:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator to create a tool from a function.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
*args: Positional arguments, either the function to decorate or the tool name.
|
||||
result_as_answer: Flag to indicate if the tool result should be used as the final agent answer.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,7 @@
|
||||
from __future__ import annotations
|
||||
|
||||
import asyncio
|
||||
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
import textwrap
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Optional, Union, get_type_hints
|
||||
@@ -239,7 +241,17 @@ class CrewStructuredTool:
|
||||
) -> Any:
|
||||
"""Main method for tool execution."""
|
||||
parsed_args = self._parse_args(input)
|
||||
return self.func(**parsed_args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
if inspect.iscoroutinefunction(self.func):
|
||||
result = asyncio.run(self.func(**parsed_args, **kwargs))
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
result = self.func(**parsed_args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
if asyncio.iscoroutine(result):
|
||||
return asyncio.run(result)
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def args(self) -> dict:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,10 @@ from crewai.utilities.errors import AgentRepositoryError
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.exceptions.context_window_exceeding_exception import (
|
||||
LLMContextLengthExceededException,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from rich.console import Console
|
||||
from crewai.cli.config import Settings
|
||||
|
||||
console = Console()
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_tools(tools: List[BaseTool]) -> List[CrewStructuredTool]:
|
||||
"""Parse tools to be used for the task."""
|
||||
@@ -215,9 +218,6 @@ def handle_agent_action_core(
|
||||
if show_logs:
|
||||
show_logs(formatted_answer)
|
||||
|
||||
if messages is not None:
|
||||
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": tool_result.result})
|
||||
|
||||
return formatted_answer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -438,6 +438,13 @@ def show_agent_logs(
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _print_current_organization():
|
||||
settings = Settings()
|
||||
if settings.org_uuid:
|
||||
console.print(f"Fetching agent from organization: {settings.org_name} ({settings.org_uuid})", style="bold blue")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
console.print("No organization currently set. We recommend setting one before using: `crewai org switch <org_id>` command.", style="yellow")
|
||||
|
||||
def load_agent_from_repository(from_repository: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
|
||||
attributes: Dict[str, Any] = {}
|
||||
if from_repository:
|
||||
@@ -447,15 +454,18 @@ def load_agent_from_repository(from_repository: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
|
||||
from crewai.cli.plus_api import PlusAPI
|
||||
|
||||
client = PlusAPI(api_key=get_auth_token())
|
||||
_print_current_organization()
|
||||
response = client.get_agent(from_repository)
|
||||
if response.status_code == 404:
|
||||
raise AgentRepositoryError(
|
||||
f"Agent {from_repository} does not exist, make sure the name is correct or the agent is available on your organization"
|
||||
f"Agent {from_repository} does not exist, make sure the name is correct or the agent is available on your organization."
|
||||
f"\nIf you are using the wrong organization, switch to the correct one using `crewai org switch <org_id>` command.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if response.status_code != 200:
|
||||
raise AgentRepositoryError(
|
||||
f"Agent {from_repository} could not be loaded: {response.text}"
|
||||
f"\nIf you are using the wrong organization, switch to the correct one using `crewai org switch <org_id>` command.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
agent = response.json()
|
||||
@@ -464,9 +474,16 @@ def load_agent_from_repository(from_repository: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
|
||||
attributes[key] = []
|
||||
for tool in value:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
module = importlib.import_module("crewai_tools")
|
||||
module = importlib.import_module(tool["module"])
|
||||
tool_class = getattr(module, tool["name"])
|
||||
attributes[key].append(tool_class())
|
||||
|
||||
tool_value = tool_class(**tool["init_params"])
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(tool_value, list):
|
||||
attributes[key].extend(tool_value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
attributes[key].append(tool_value)
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
raise AgentRepositoryError(
|
||||
f"Tool {tool['name']} could not be loaded: {e}"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ def is_ipv4_pattern(name: str) -> bool:
|
||||
return bool(IPV4_PATTERN.match(name))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sanitize_collection_name(name: Optional[str]) -> str:
|
||||
def sanitize_collection_name(name: Optional[str], max_collection_length: int = MAX_COLLECTION_LENGTH) -> str:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sanitize a collection name to meet ChromaDB requirements:
|
||||
1. 3-63 characters long
|
||||
@@ -54,8 +54,8 @@ def sanitize_collection_name(name: Optional[str]) -> str:
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sanitized) < MIN_COLLECTION_LENGTH:
|
||||
sanitized = sanitized + "x" * (MIN_COLLECTION_LENGTH - len(sanitized))
|
||||
if len(sanitized) > MAX_COLLECTION_LENGTH:
|
||||
sanitized = sanitized[:MAX_COLLECTION_LENGTH]
|
||||
if len(sanitized) > max_collection_length:
|
||||
sanitized = sanitized[:max_collection_length]
|
||||
if not sanitized[-1].isalnum():
|
||||
sanitized = sanitized[:-1] + "z"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -102,3 +102,24 @@ class LiteAgentExecutionErrorEvent(BaseEvent):
|
||||
agent_info: Dict[str, Any]
|
||||
error: str
|
||||
type: str = "lite_agent_execution_error"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# New logging events
|
||||
class AgentLogsStartedEvent(BaseEvent):
|
||||
"""Event emitted when agent logs should be shown at start"""
|
||||
|
||||
agent_role: str
|
||||
task_description: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
verbose: bool = False
|
||||
type: str = "agent_logs_started"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AgentLogsExecutionEvent(BaseEvent):
|
||||
"""Event emitted when agent logs should be shown during execution"""
|
||||
|
||||
agent_role: str
|
||||
formatted_answer: Any
|
||||
verbose: bool = False
|
||||
type: str = "agent_logs_execution"
|
||||
|
||||
model_config = {"arbitrary_types_allowed": True}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ from io import StringIO
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import Field, PrivateAttr
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.llm import LLM
|
||||
from crewai.task import Task
|
||||
from crewai.telemetry.telemetry import Telemetry
|
||||
from crewai.utilities import Logger
|
||||
@@ -27,6 +27,8 @@ from crewai.utilities.events.utils.console_formatter import ConsoleFormatter
|
||||
from .agent_events import (
|
||||
AgentExecutionCompletedEvent,
|
||||
AgentExecutionStartedEvent,
|
||||
AgentLogsStartedEvent,
|
||||
AgentLogsExecutionEvent,
|
||||
LiteAgentExecutionCompletedEvent,
|
||||
LiteAgentExecutionErrorEvent,
|
||||
LiteAgentExecutionStartedEvent,
|
||||
@@ -108,6 +110,7 @@ class EventListener(BaseEventListener):
|
||||
event.crew_name or "Crew",
|
||||
source.id,
|
||||
"completed",
|
||||
final_string_output,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(CrewKickoffFailedEvent)
|
||||
@@ -283,37 +286,58 @@ class EventListener(BaseEventListener):
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(ToolUsageStartedEvent)
|
||||
def on_tool_usage_started(source, event: ToolUsageStartedEvent):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_tool_usage_started(
|
||||
self.formatter.current_agent_branch,
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if isinstance(source, LLM):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_llm_tool_usage_started(
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
event.tool_args,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_tool_usage_started(
|
||||
self.formatter.current_agent_branch,
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(ToolUsageFinishedEvent)
|
||||
def on_tool_usage_finished(source, event: ToolUsageFinishedEvent):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_tool_usage_finished(
|
||||
self.formatter.current_tool_branch,
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if isinstance(source, LLM):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_llm_tool_usage_finished(
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_tool_usage_finished(
|
||||
self.formatter.current_tool_branch,
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(ToolUsageErrorEvent)
|
||||
def on_tool_usage_error(source, event: ToolUsageErrorEvent):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_tool_usage_error(
|
||||
self.formatter.current_tool_branch,
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
event.error,
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if isinstance(source, LLM):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_llm_tool_usage_error(
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
event.error,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_tool_usage_error(
|
||||
self.formatter.current_tool_branch,
|
||||
event.tool_name,
|
||||
event.error,
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------- LLM EVENTS -----------
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(LLMCallStartedEvent)
|
||||
def on_llm_call_started(source, event: LLMCallStartedEvent):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_llm_call_started(
|
||||
# Capture the returned tool branch and update the current_tool_branch reference
|
||||
thinking_branch = self.formatter.handle_llm_call_started(
|
||||
self.formatter.current_agent_branch,
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Update the formatter's current_tool_branch to ensure proper cleanup
|
||||
if thinking_branch is not None:
|
||||
self.formatter.current_tool_branch = thinking_branch
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(LLMCallCompletedEvent)
|
||||
def on_llm_call_completed(source, event: LLMCallCompletedEvent):
|
||||
@@ -446,5 +470,23 @@ class EventListener(BaseEventListener):
|
||||
self.formatter.current_crew_tree,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------- AGENT LOGGING EVENTS -----------
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(AgentLogsStartedEvent)
|
||||
def on_agent_logs_started(source, event: AgentLogsStartedEvent):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_agent_logs_started(
|
||||
event.agent_role,
|
||||
event.task_description,
|
||||
event.verbose,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@crewai_event_bus.on(AgentLogsExecutionEvent)
|
||||
def on_agent_logs_execution(source, event: AgentLogsExecutionEvent):
|
||||
self.formatter.handle_agent_logs_execution(
|
||||
event.agent_role,
|
||||
event.formatted_answer,
|
||||
event.verbose,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
event_listener = EventListener()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,11 +7,11 @@ from .base_events import BaseEvent
|
||||
class ToolUsageEvent(BaseEvent):
|
||||
"""Base event for tool usage tracking"""
|
||||
|
||||
agent_key: str
|
||||
agent_role: str
|
||||
agent_key: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
agent_role: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
tool_name: str
|
||||
tool_args: Dict[str, Any] | str
|
||||
tool_class: str
|
||||
tool_class: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
run_attempts: int | None = None
|
||||
delegations: int | None = None
|
||||
agent: Optional[Any] = None
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ from rich.panel import Panel
|
||||
from rich.text import Text
|
||||
from rich.tree import Tree
|
||||
from rich.live import Live
|
||||
from rich.syntax import Syntax
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
@@ -17,6 +18,8 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
current_lite_agent_branch: Optional[Tree] = None
|
||||
tool_usage_counts: Dict[str, int] = {}
|
||||
current_reasoning_branch: Optional[Tree] = None # Track reasoning status
|
||||
_live_paused: bool = False
|
||||
current_llm_tool_tree: Optional[Tree] = None
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, verbose: bool = False):
|
||||
self.console = Console(width=None)
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +41,12 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def create_status_content(
|
||||
self, title: str, name: str, status_style: str = "blue", **fields
|
||||
self,
|
||||
title: str,
|
||||
name: str,
|
||||
status_style: str = "blue",
|
||||
tool_args: Dict[str, Any] | str = "",
|
||||
**fields,
|
||||
) -> Text:
|
||||
"""Create standardized status content with consistent formatting."""
|
||||
content = Text()
|
||||
@@ -51,6 +59,8 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
content.append(
|
||||
f"{value}\n", style=fields.get(f"{label}_style", status_style)
|
||||
)
|
||||
content.append("Tool Args: ", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{tool_args}\n", style=status_style)
|
||||
|
||||
return content
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -118,6 +128,19 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
# Finally, pass through to the regular Console.print implementation
|
||||
self.console.print(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def pause_live_updates(self) -> None:
|
||||
"""Pause Live session updates to allow for human input without interference."""
|
||||
if not self._live_paused:
|
||||
if self._live:
|
||||
self._live.stop()
|
||||
self._live = None
|
||||
self._live_paused = True
|
||||
|
||||
def resume_live_updates(self) -> None:
|
||||
"""Resume Live session updates after human input is complete."""
|
||||
if self._live_paused:
|
||||
self._live_paused = False
|
||||
|
||||
def print_panel(
|
||||
self, content: Text, title: str, style: str = "blue", is_flow: bool = False
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
@@ -137,6 +160,7 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
crew_name: str,
|
||||
source_id: str,
|
||||
status: str = "completed",
|
||||
final_string_output: str = "",
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
"""Handle crew tree updates with consistent formatting."""
|
||||
if not self.verbose or tree is None:
|
||||
@@ -168,6 +192,7 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
style,
|
||||
ID=source_id,
|
||||
)
|
||||
content.append(f"Final Output: {final_string_output}\n", style="white")
|
||||
|
||||
self.print_panel(content, title, style)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -426,11 +451,64 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
return method_branch
|
||||
|
||||
def get_llm_tree(self, tool_name: str):
|
||||
text = Text()
|
||||
text.append(f"🔧 Using {tool_name} from LLM available_function", style="yellow")
|
||||
|
||||
tree = self.current_flow_tree or self.current_crew_tree
|
||||
|
||||
if tree:
|
||||
tree.add(text)
|
||||
|
||||
return tree or Tree(text)
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_llm_tool_usage_started(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tool_name: str,
|
||||
tool_args: Dict[str, Any] | str,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# Create status content for the tool usage
|
||||
content = self.create_status_content(
|
||||
"Tool Usage Started", tool_name, Status="In Progress", tool_args=tool_args
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create and print the panel
|
||||
self.print_panel(content, "Tool Usage", "green")
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
|
||||
# Still return the tree for compatibility with existing code
|
||||
return self.get_llm_tree(tool_name)
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_llm_tool_usage_finished(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tool_name: str,
|
||||
):
|
||||
tree = self.get_llm_tree(tool_name)
|
||||
self.add_tree_node(tree, "✅ Tool Usage Completed", "green")
|
||||
self.print(tree)
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_llm_tool_usage_error(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tool_name: str,
|
||||
error: str,
|
||||
):
|
||||
tree = self.get_llm_tree(tool_name)
|
||||
self.add_tree_node(tree, "❌ Tool Usage Failed", "red")
|
||||
self.print(tree)
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
|
||||
error_content = self.create_status_content(
|
||||
"Tool Usage Failed", tool_name, "red", Error=error
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.print_panel(error_content, "Tool Error", "red")
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_tool_usage_started(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
agent_branch: Optional[Tree],
|
||||
tool_name: str,
|
||||
crew_tree: Optional[Tree],
|
||||
tool_args: Dict[str, Any] | str = "",
|
||||
) -> Optional[Tree]:
|
||||
"""Handle tool usage started event."""
|
||||
if not self.verbose:
|
||||
@@ -438,9 +516,7 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
|
||||
# Parent for tool usage: LiteAgent > Agent > Task
|
||||
branch_to_use = (
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch
|
||||
or agent_branch
|
||||
or self.current_task_branch
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch or agent_branch or self.current_task_branch
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Render full crew tree when available for consistent live updates
|
||||
@@ -549,9 +625,7 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
|
||||
# Parent for tool usage: LiteAgent > Agent > Task
|
||||
branch_to_use = (
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch
|
||||
or agent_branch
|
||||
or self.current_task_branch
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch or agent_branch or self.current_task_branch
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Render full crew tree when available for consistent live updates
|
||||
@@ -565,14 +639,21 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# Only add thinking status if we don't have a current tool branch
|
||||
if self.current_tool_branch is None:
|
||||
# or if the current tool branch is not a thinking node
|
||||
should_add_thinking = self.current_tool_branch is None or "Thinking" not in str(
|
||||
self.current_tool_branch.label
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if should_add_thinking:
|
||||
tool_branch = branch_to_use.add("")
|
||||
self.update_tree_label(tool_branch, "🧠", "Thinking...", "blue")
|
||||
self.current_tool_branch = tool_branch
|
||||
self.print(tree_to_use)
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
return tool_branch
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# Return the existing tool branch if it's already a thinking node
|
||||
return self.current_tool_branch
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_llm_call_completed(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
@@ -581,7 +662,7 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
crew_tree: Optional[Tree],
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
"""Handle LLM call completed event."""
|
||||
if not self.verbose or tool_branch is None:
|
||||
if not self.verbose:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Decide which tree to render: prefer full crew tree, else parent branch
|
||||
@@ -589,23 +670,50 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
if tree_to_use is None:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove the thinking status node when complete
|
||||
if "Thinking" in str(tool_branch.label):
|
||||
# Try to remove the thinking status node - first try the provided tool_branch
|
||||
thinking_branch_to_remove = None
|
||||
removed = False
|
||||
|
||||
# Method 1: Use the provided tool_branch if it's a thinking node
|
||||
if tool_branch is not None and "Thinking" in str(tool_branch.label):
|
||||
thinking_branch_to_remove = tool_branch
|
||||
|
||||
# Method 2: Fallback - search for any thinking node if tool_branch is None or not thinking
|
||||
if thinking_branch_to_remove is None:
|
||||
parents = [
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch,
|
||||
self.current_agent_branch,
|
||||
self.current_task_branch,
|
||||
tree_to_use,
|
||||
]
|
||||
removed = False
|
||||
for parent in parents:
|
||||
if isinstance(parent, Tree) and tool_branch in parent.children:
|
||||
parent.children.remove(tool_branch)
|
||||
if isinstance(parent, Tree):
|
||||
for child in parent.children:
|
||||
if "Thinking" in str(child.label):
|
||||
thinking_branch_to_remove = child
|
||||
break
|
||||
if thinking_branch_to_remove:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove the thinking node if found
|
||||
if thinking_branch_to_remove:
|
||||
parents = [
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch,
|
||||
self.current_agent_branch,
|
||||
self.current_task_branch,
|
||||
tree_to_use,
|
||||
]
|
||||
for parent in parents:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
isinstance(parent, Tree)
|
||||
and thinking_branch_to_remove in parent.children
|
||||
):
|
||||
parent.children.remove(thinking_branch_to_remove)
|
||||
removed = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# Clear pointer if we just removed the current_tool_branch
|
||||
if self.current_tool_branch is tool_branch:
|
||||
if self.current_tool_branch is thinking_branch_to_remove:
|
||||
self.current_tool_branch = None
|
||||
|
||||
if removed:
|
||||
@@ -622,9 +730,36 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
# Decide which tree to render: prefer full crew tree, else parent branch
|
||||
tree_to_use = self.current_crew_tree or crew_tree or self.current_task_branch
|
||||
|
||||
# Update tool branch if it exists
|
||||
if tool_branch:
|
||||
tool_branch.label = Text("❌ LLM Failed", style="red bold")
|
||||
# Find the thinking branch to update (similar to completion logic)
|
||||
thinking_branch_to_update = None
|
||||
|
||||
# Method 1: Use the provided tool_branch if it's a thinking node
|
||||
if tool_branch is not None and "Thinking" in str(tool_branch.label):
|
||||
thinking_branch_to_update = tool_branch
|
||||
|
||||
# Method 2: Fallback - search for any thinking node if tool_branch is None or not thinking
|
||||
if thinking_branch_to_update is None:
|
||||
parents = [
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch,
|
||||
self.current_agent_branch,
|
||||
self.current_task_branch,
|
||||
tree_to_use,
|
||||
]
|
||||
for parent in parents:
|
||||
if isinstance(parent, Tree):
|
||||
for child in parent.children:
|
||||
if "Thinking" in str(child.label):
|
||||
thinking_branch_to_update = child
|
||||
break
|
||||
if thinking_branch_to_update:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# Update the thinking branch to show failure
|
||||
if thinking_branch_to_update:
|
||||
thinking_branch_to_update.label = Text("❌ LLM Failed", style="red bold")
|
||||
# Clear the current_tool_branch reference
|
||||
if self.current_tool_branch is thinking_branch_to_update:
|
||||
self.current_tool_branch = None
|
||||
if tree_to_use:
|
||||
self.print(tree_to_use)
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
@@ -1067,9 +1202,7 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
|
||||
# Prefer LiteAgent > Agent > Task branch as the parent for reasoning
|
||||
branch_to_use = (
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch
|
||||
or agent_branch
|
||||
or self.current_task_branch
|
||||
self.current_lite_agent_branch or agent_branch or self.current_task_branch
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# We always want to render the full crew tree when possible so the
|
||||
@@ -1116,7 +1249,9 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
style = "green" if ready else "yellow"
|
||||
status_text = "Reasoning Completed" if ready else "Reasoning Completed (Not Ready)"
|
||||
status_text = (
|
||||
"Reasoning Completed" if ready else "Reasoning Completed (Not Ready)"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if reasoning_branch is not None:
|
||||
self.update_tree_label(reasoning_branch, "✅", status_text, style)
|
||||
@@ -1173,3 +1308,149 @@ class ConsoleFormatter:
|
||||
|
||||
# Clear stored branch after failure
|
||||
self.current_reasoning_branch = None
|
||||
|
||||
# ----------- AGENT LOGGING EVENTS -----------
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_agent_logs_started(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
agent_role: str,
|
||||
task_description: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
verbose: bool = False,
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
"""Handle agent logs started event."""
|
||||
if not verbose:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
agent_role = agent_role.split("\n")[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Create panel content
|
||||
content = Text()
|
||||
content.append("Agent: ", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{agent_role}", style="bright_green bold")
|
||||
|
||||
if task_description:
|
||||
content.append("\n\nTask: ", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{task_description}", style="bright_green")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create and display the panel
|
||||
agent_panel = Panel(
|
||||
content,
|
||||
title="🤖 Agent Started",
|
||||
border_style="magenta",
|
||||
padding=(1, 2),
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.print(agent_panel)
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_agent_logs_execution(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
agent_role: str,
|
||||
formatted_answer: Any,
|
||||
verbose: bool = False,
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
"""Handle agent logs execution event."""
|
||||
if not verbose:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.agents.parser import AgentAction, AgentFinish
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
agent_role = agent_role.split("\n")[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(formatted_answer, AgentAction):
|
||||
thought = re.sub(r"\n+", "\n", formatted_answer.thought)
|
||||
formatted_json = json.dumps(
|
||||
formatted_answer.tool_input,
|
||||
indent=2,
|
||||
ensure_ascii=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create content for the action panel
|
||||
content = Text()
|
||||
content.append("Agent: ", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{agent_role}\n\n", style="bright_green bold")
|
||||
|
||||
if thought and thought != "":
|
||||
content.append("Thought: ", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{thought}\n\n", style="bright_green")
|
||||
|
||||
content.append("Using Tool: ", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{formatted_answer.tool}\n\n", style="bright_green bold")
|
||||
|
||||
content.append("Tool Input:\n", style="white")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a syntax-highlighted JSON code block
|
||||
json_syntax = Syntax(
|
||||
formatted_json,
|
||||
"json",
|
||||
theme="monokai",
|
||||
line_numbers=False,
|
||||
background_color="default",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
content.append("\n")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create separate panels for better organization
|
||||
main_content = Text()
|
||||
main_content.append("Agent: ", style="white")
|
||||
main_content.append(f"{agent_role}\n\n", style="bright_green bold")
|
||||
|
||||
if thought and thought != "":
|
||||
main_content.append("Thought: ", style="white")
|
||||
main_content.append(f"{thought}\n\n", style="bright_green")
|
||||
|
||||
main_content.append("Using Tool: ", style="white")
|
||||
main_content.append(f"{formatted_answer.tool}", style="bright_green bold")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create the main action panel
|
||||
action_panel = Panel(
|
||||
main_content,
|
||||
title="🔧 Agent Tool Execution",
|
||||
border_style="magenta",
|
||||
padding=(1, 2),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create the JSON input panel
|
||||
input_panel = Panel(
|
||||
json_syntax,
|
||||
title="Tool Input",
|
||||
border_style="blue",
|
||||
padding=(1, 2),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create tool output content with better formatting
|
||||
output_text = str(formatted_answer.result)
|
||||
if len(output_text) > 2000:
|
||||
output_text = output_text[:1997] + "..."
|
||||
|
||||
output_panel = Panel(
|
||||
Text(output_text, style="bright_green"),
|
||||
title="Tool Output",
|
||||
border_style="green",
|
||||
padding=(1, 2),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Print all panels
|
||||
self.print(action_panel)
|
||||
self.print(input_panel)
|
||||
self.print(output_panel)
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
|
||||
elif isinstance(formatted_answer, AgentFinish):
|
||||
# Create content for the finish panel
|
||||
content = Text()
|
||||
content.append("Agent: ", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{agent_role}\n\n", style="bright_green bold")
|
||||
content.append("Final Answer:\n", style="white")
|
||||
content.append(f"{formatted_answer.output}", style="bright_green")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create and display the finish panel
|
||||
finish_panel = Panel(
|
||||
content,
|
||||
title="✅ Agent Final Answer",
|
||||
border_style="green",
|
||||
padding=(1, 2),
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.print(finish_panel)
|
||||
self.print()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, List
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, List, Union
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.constants import _NotSpecified
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from crewai.task import Task
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ def aggregate_raw_outputs_from_task_outputs(task_outputs: List["TaskOutput"]) ->
|
||||
return context
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def aggregate_raw_outputs_from_tasks(tasks: List["Task"]) -> str:
|
||||
def aggregate_raw_outputs_from_tasks(tasks: Union[List["Task"],_NotSpecified]) -> str:
|
||||
"""Generate string context from the tasks."""
|
||||
|
||||
task_outputs = (
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +1,7 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Module for handling task guardrail validation results.
|
||||
|
||||
This module provides the GuardrailResult class which standardizes
|
||||
the way task guardrails return their validation results.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Any, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel, field_validator
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GuardrailResult(BaseModel):
|
||||
"""Result from a task guardrail execution.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54,3 +46,48 @@ class GuardrailResult(BaseModel):
|
||||
result=data if success else None,
|
||||
error=data if not success else None
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def process_guardrail(output: Any, guardrail: Callable, retry_count: int) -> GuardrailResult:
|
||||
"""Process the guardrail for the agent output.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
output: The output to validate with the guardrail
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
GuardrailResult: The result of the guardrail validation
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from crewai.task import TaskOutput
|
||||
from crewai.lite_agent import LiteAgentOutput
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(output, TaskOutput) or isinstance(output, LiteAgentOutput), "Output must be a TaskOutput or LiteAgentOutput"
|
||||
|
||||
assert guardrail is not None
|
||||
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events import (
|
||||
LLMGuardrailCompletedEvent,
|
||||
LLMGuardrailStartedEvent,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from crewai.utilities.events.crewai_event_bus import crewai_event_bus
|
||||
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
LLMGuardrailStartedEvent(
|
||||
guardrail=guardrail, retry_count=retry_count
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = guardrail(output)
|
||||
guardrail_result = GuardrailResult.from_tuple(result)
|
||||
|
||||
crewai_event_bus.emit(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
LLMGuardrailCompletedEvent(
|
||||
success=guardrail_result.success,
|
||||
result=guardrail_result.result,
|
||||
error=guardrail_result.error,
|
||||
retry_count=retry_count,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return guardrail_result
|
||||
@@ -309,7 +309,9 @@ def test_cache_hitting():
|
||||
def handle_tool_end(source, event):
|
||||
received_events.append(event)
|
||||
|
||||
with (patch.object(CacheHandler, "read") as read,):
|
||||
with (
|
||||
patch.object(CacheHandler, "read") as read,
|
||||
):
|
||||
read.return_value = "0"
|
||||
task = Task(
|
||||
description="What is 2 times 6? Ignore correctness and just return the result of the multiplication tool, you must use the tool.",
|
||||
@@ -499,8 +501,7 @@ def test_agent_custom_max_iterations():
|
||||
def test_agent_repeated_tool_usage(capsys):
|
||||
@tool
|
||||
def get_final_answer() -> float:
|
||||
"""Get the final answer but don't give it yet, just re-use this
|
||||
tool non-stop."""
|
||||
"""Get the final answer but don't give it yet, just re-use this tool non-stop."""
|
||||
return 42
|
||||
|
||||
agent = Agent(
|
||||
@@ -525,12 +526,42 @@ def test_agent_repeated_tool_usage(capsys):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
captured = capsys.readouterr()
|
||||
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
"I tried reusing the same input, I must stop using this action input. I'll try something else instead."
|
||||
in captured.out
|
||||
output = (
|
||||
captured.out.replace("\n", " ")
|
||||
.replace(" ", " ")
|
||||
.strip()
|
||||
.replace("╭", "")
|
||||
.replace("╮", "")
|
||||
.replace("╯", "")
|
||||
.replace("╰", "")
|
||||
.replace("│", "")
|
||||
.replace("─", "")
|
||||
.replace("[", "")
|
||||
.replace("]", "")
|
||||
.replace("bold", "")
|
||||
.replace("blue", "")
|
||||
.replace("yellow", "")
|
||||
.replace("green", "")
|
||||
.replace("red", "")
|
||||
.replace("dim", "")
|
||||
.replace("🤖", "")
|
||||
.replace("🔧", "")
|
||||
.replace("✅", "")
|
||||
.replace("\x1b[93m", "")
|
||||
.replace("\x1b[00m", "")
|
||||
.replace("\\", "")
|
||||
.replace('"', "")
|
||||
.replace("'", "")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Look for the message in the normalized output, handling the apostrophe difference
|
||||
expected_message = (
|
||||
"I tried reusing the same input, I must stop using this action input."
|
||||
)
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
expected_message in output
|
||||
), f"Expected message not found in output. Output was: {output}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.vcr(filter_headers=["authorization"])
|
||||
def test_agent_repeated_tool_usage_check_even_with_disabled_cache(capsys):
|
||||
@@ -562,11 +593,43 @@ def test_agent_repeated_tool_usage_check_even_with_disabled_cache(capsys):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
captured = capsys.readouterr()
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
"I tried reusing the same input, I must stop using this action input. I'll try something else instead."
|
||||
in captured.out
|
||||
output = (
|
||||
captured.out.replace("\n", " ")
|
||||
.replace(" ", " ")
|
||||
.strip()
|
||||
.replace("╭", "")
|
||||
.replace("╮", "")
|
||||
.replace("╯", "")
|
||||
.replace("╰", "")
|
||||
.replace("│", "")
|
||||
.replace("─", "")
|
||||
.replace("[", "")
|
||||
.replace("]", "")
|
||||
.replace("bold", "")
|
||||
.replace("blue", "")
|
||||
.replace("yellow", "")
|
||||
.replace("green", "")
|
||||
.replace("red", "")
|
||||
.replace("dim", "")
|
||||
.replace("🤖", "")
|
||||
.replace("🔧", "")
|
||||
.replace("✅", "")
|
||||
.replace("\x1b[93m", "")
|
||||
.replace("\x1b[00m", "")
|
||||
.replace("\\", "")
|
||||
.replace('"', "")
|
||||
.replace("'", "")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Look for the message in the normalized output, handling the apostrophe difference
|
||||
expected_message = (
|
||||
"I tried reusing the same input, I must stop using this action input"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
expected_message in output
|
||||
), f"Expected message not found in output. Output was: {output}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.vcr(filter_headers=["authorization"])
|
||||
def test_agent_moved_on_after_max_iterations():
|
||||
@@ -1628,13 +1691,13 @@ def test_agent_execute_task_with_ollama():
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.vcr(filter_headers=["authorization"])
|
||||
def test_agent_with_knowledge_sources():
|
||||
# Create a knowledge source with some content
|
||||
content = "Brandon's favorite color is red and he likes Mexican food."
|
||||
string_source = StringKnowledgeSource(content=content)
|
||||
with patch("crewai.knowledge") as MockKnowledge:
|
||||
mock_knowledge_instance = MockKnowledge.return_value
|
||||
mock_knowledge_instance.sources = [string_source]
|
||||
mock_knowledge_instance.search.return_value = [{"content": content}]
|
||||
MockKnowledge.add_sources.return_value = [string_source]
|
||||
|
||||
agent = Agent(
|
||||
role="Information Agent",
|
||||
@@ -1644,7 +1707,6 @@ def test_agent_with_knowledge_sources():
|
||||
knowledge_sources=[string_source],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a task that requires the agent to use the knowledge
|
||||
task = Task(
|
||||
description="What is Brandon's favorite color?",
|
||||
expected_output="Brandon's favorite color.",
|
||||
@@ -1652,10 +1714,11 @@ def test_agent_with_knowledge_sources():
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
crew = Crew(agents=[agent], tasks=[task])
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
|
||||
# Assert that the agent provides the correct information
|
||||
assert "red" in result.raw.lower()
|
||||
with patch.object(Knowledge, "add_sources") as mock_add_sources:
|
||||
result = crew.kickoff()
|
||||
assert mock_add_sources.called, "add_sources() should have been called"
|
||||
mock_add_sources.assert_called_once()
|
||||
assert "red" in result.raw.lower()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.vcr(filter_headers=["authorization"])
|
||||
@@ -2036,7 +2099,7 @@ def mock_get_auth_token():
|
||||
|
||||
@patch("crewai.cli.plus_api.PlusAPI.get_agent")
|
||||
def test_agent_from_repository(mock_get_agent, mock_get_auth_token):
|
||||
from crewai_tools import SerperDevTool
|
||||
from crewai_tools import SerperDevTool, XMLSearchTool, CSVSearchTool, EnterpriseActionTool
|
||||
|
||||
mock_get_response = MagicMock()
|
||||
mock_get_response.status_code = 200
|
||||
@@ -2044,16 +2107,43 @@ def test_agent_from_repository(mock_get_agent, mock_get_auth_token):
|
||||
"role": "test role",
|
||||
"goal": "test goal",
|
||||
"backstory": "test backstory",
|
||||
"tools": [{"name": "SerperDevTool"}],
|
||||
"tools": [
|
||||
{"module": "crewai_tools", "name": "SerperDevTool", "init_params": {"n_results": 30}},
|
||||
{"module": "crewai_tools", "name": "XMLSearchTool", "init_params": {"summarize": True}},
|
||||
{"module": "crewai_tools", "name": "CSVSearchTool", "init_params": {}},
|
||||
|
||||
# using a tools that returns a list of BaseTools
|
||||
{"module": "crewai_tools", "name": "CrewaiEnterpriseTools", "init_params": {"actions_list": [], "enterprise_token": "test_key"}},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
mock_get_agent.return_value = mock_get_response
|
||||
agent = Agent(from_repository="test_agent")
|
||||
|
||||
tool_action = EnterpriseActionTool(
|
||||
name="test_name",
|
||||
description="test_description",
|
||||
enterprise_action_token="test_token",
|
||||
action_name="test_action_name",
|
||||
action_schema={"test": "test"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with patch("crewai_tools.CrewaiEnterpriseTools", return_value=[tool_action]):
|
||||
agent = Agent(from_repository="test_agent")
|
||||
|
||||
assert agent.role == "test role"
|
||||
assert agent.goal == "test goal"
|
||||
assert agent.backstory == "test backstory"
|
||||
assert len(agent.tools) == 1
|
||||
assert len(agent.tools) == 4
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(agent.tools[0], SerperDevTool)
|
||||
assert agent.tools[0].n_results == 30
|
||||
assert isinstance(agent.tools[1], XMLSearchTool)
|
||||
assert agent.tools[1].summarize
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(agent.tools[2], CSVSearchTool)
|
||||
assert not agent.tools[2].summarize
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(agent.tools[3], EnterpriseActionTool)
|
||||
assert agent.tools[3].name == "test_name"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@patch("crewai.cli.plus_api.PlusAPI.get_agent")
|
||||
@@ -2066,7 +2156,7 @@ def test_agent_from_repository_override_attributes(mock_get_agent, mock_get_auth
|
||||
"role": "test role",
|
||||
"goal": "test goal",
|
||||
"backstory": "test backstory",
|
||||
"tools": [{"name": "SerperDevTool"}],
|
||||
"tools": [{"name": "SerperDevTool", "module": "crewai_tools", "init_params": {}}],
|
||||
}
|
||||
mock_get_agent.return_value = mock_get_response
|
||||
agent = Agent(from_repository="test_agent", role="Custom Role")
|
||||
@@ -2086,7 +2176,12 @@ def test_agent_from_repository_with_invalid_tools(mock_get_agent, mock_get_auth_
|
||||
"role": "test role",
|
||||
"goal": "test goal",
|
||||
"backstory": "test backstory",
|
||||
"tools": [{"name": "DoesNotExist"}],
|
||||
"tools": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "DoesNotExist",
|
||||
"module": "crewai_tools",
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
mock_get_agent.return_value = mock_get_response
|
||||
with pytest.raises(
|
||||
@@ -2120,3 +2215,64 @@ def test_agent_from_repository_agent_not_found(mock_get_agent, mock_get_auth_tok
|
||||
match="Agent test_agent does not exist, make sure the name is correct or the agent is available on your organization",
|
||||
):
|
||||
Agent(from_repository="test_agent")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@patch("crewai.cli.plus_api.PlusAPI.get_agent")
|
||||
@patch("crewai.utilities.agent_utils.Settings")
|
||||
@patch("crewai.utilities.agent_utils.console")
|
||||
def test_agent_from_repository_displays_org_info(
|
||||
mock_console, mock_settings, mock_get_agent, mock_get_auth_token
|
||||
):
|
||||
mock_settings_instance = MagicMock()
|
||||
mock_settings_instance.org_uuid = "test-org-uuid"
|
||||
mock_settings_instance.org_name = "Test Organization"
|
||||
mock_settings.return_value = mock_settings_instance
|
||||
|
||||
mock_get_response = MagicMock()
|
||||
mock_get_response.status_code = 200
|
||||
mock_get_response.json.return_value = {
|
||||
"role": "test role",
|
||||
"goal": "test goal",
|
||||
"backstory": "test backstory",
|
||||
"tools": [],
|
||||
}
|
||||
mock_get_agent.return_value = mock_get_response
|
||||
|
||||
agent = Agent(from_repository="test_agent")
|
||||
|
||||
mock_console.print.assert_any_call(
|
||||
"Fetching agent from organization: Test Organization (test-org-uuid)",
|
||||
style="bold blue",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert agent.role == "test role"
|
||||
assert agent.goal == "test goal"
|
||||
assert agent.backstory == "test backstory"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@patch("crewai.cli.plus_api.PlusAPI.get_agent")
|
||||
@patch("crewai.utilities.agent_utils.Settings")
|
||||
@patch("crewai.utilities.agent_utils.console")
|
||||
def test_agent_from_repository_without_org_set(
|
||||
mock_console, mock_settings, mock_get_agent, mock_get_auth_token
|
||||
):
|
||||
mock_settings_instance = MagicMock()
|
||||
mock_settings_instance.org_uuid = None
|
||||
mock_settings_instance.org_name = None
|
||||
mock_settings.return_value = mock_settings_instance
|
||||
|
||||
mock_get_response = MagicMock()
|
||||
mock_get_response.status_code = 401
|
||||
mock_get_response.text = "Unauthorized access"
|
||||
mock_get_agent.return_value = mock_get_response
|
||||
|
||||
with pytest.raises(
|
||||
AgentRepositoryError,
|
||||
match="Agent test_agent could not be loaded: Unauthorized access",
|
||||
):
|
||||
Agent(from_repository="test_agent")
|
||||
|
||||
mock_console.print.assert_any_call(
|
||||
"No organization currently set. We recommend setting one before using: `crewai org switch <org_id>` command.",
|
||||
style="yellow",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
|
||||
interactions:
|
||||
- request:
|
||||
body: '{"messages": [{"role": "system", "content": "You are Sports Analyst. You
|
||||
are an expert at gathering and organizing information. You carefully collect
|
||||
details and present them in a structured way.\nYour personal goal is: Gather
|
||||
information about the best soccer players\n\nTo give my best complete final
|
||||
answer to the task respond using the exact following format:\n\nThought: I now
|
||||
can give a great answer\nFinal Answer: Your final answer must be the great and
|
||||
the most complete as possible, it must be outcome described.\n\nI MUST use these
|
||||
formats, my job depends on it!"}, {"role": "user", "content": "Top 10 best players
|
||||
in the world?"}], "model": "gpt-4o-mini", "stop": ["\nObservation:"]}'
|
||||
headers:
|
||||
accept:
|
||||
- application/json
|
||||
accept-encoding:
|
||||
- gzip, deflate, zstd
|
||||
connection:
|
||||
- keep-alive
|
||||
content-length:
|
||||
- '694'
|
||||
content-type:
|
||||
- application/json
|
||||
host:
|
||||
- api.openai.com
|
||||
user-agent:
|
||||
- OpenAI/Python 1.78.0
|
||||
x-stainless-arch:
|
||||
- arm64
|
||||
x-stainless-async:
|
||||
- 'false'
|
||||
x-stainless-lang:
|
||||
- python
|
||||
x-stainless-os:
|
||||
- MacOS
|
||||
x-stainless-package-version:
|
||||
- 1.78.0
|
||||
x-stainless-raw-response:
|
||||
- 'true'
|
||||
x-stainless-read-timeout:
|
||||
- '600.0'
|
||||
x-stainless-retry-count:
|
||||
- '0'
|
||||
x-stainless-runtime:
|
||||
- CPython
|
||||
x-stainless-runtime-version:
|
||||
- 3.12.9
|
||||
method: POST
|
||||
uri: https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
|
||||
response:
|
||||
body:
|
||||
string: !!binary |
|
||||
H4sIAAAAAAAAAwAAAP//nFfNchtHDr7rKVBz0a6KVJGUZMm6SVrJcSw6Ktmb7NY6pQJ7wBlEPd1T
|
||||
6B5S3JTP+yw55AVy9T7YFnr4Jy7pRLmwioP+wfcB+Br4eQ8g4zw7h8yUGE1V2+5l0dh/xOvXo5MT
|
||||
ufDvJk//lNvJm+9HvR9+errPOrrDj34iExe7Do2vakuRvWvNRggj6an90+PXJ69OX50dJUPlc7K6
|
||||
rahj99h3K3bcHfQGx93eabd/Nt9dejYUsnP41x4AwM/pV/10OT1l59DrLL5UFAIWlJ0vFwFk4q1+
|
||||
yTAEDhFdzDoro/Eukkuufyx9U5TxHN6C81Mw6KDgCQFCof4DujAlAfjkbtihhYv0/xw+lgRjb62f
|
||||
siuAAyCEKI2JjVAOfkIyYZqCH0MsCUwjQi5C9DX0exC8MSRQW5yRBGCXFk292BxGGPSA9IkFapKx
|
||||
lwqdodABNCXThCpyUf+59ia0Friq0cT5PiiwIsCg139noh+RwKA3ODr/5D65/iEcHNyyd2RhSCHw
|
||||
wQH85a2LJDBkrPivnxwAdOHg4M4H1ngeHJzDjZcpSr60XfnGRZmp6UIKcpEdLo0Xa27qilO4RGu9
|
||||
g3z/OwHUg0IHqsZGri3B369vLuCqxKpm7wLcEhYNQeRoFbMlzJXj5TUQvaLpw5WvES6qL78IG0xs
|
||||
DHqDAdy8vbmAHxKZV00NEzbRy+xQsQ8U+7uZZXQwHGFdf/lF0d+hcIAPyC5235BUyO7FLNyIxmgn
|
||||
BRtOTdk5Eo38oNc/64BrKhLfBLhlxd5fon90fupg7AVKDhBqorwDufBoZNkVbQ4UHm03GC9KUy1+
|
||||
SiEkuEcK91p0JXyDaNHlCneIzpQUNOJXHGcvhvpeTbPdUDFECnGe3hotITTlCqP6m7J+a+A7aaO6
|
||||
jGCkMYwWtJp1w4bn+wGi0MhSV/nULYEweNfyOhioqhwlJo5T4GnCDv5GcCnNzNEfpmLI+ZjJ5iTb
|
||||
2LgkW3BT7aTjHc0SogofSVIkNy5dq4Q7oYpJNktAg/w8EejJUK3+oYUJB/YuLapV7pS5EVuObc6f
|
||||
KPQr4RAZnYd73ZN7BX9hu+8xBHlxAtx5iU2Bdifmk60Fj9Z2I1e0LGlNBNDEbUtBlWtHSszrxY9X
|
||||
XNl1jnT7tSs0wzvwoUZ2LWtvI9qWhldKw3uaVSjwrRzO8X/DFu2L8V8K/pt3o3/3LFRjiyzJmfDI
|
||||
1nagJCgxwNS7jWpvQ6hVkwPChONa5rdX7gdwOA97JKwgNMZQCB1gZ2yTSF2UgrI5V0hSgUwsnCoL
|
||||
9/ogRLilKbrcT8NjegIuUQxZ7/BPpIPyvpOOe1I+KE+MPNOqeZp2Ehfqb1LJSxWPIbn9AHethKQE
|
||||
mhd1byH0/Q7oOy48aqIeVhJO2M5Uby51l4Nh49iU+2HBEgUY0dgLQeUniSJdOked6DlLb2PziDD0
|
||||
ufB//6PE3BNaGGIunP8ZfbgSj5F3P476ADwrlzbXNaTaUeg6tAp+zY/9sOW9FG6qumyzaFFh88sV
|
||||
qfI71h4mLLqSdPPyTUoEvFYChr7EinL4gBZLZeCWJyS19y+vlOtiVsfflca5Li6v0Rqx9TyJKyUk
|
||||
+buhjorz662DrljqxRtvc3Jw6X2cKxJsPTfx0O8pEd+z+/Kr4SbAt19+c+xlazp8lY+vSMf2YuEk
|
||||
4CGibEg+FqlY1pVkqRU1T/y6WvxOqsxbogV+LaZuap3a5zMx8LGkQMsWtcQJablpM00u2hnkZDVc
|
||||
lAM9RUEvOTuU2bOGddGOpupIjpfe5hC4cDxmgy4Cu7FtyBmCKcfyWSfsx/NGeaPQ21xmSQoY9teq
|
||||
OzVDKI6SurDLecJ5gxbQGG8xp3C4PgYIjZuAOoq4xto1AzrnY9LZNID8OLd8Xo4c1he1+FHY2JqN
|
||||
2XEoHyTRqONFiL7OkvXzHsCPabRpnk0rWS2+quND9I+UrusPBu152WqiWllPjxbWqBFfGc5Ojjtb
|
||||
DnzIKSLbsDYdZQZNSflq62qUwiZnv2bYW4P9/+5sO7uFzq74I8evDEbbGcofaqGczXPIq2VCOnHu
|
||||
WrakOTmcBR3BDD1EJtFQ5DTGxrZzYBZmIVL1MGZXkNTC7TA4rh9eDXBwhGd9Gmd7n/f+BwAA//8D
|
||||
AMMI9CsaDwAA
|
||||
headers:
|
||||
CF-RAY:
|
||||
- 94d9be627c40f260-GRU
|
||||
Connection:
|
||||
- keep-alive
|
||||
Content-Encoding:
|
||||
- gzip
|
||||
Content-Type:
|
||||
- application/json
|
||||
Date:
|
||||
- Tue, 10 Jun 2025 15:02:05 GMT
|
||||
Server:
|
||||
- cloudflare
|
||||
Set-Cookie:
|
||||
- __cf_bm=qYkxv9nLxeWAtPBvECxNw8fLnoBHLorJdRI8.xVEVEA-1749567725-1.0.1.1-75sp4gwHGJocK1MFkSgRcB4xJUiCwz31VRD4LAmQGEmfYB0BMQZ5sgWS8e_UMbjCaEhaPNO88q5XdbLOCWA85_rO0vYTb4hp6tmIiaerhsM;
|
||||
path=/; expires=Tue, 10-Jun-25 15:32:05 GMT; domain=.api.openai.com; HttpOnly;
|
||||
Secure; SameSite=None
|
||||
- _cfuvid=HRKCwkyTqSXpCj9_i_T5lDtlr_INA290o0b3k.26oi8-1749567725794-0.0.1.1-604800000;
|
||||
path=/; domain=.api.openai.com; HttpOnly; Secure; SameSite=None
|
||||
Transfer-Encoding:
|
||||
- chunked
|
||||
X-Content-Type-Options:
|
||||
- nosniff
|
||||
access-control-expose-headers:
|
||||
- X-Request-ID
|
||||
alt-svc:
|
||||
- h3=":443"; ma=86400
|
||||
cf-cache-status:
|
||||
- DYNAMIC
|
||||
openai-organization:
|
||||
- crewai-iuxna1
|
||||
openai-processing-ms:
|
||||
- '42674'
|
||||
openai-version:
|
||||
- '2020-10-01'
|
||||
strict-transport-security:
|
||||
- max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload
|
||||
x-envoy-upstream-service-time:
|
||||
- '42684'
|
||||
x-ratelimit-limit-requests:
|
||||
- '30000'
|
||||
x-ratelimit-limit-tokens:
|
||||
- '150000000'
|
||||
x-ratelimit-remaining-requests:
|
||||
- '29999'
|
||||
x-ratelimit-remaining-tokens:
|
||||
- '149999859'
|
||||
x-ratelimit-reset-requests:
|
||||
- 2ms
|
||||
x-ratelimit-reset-tokens:
|
||||
- 0s
|
||||
x-request-id:
|
||||
- req_d92e6f33fa5e0fbe43349afee8f55921
|
||||
status:
|
||||
code: 200
|
||||
message: OK
|
||||
version: 1
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user